Waqas Ahmed
Learning to be Reproducible: Custom Loss Design for Robust Neural Networks
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:To enhance the reproducibility and reliability of deep learning models, we address a critical gap in current training methodologies: the lack of mechanisms that ensure consistent and robust performance across runs. Our empirical analysis reveals that even under controlled initialization and training conditions, the accuracy of the model can exhibit significant variability. To address this issue, we propose a Custom Loss Function (CLF) that reduces the sensitivity of training outcomes to stochastic factors such as weight initialization and data shuffling. By fine-tuning its parameters, CLF explicitly balances predictive accuracy with training stability, leading to more consistent and reliable model performance. Extensive experiments across diverse architectures for both image classification and time series forecasting demonstrate that our approach significantly improves training robustness without sacrificing predictive performance. These results establish CLF as an effective and efficient strategy for developing more stable, reliable and trustworthy neural networks.
Hybrid Ensemble Method for Detecting Cyber-Attacks in Water Distribution Systems Using the BATADAL Dataset
Dec 16, 2025



Abstract:The cybersecurity of Industrial Control Systems that manage critical infrastructure such as Water Distribution Systems has become increasingly important as digital connectivity expands. BATADAL benchmark data is a good source of testing intrusion detection techniques, but it presents several important problems, such as imbalance in the number of classes, multivariate time dependence, and stealthy attacks. We consider a hybrid ensemble learning model that will enhance the detection ability of cyber-attacks in WDS by using the complementary capabilities of machine learning and deep learning models. Three base learners, namely, Random Forest , eXtreme Gradient Boosting , and Long Short-Term Memory network, have been strictly compared and seven ensemble types using simple averaged and stacked learning with a logistic regression meta-learner. Random Forest analysis identified top predictors turned into temporal and statistical features, and Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE) was used to overcome the class imbalance issue. The analyics indicates that the single Long Short-Term Memory network model is of poor performance (F1 = 0.000, AUC = 0.4460), but tree-based models, especially eXtreme Gradient Boosting, perform well (F1 = 0.7470, AUC=0.9684). The hybrid stacked ensemble of Random Forest , eXtreme Gradient Boosting , and Long Short-Term Memory network scored the highest, with the attack class of 0.7205 with an F1-score and a AUC of 0.9826 indicating that the heterogeneous stacking between model precision and generalization can work. The proposed framework establishes a robust and scalable solution for cyber-attack detection in time-dependent industrial systems, integrating temporal learning and ensemble diversity to support the secure operation of critical infrastructure.
Evaluating the method reproducibility of deep learning models in the biodiversity domain
Jul 10, 2024Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing biodiversity research by enabling advanced data analysis, species identification, and habitats monitoring, thereby enhancing conservation efforts. Ensuring reproducibility in AI-driven biodiversity research is crucial for fostering transparency, verifying results, and promoting the credibility of ecological findings.This study investigates the reproducibility of deep learning (DL) methods within the biodiversity domain. We design a methodology for evaluating the reproducibility of biodiversity-related publications that employ DL techniques across three stages. We define ten variables essential for method reproducibility, divided into four categories: resource requirements, methodological information, uncontrolled randomness, and statistical considerations. These categories subsequently serve as the basis for defining different levels of reproducibility. We manually extract the availability of these variables from a curated dataset comprising 61 publications identified using the keywords provided by biodiversity experts. Our study shows that the dataset is shared in 47% of the publications; however, a significant number of the publications lack comprehensive information on deep learning methods, including details regarding randomness.
Human Activity Recognition using Attribute-Based Neural Networks and Context Information
Oct 28, 2021
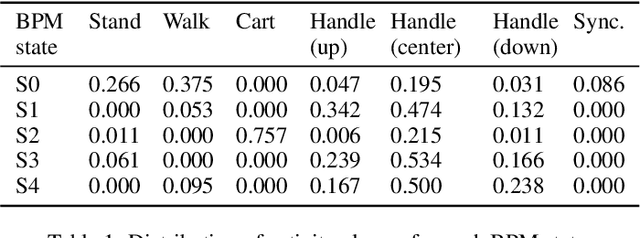
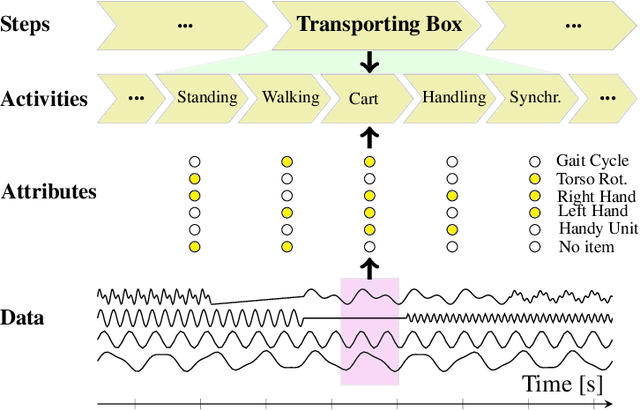
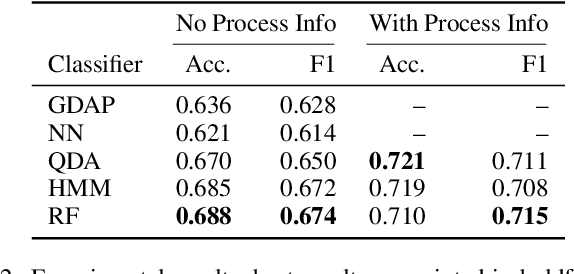
Abstract:We consider human activity recognition (HAR) from wearable sensor data in manual-work processes, like warehouse order-picking. Such structured domains can often be partitioned into distinct process steps, e.g., packaging or transporting. Each process step can have a different prior distribution over activity classes, e.g., standing or walking, and different system dynamics. Here, we show how such context information can be integrated systematically into a deep neural network-based HAR system. Specifically, we propose a hybrid architecture that combines a deep neural network-that estimates high-level movement descriptors, attributes, from the raw-sensor data-and a shallow classifier, which predicts activity classes from the estimated attributes and (optional) context information, like the currently executed process step. We empirically show that our proposed architecture increases HAR performance, compared to state-of-the-art methods. Additionally, we show that HAR performance can be further increased when information about process steps is incorporated, even when that information is only partially correct.
Security in Next Generation Mobile Payment Systems: A Comprehensive Survey
May 25, 2021



Abstract:Cash payment is still king in several markets, accounting for more than 90\ of the payments in almost all the developing countries. The usage of mobile phones is pretty ordinary in this present era. Mobile phones have become an inseparable friend for many users, serving much more than just communication tools. Every subsequent person is heavily relying on them due to multifaceted usage and affordability. Every person wants to manage his/her daily transactions and related issues by using his/her mobile phone. With the rise and advancements of mobile-specific security, threats are evolving as well. In this paper, we provide a survey of various security models for mobile phones. We explore multiple proposed models of the mobile payment system (MPS), their technologies and comparisons, payment methods, different security mechanisms involved in MPS, and provide analysis of the encryption technologies, authentication methods, and firewall in MPS. We also present current challenges and future directions of mobile phone security.
Social network analytics for supervised fraud detection in insurance
Sep 15, 2020



Abstract:Insurance fraud occurs when policyholders file claims that are exaggerated or based on intentional damages. This contribution develops a fraud detection strategy by extracting insightful information from the social network of a claim. First, we construct a network by linking claims with all their involved parties, including the policyholders, brokers, experts, and garages. Next, we establish fraud as a social phenomenon in the network and use the BiRank algorithm with a fraud specific query vector to compute a fraud score for each claim. From the network, we extract features related to the fraud scores as well as the claims' neighborhood structure. Finally, we combine these network features with the claim-specific features and build a supervised model with fraud in motor insurance as the target variable. Although we build a model for only motor insurance, the network includes claims from all available lines of business. Our results show that models with features derived from the network perform well when detecting fraud and even outperform the models using only the classical claim-specific features. Combining network and claim-specific features further improves the performance of supervised learning models to detect fraud. The resulting model flags highly suspicions claims that need to be further investigated. Our approach provides a guided and intelligent selection of claims and contributes to a more effective fraud investigation process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge