Waleed Malik
Large Language Models for Social Networks: Applications, Challenges, and Solutions
Jan 04, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are transforming the way people generate, explore, and engage with content. We study how we can develop LLM applications for online social networks. Despite LLMs' successes in other domains, it is challenging to develop LLM-based products for social networks for numerous reasons, and it has been relatively under-reported in the research community. We categorize LLM applications for social networks into three categories. First is knowledge tasks where users want to find new knowledge and information, such as search and question-answering. Second is entertainment tasks where users want to consume interesting content, such as getting entertaining notification content. Third is foundational tasks that need to be done to moderate and operate the social networks, such as content annotation and LLM monitoring. For each task, we share the challenges we found, solutions we developed, and lessons we learned. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive paper about developing LLM applications for social networks.
Let AI Entertain You: Increasing User Engagement with Generative AI and Rejection Sampling
Dec 16, 2023Abstract:While generative AI excels in content generation, it does not always increase user engagement. This can be attributed to two main factors. First, generative AI generates content without incorporating explicit or implicit feedback about user interactions. Even if the generated content seems to be more informative or well-written, it does not necessarily lead to an increase in user activities, such as clicks. Second, there is a concern with the quality of the content generative AI produces, which often lacks the distinctiveness and authenticity that human-created content possesses. These two factors can lead to content that fails to meet specific needs and preferences of users, ultimately reducing its potential to be engaging. This paper presents a generic framework of how to improve user engagement with generative AI by leveraging user feedback. Our solutions employ rejection sampling, a technique used in reinforcement learning, to boost engagement metrics. We leveraged the framework in the context of email notification subject lines generation for an online social network, and achieved significant engagement metric lift including +1% Session and +0.4% Weekly Active Users. We believe our work offers a universal framework that enhances user engagement with generative AI, particularly when standard generative AI reaches its limits in terms of enhancing content to be more captivating. To the best of our knowledge, this represents an early milestone in the industry's successful use of generative AI to enhance user engagement.
Less is More: Pre-training a Strong Siamese Encoder Using a Weak Decoder
Feb 18, 2021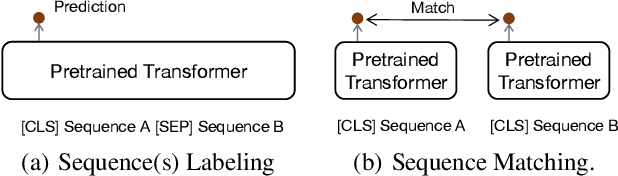
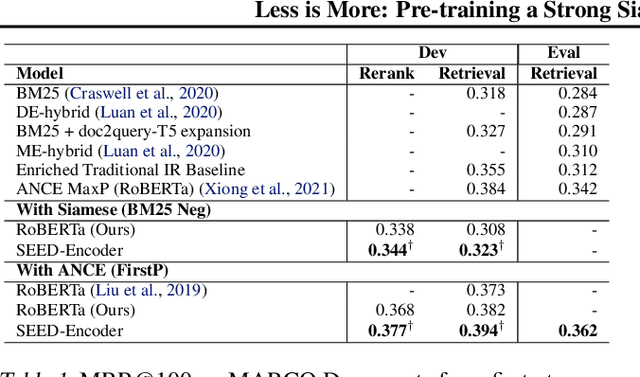
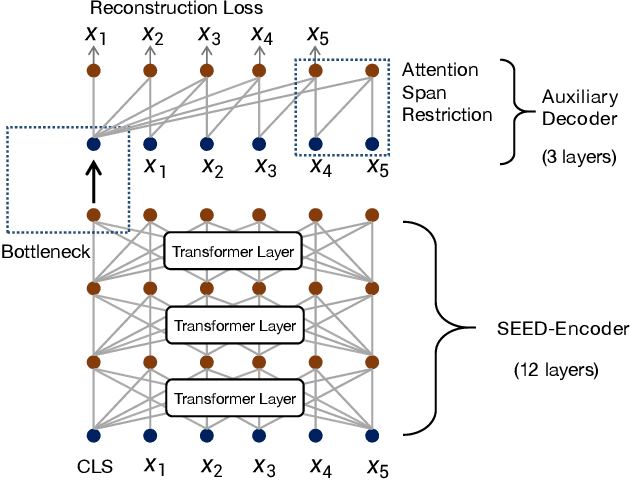
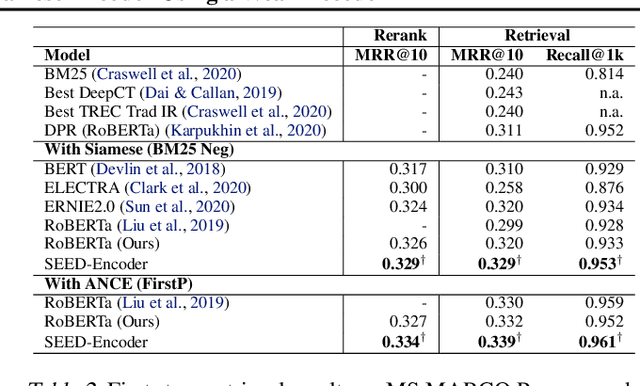
Abstract:Many real-world applications use Siamese networks to efficiently match text sequences at scale, which require high-quality sequence encodings. This paper pre-trains language models dedicated to sequence matching in Siamese architectures. We first hypothesize that a representation is better for sequence matching if the entire sequence can be reconstructed from it, which, however, is unlikely to be achieved in standard autoencoders: A strong decoder can rely on its capacity and natural language patterns to reconstruct and bypass the needs of better sequence encodings. Therefore we propose a new self-learning method that pretrains the encoder with a weak decoder, which reconstructs the original sequence from the encoder's [CLS] representations but is restricted in both capacity and attention span. In our experiments on web search and recommendation, the pre-trained SEED-Encoder, "SiamEsE oriented encoder by reconstructing from weak decoder", shows significantly better generalization ability when fine-tuned in Siamese networks, improving overall accuracy and few-shot performances. Our code and models will be released.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge