Vinh-Thong Ta
Bordeaux INP
POPCORN: Progressive Pseudo-labeling with Consistency Regularization and Neighboring
Sep 13, 2021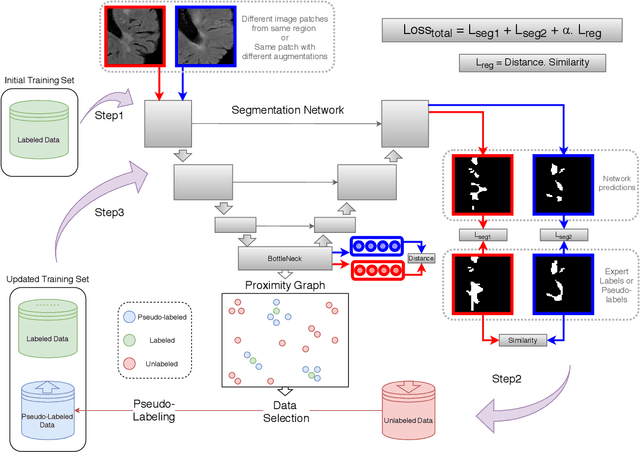
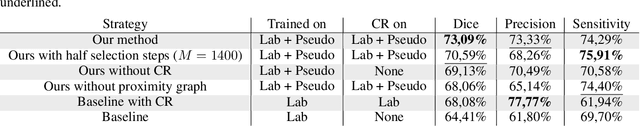
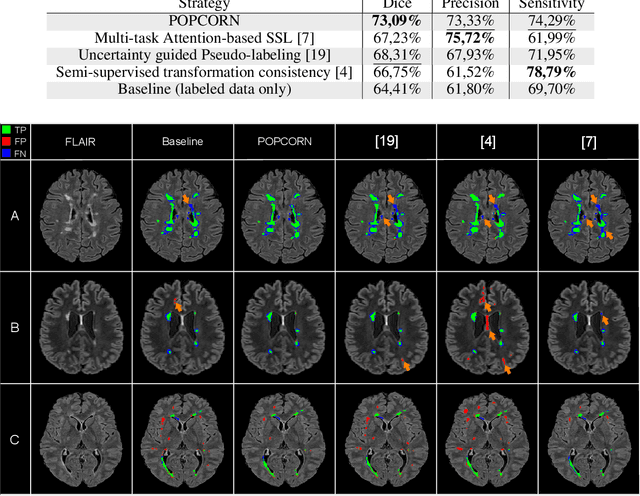
Abstract:Semi-supervised learning (SSL) uses unlabeled data to compensate for the scarcity of annotated images and the lack of method generalization to unseen domains, two usual problems in medical segmentation tasks. In this work, we propose POPCORN, a novel method combining consistency regularization and pseudo-labeling designed for image segmentation. The proposed framework uses high-level regularization to constrain our segmentation model to use similar latent features for images with similar segmentations. POPCORN estimates a proximity graph to select data from easiest ones to more difficult ones, in order to ensure accurate pseudo-labeling and to limit confirmation bias. Applied to multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation, our method demonstrates competitive results compared to other state-of-the-art SSL strategies.
Towards broader generalization of deep learning methods for multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation
Dec 14, 2020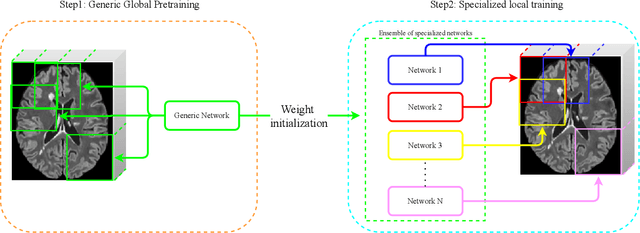
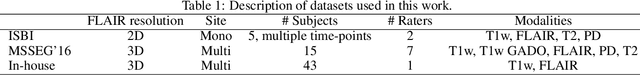
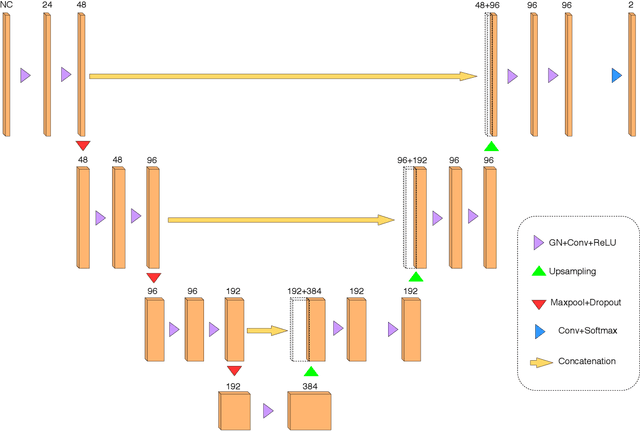
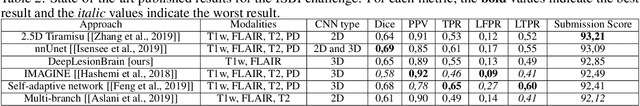
Abstract:Recently, segmentation methods based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) showed promising performance in automatic Multiple Sclerosis (MS) lesions segmentation. These techniques have even outperformed human experts in controlled evaluation condition. However state-of-the-art approaches trained to perform well on highly-controlled datasets fail to generalize on clinical data from unseen datasets. Instead of proposing another improvement of the segmentation accuracy, we propose a novel method robust to domain shift and performing well on unseen datasets, called DeepLesionBrain (DLB). This generalization property results from three main contributions. First, DLB is based on a large ensemble of compact 3D CNNs. This ensemble strategy ensures a robust prediction despite the risk of generalization failure of some individual networks. Second, DLB includes a new image quality data augmentation to reduce dependency to training data specificity (e.g., acquisition protocol). Finally, to learn a more generalizable representation of MS lesions, we propose a hierarchical specialization learning (HSL). HSL is performed by pre-training a generic network over the whole brain, before using its weights as initialization to locally specialized networks. By this end, DLB learns both generic features extracted at global image level and specific features extracted at local image level. At the time of publishing this paper, DLB is among the Top 3 performing published methods on ISBI Challenge while using only half of the available modalities. DLB generalization has also been compared to other state-of-the-art approaches, during cross-dataset experiments on MSSEG'16, ISBI challenge, and in-house datasets. DLB improves the segmentation performance and generalization over classical techniques, and thus proposes a robust approach better suited for clinical practice.
AssemblyNet: A large ensemble of CNNs for 3D Whole Brain MRI Segmentation
Nov 20, 2019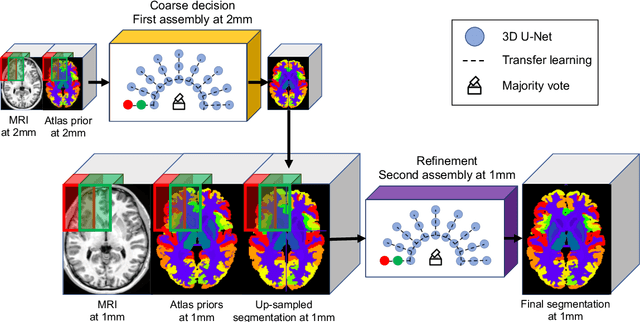
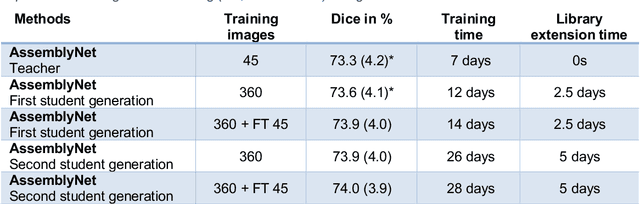
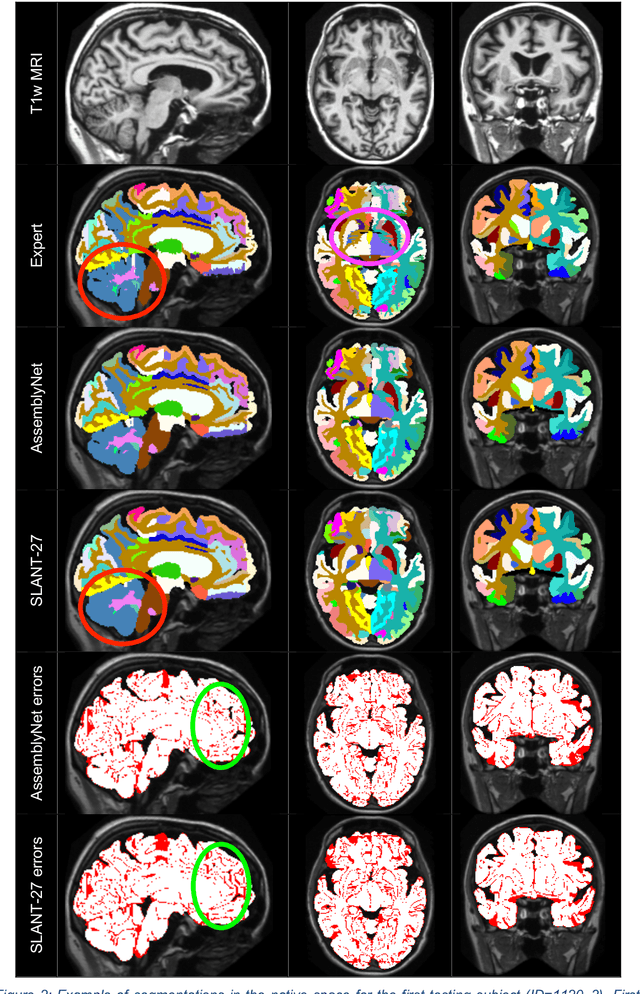
Abstract:Whole brain segmentation using deep learning (DL) is a very challenging task since the number of anatomical labels is very high compared to the number of available training images. To address this problem, previous DL methods proposed to use a single convolution neural network (CNN) or few independent CNNs. In this paper, we present a novel ensemble method based on a large number of CNNs processing different overlapping brain areas. Inspired by parliamentary decision-making systems, we propose a framework called AssemblyNet, made of two "assemblies" of U-Nets. Such a parliamentary system is capable of dealing with complex decisions, unseen problem and reaching a consensus quickly. AssemblyNet introduces sharing of knowledge among neighboring U-Nets, an "amendment" procedure made by the second assembly at higher-resolution to refine the decision taken by the first one, and a final decision obtained by majority voting. During our validation, AssemblyNet showed competitive performance compared to state-of-the-art methods such as U-Net, Joint label fusion and SLANT. Moreover, we investigated the scan-rescan consistency and the robustness to disease effects of our method. These experiences demonstrated the reliability of AssemblyNet. Finally, we showed the interest of using semi-supervised learning to improve the performance of our method.
Multi-scale Graph-based Grading for Alzheimer's Disease Prediction
Jul 15, 2019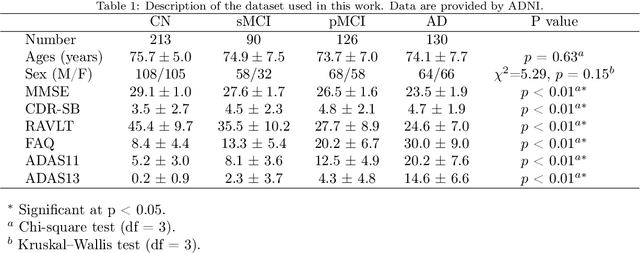
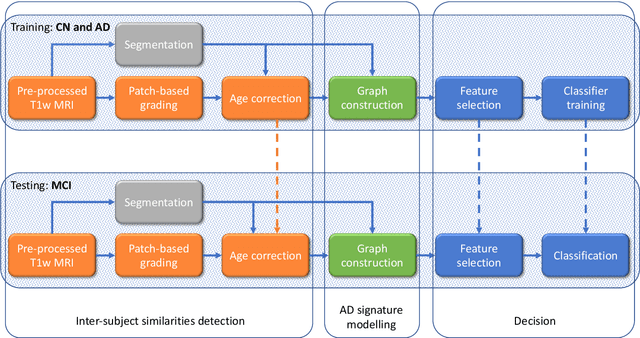
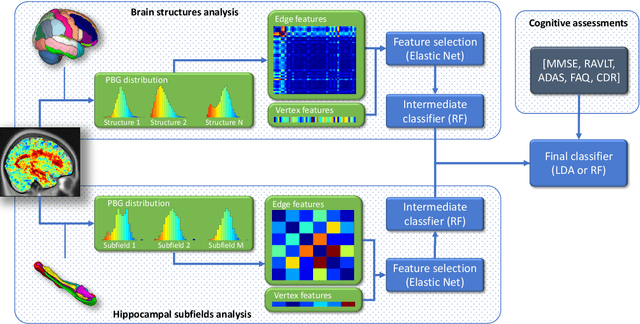
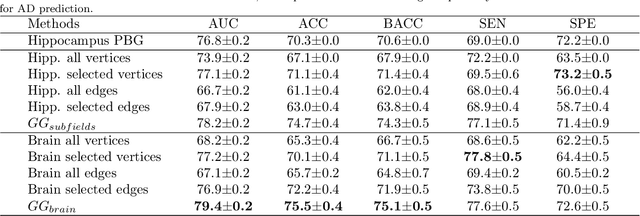
Abstract:The prediction of subjects with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) who will progress to Alzheimer's disease (AD) is clinically relevant, and may above all have a significant impact on accelerate the development of new treatments. In this paper, we present a new MRI-based biomarker that enables us to predict conversion of MCI subjects to AD accurately. In order to better capture the AD signature, we introduce two main contributions. First, we present a new graph-based grading framework to combine inter-subject similarity features and intra-subject variability features. This framework involves patch-based grading of anatomical structures and graph-based modeling of structure alteration relationships. Second, we propose an innovative multiscale brain analysis to capture alterations caused by AD at different anatomical levels. Based on a cascade of classifiers, this multiscale approach enables the analysis of alterations of whole brain structures and hippocampus subfields at the same time. During our experiments using the ADNI-1 dataset, the proposed multiscale graph-based grading method obtained an area under the curve (AUC) of 81% to predict conversion of MCI subjects to AD within three years. Moreover, when combined with cognitive scores, the proposed method obtained 85% of AUC. These results are competitive in comparison to state-of-the-art methods evaluated on the same dataset.
AssemblyNet: A Novel Deep Decision-Making Process for Whole Brain MRI Segmentation
Jun 05, 2019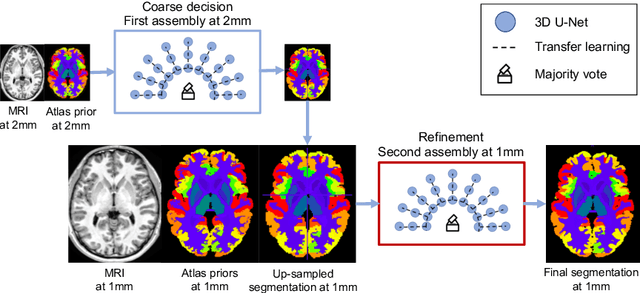
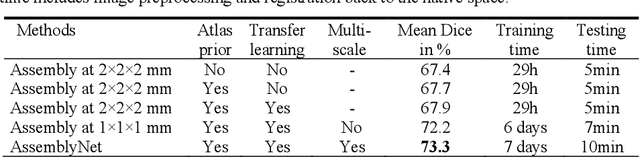
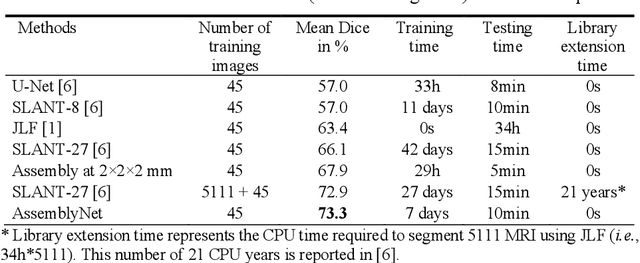
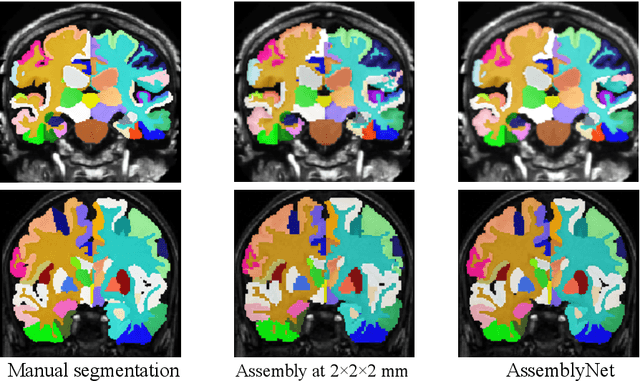
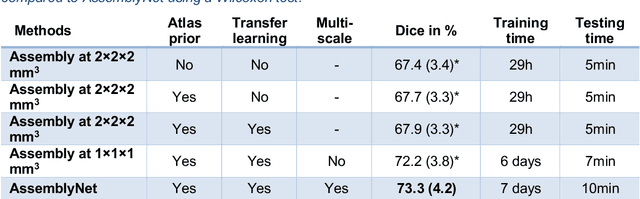
Abstract:Whole brain segmentation using deep learning (DL) is a very challenging task since the number of anatomical labels is very high compared to the number of available training images. To address this problem, previous DL methods proposed to use a global convolution neural network (CNN) or few independent CNNs. In this paper, we present a novel ensemble method based on a large number of CNNs processing different overlapping brain areas. Inspired by parliamentary decision-making systems, we propose a framework called AssemblyNet, made of two "assemblies" of U-Nets. Such a parliamentary system is capable of dealing with complex decisions and reaching a consensus quickly. AssemblyNet introduces sharing of knowledge among neighboring U-Nets, an "amendment" procedure made by the second assembly at higher-resolution to refine the decision taken by the first one, and a final decision obtained by majority voting. When using the same 45 training images, AssemblyNet outperforms global U-Net by 28% in terms of the Dice metric, patch-based joint label fusion by 15% and SLANT-27 by 10%. Finally, AssemblyNet demonstrates high capacity to deal with limited training data to achieve whole brain segmentation in practical training and testing times.
Robust superpixels using color and contour features along linear path
Mar 17, 2019
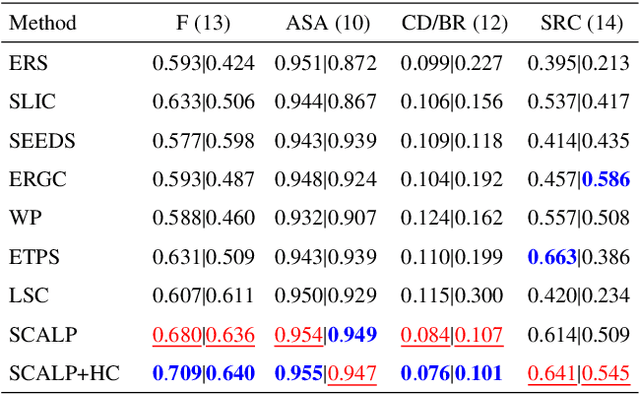
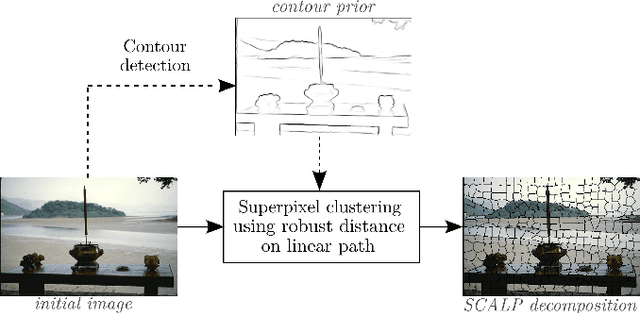
Abstract:Superpixel decomposition methods are widely used in computer vision and image processing applications. By grouping homogeneous pixels, the accuracy can be increased and the decrease of the number of elements to process can drastically reduce the computational burden. For most superpixel methods, a trade-off is computed between 1) color homogeneity, 2) adherence to the image contours and 3) shape regularity of the decomposition. In this paper, we propose a framework that jointly enforces all these aspects and provides accurate and regular Superpixels with Contour Adherence using Linear Path (SCALP). During the decomposition, we propose to consider color features along the linear path between the pixel and the corresponding superpixel barycenter. A contour prior is also used to prevent the crossing of image boundaries when associating a pixel to a superpixel. Finally, in order to improve the decomposition accuracy and the robustness to noise, we propose to integrate the pixel neighborhood information, while preserving the same computational complexity. SCALP is extensively evaluated on standard segmentation dataset, and the obtained results outperform the ones of the state-of-the-art methods. SCALP is also extended for supervoxel decomposition on MRI images.
SuperPatchMatch: an Algorithm for Robust Correspondences using Superpixel Patches
Mar 17, 2019


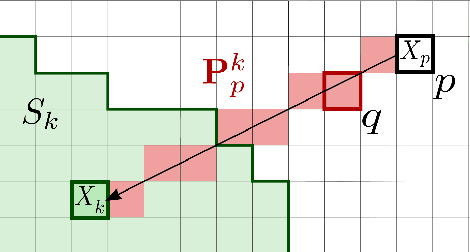
Abstract:Superpixels have become very popular in many computer vision applications. Nevertheless, they remain underexploited since the superpixel decomposition may produce irregular and non stable segmentation results due to the dependency to the image content. In this paper, we first introduce a novel structure, a superpixel-based patch, called SuperPatch. The proposed structure, based on superpixel neighborhood, leads to a robust descriptor since spatial information is naturally included. The generalization of the PatchMatch method to SuperPatches, named SuperPatchMatch, is introduced. Finally, we propose a framework to perform fast segmentation and labeling from an image database, and demonstrate the potential of our approach since we outperform, in terms of computational cost and accuracy, the results of state-of-the-art methods on both face labeling and medical image segmentation.
An Optimized PatchMatch for Multi-scale and Multi-feature Label Fusion
Mar 17, 2019


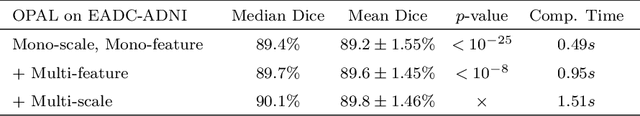
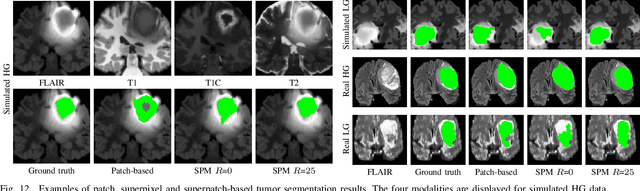
Abstract:Automatic segmentation methods are important tools for quantitative analysis of Magnetic Resonance Images (MRI). Recently, patch-based label fusion approaches have demonstrated state-of-the-art segmentation accuracy. In this paper, we introduce a new patch-based label fusion framework to perform segmentation of anatomical structures. The proposed approach uses an Optimized PAtchMatch Label fusion (OPAL) strategy that drastically reduces the computation time required for the search of similar patches. The reduced computation time of OPAL opens the way for new strategies and facilitates processing on large databases. In this paper, we investigate new perspectives offered by OPAL, by introducing a new multi-scale and multi-feature framework. During our validation on hippocampus segmentation we use two datasets: young adults in the ICBM cohort and elderly adults in the EADC-ADNI dataset. For both, OPAL is compared to state-of-the-art methods. Results show that OPAL obtained the highest median Dice coefficient (89.9% for ICBM and 90.1% for EADC-ADNI). Moreover, in both cases, OPAL produced a segmentation accuracy similar to inter-expert variability. On the EADC-ADNI dataset, we compare the hippocampal volumes obtained by manual and automatic segmentation. The volumes appear to be highly correlated that enables to perform more accurate separation of pathological populations.
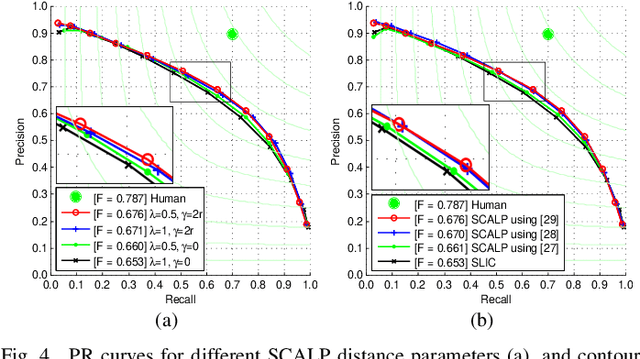
Evaluation Framework of Superpixel Methods with a Global Regularity Measure
Mar 17, 2019Abstract:In the superpixel literature, the comparison of state-of-the-art methods can be biased by the non-robustness of some metrics to decomposition aspects, such as the superpixel scale. Moreover, most recent decomposition methods allow to set a shape regularity parameter, which can have a substantial impact on the measured performances. In this paper, we introduce an evaluation framework, that aims to unify the comparison process of superpixel methods. We investigate the limitations of existing metrics, and propose to evaluate each of the three core decomposition aspects: color homogeneity, respect of image objects and shape regularity. To measure the regularity aspect, we propose a new global regularity measure (GR), which addresses the non-robustness of state-of-the-art metrics. We evaluate recent superpixel methods with these criteria, at several superpixel scales and regularity levels. The proposed framework reduces the bias in the comparison process of state-of-the-art superpixel methods. Finally, we demonstrate that the proposed GR measure is correlated with the performances of various applications.
SCALP: Superpixels with Contour Adherence using Linear Path
Mar 17, 2019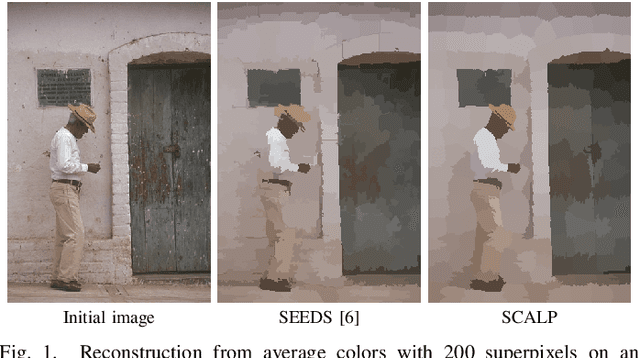
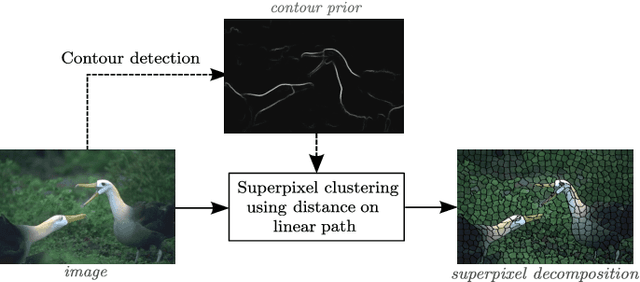
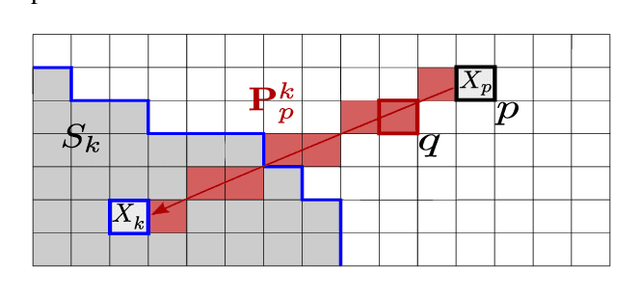
Abstract:Superpixel decomposition methods are generally used as a pre-processing step to speed up image processing tasks. They group the pixels of an image into homogeneous regions while trying to respect existing contours. For all state-of-the-art superpixel decomposition methods, a trade-off is made between 1) computational time, 2) adherence to image contours and 3) regularity and compactness of the decomposition. In this paper, we propose a fast method to compute Superpixels with Contour Adherence using Linear Path (SCALP) in an iterative clustering framework. The distance computed when trying to associate a pixel to a superpixel during the clustering is enhanced by considering the linear path to the superpixel barycenter. The proposed framework produces regular and compact superpixels that adhere to the image contours. We provide a detailed evaluation of SCALP on the standard Berkeley Segmentation Dataset. The obtained results outperform state-of-the-art methods in terms of standard superpixel and contour detection metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge