AssemblyNet: A Novel Deep Decision-Making Process for Whole Brain MRI Segmentation
Paper and Code
Jun 05, 2019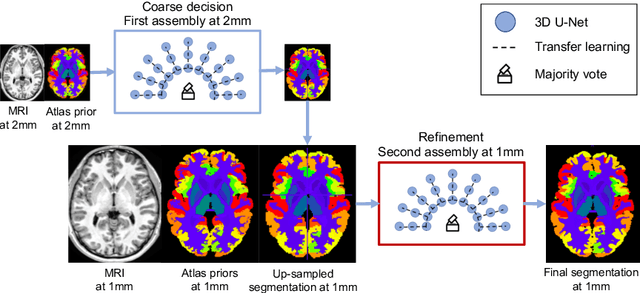
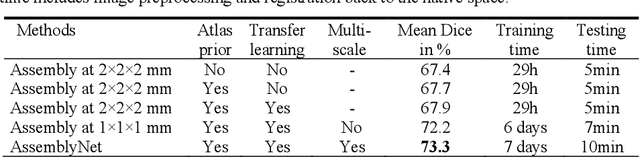
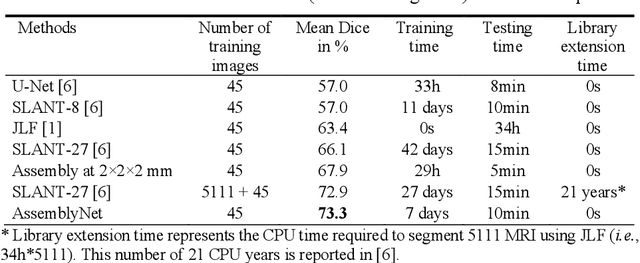
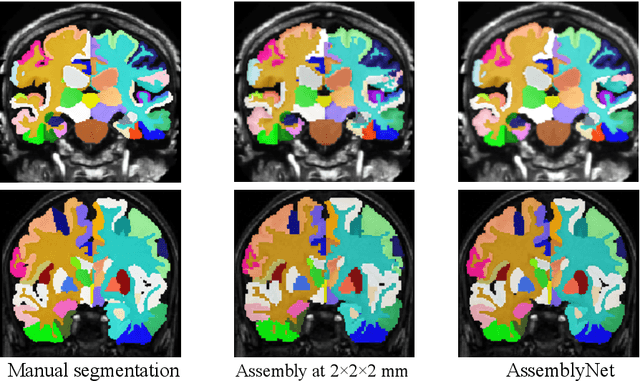
Whole brain segmentation using deep learning (DL) is a very challenging task since the number of anatomical labels is very high compared to the number of available training images. To address this problem, previous DL methods proposed to use a global convolution neural network (CNN) or few independent CNNs. In this paper, we present a novel ensemble method based on a large number of CNNs processing different overlapping brain areas. Inspired by parliamentary decision-making systems, we propose a framework called AssemblyNet, made of two "assemblies" of U-Nets. Such a parliamentary system is capable of dealing with complex decisions and reaching a consensus quickly. AssemblyNet introduces sharing of knowledge among neighboring U-Nets, an "amendment" procedure made by the second assembly at higher-resolution to refine the decision taken by the first one, and a final decision obtained by majority voting. When using the same 45 training images, AssemblyNet outperforms global U-Net by 28% in terms of the Dice metric, patch-based joint label fusion by 15% and SLANT-27 by 10%. Finally, AssemblyNet demonstrates high capacity to deal with limited training data to achieve whole brain segmentation in practical training and testing times.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge