Verena Kaynig
Guided Proofreading of Automatic Segmentations for Connectomics
Apr 04, 2017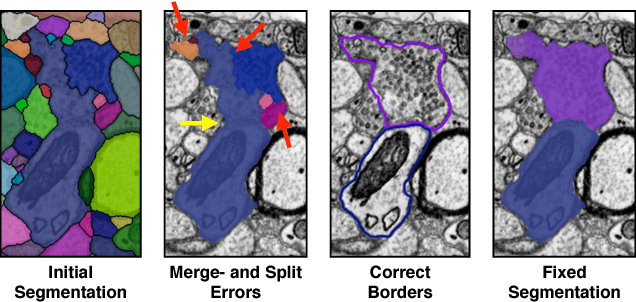
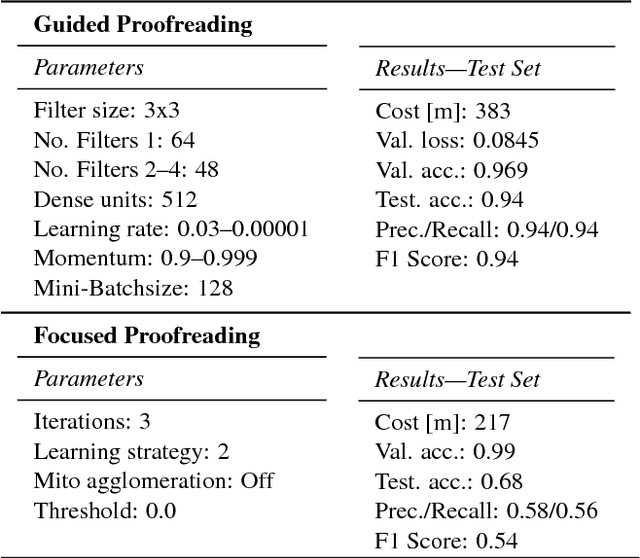
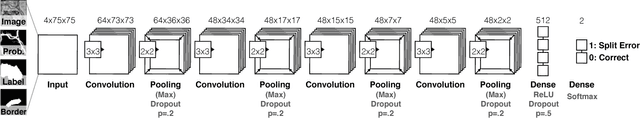
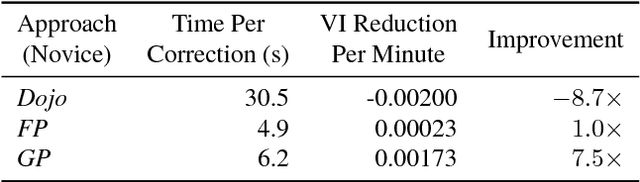
Abstract:Automatic cell image segmentation methods in connectomics produce merge and split errors, which require correction through proofreading. Previous research has identified the visual search for these errors as the bottleneck in interactive proofreading. To aid error correction, we develop two classifiers that automatically recommend candidate merges and splits to the user. These classifiers use a convolutional neural network (CNN) that has been trained with errors in automatic segmentations against expert-labeled ground truth. Our classifiers detect potentially-erroneous regions by considering a large context region around a segmentation boundary. Corrections can then be performed by a user with yes/no decisions, which reduces variation of information 7.5x faster than previous proofreading methods. We also present a fully-automatic mode that uses a probability threshold to make merge/split decisions. Extensive experiments using the automatic approach and comparing performance of novice and expert users demonstrate that our method performs favorably against state-of-the-art proofreading methods on different connectomics datasets.
RhoanaNet Pipeline: Dense Automatic Neural Annotation
Nov 21, 2016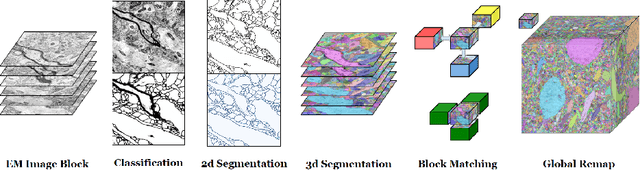
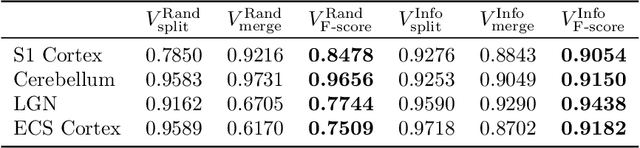
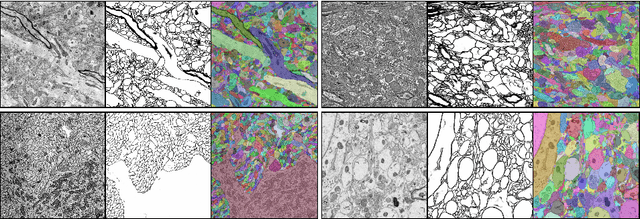
Abstract:Reconstructing a synaptic wiring diagram, or connectome, from electron microscopy (EM) images of brain tissue currently requires many hours of manual annotation or proofreading (Kasthuri and Lichtman, 2010; Lichtman and Sanes, 2008; Seung, 2009). The desire to reconstruct ever larger and more complex networks has pushed the collection of ever larger EM datasets. A cubic millimeter of raw imaging data would take up 1 PB of storage and present an annotation project that would be impractical without relying heavily on automatic segmentation methods. The RhoanaNet image processing pipeline was developed to automatically segment large volumes of EM data and ease the burden of manual proofreading and annotation. Based on (Kaynig et al., 2015), we updated every stage of the software pipeline to provide better throughput performance and higher quality segmentation results. We used state of the art deep learning techniques to generate improved membrane probability maps, and Gala (Nunez-Iglesias et al., 2014) was used to agglomerate 2D segments into 3D objects. We applied the RhoanaNet pipeline to four densely annotated EM datasets, two from mouse cortex, one from cerebellum and one from mouse lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN). All training and test data is made available for benchmark comparisons. The best segmentation results obtained gave $V^\text{Info}_\text{F-score}$ scores of 0.9054 and 09182 for the cortex datasets, 0.9438 for LGN, and 0.9150 for Cerebellum. The RhoanaNet pipeline is open source software. All source code, training data, test data, and annotations for all four benchmark datasets are available at www.rhoana.org.
Icon: An Interactive Approach to Train Deep Neural Networks for Segmentation of Neuronal Structures
Oct 27, 2016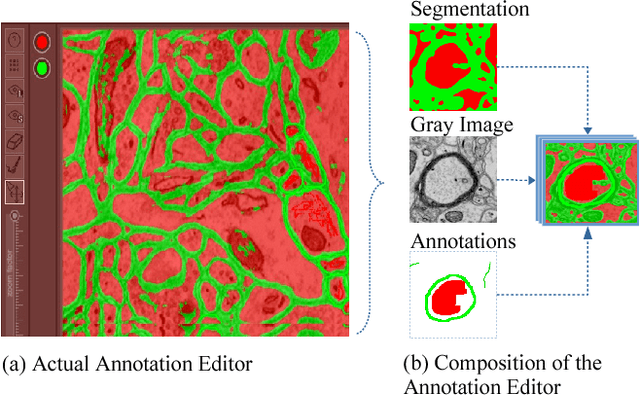
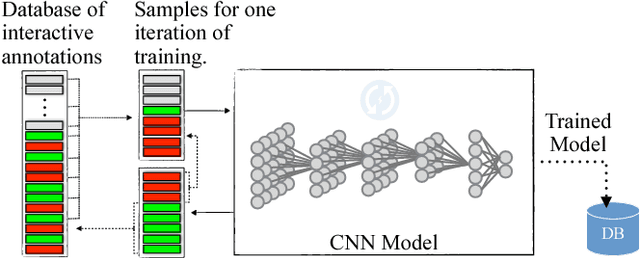
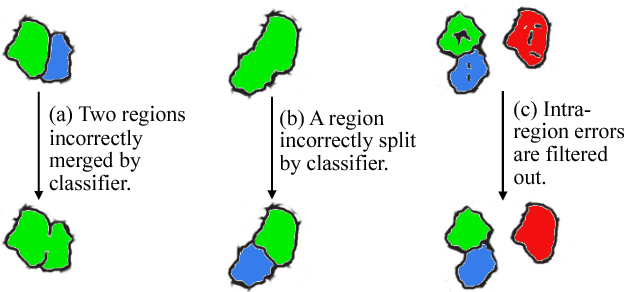
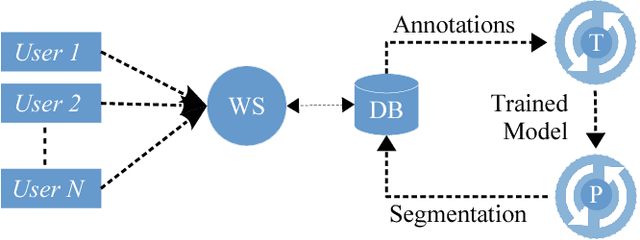
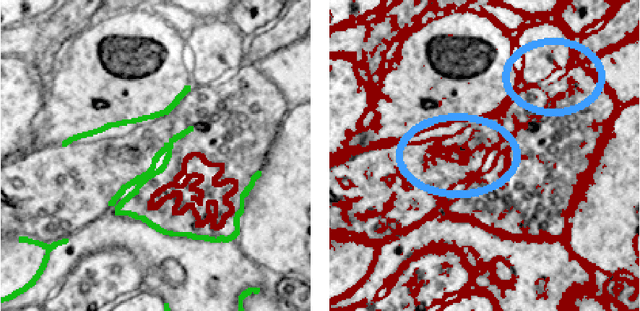
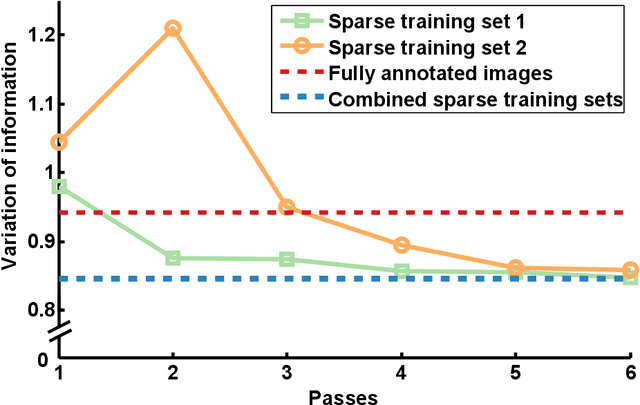
Abstract:We present an interactive approach to train a deep neural network pixel classifier for the segmentation of neuronal structures. An interactive training scheme reduces the extremely tedious manual annotation task that is typically required for deep networks to perform well on image segmentation problems. Our proposed method employs a feedback loop that captures sparse annotations using a graphical user interface, trains a deep neural network based on recent and past annotations, and displays the prediction output to users in almost real-time. Our implementation of the algorithm also allows multiple users to provide annotations in parallel and receive feedback from the same classifier. Quick feedback on classifier performance in an interactive setting enables users to identify and label examples that are more important than others for segmentation purposes. Our experiments show that an interactively-trained pixel classifier produces better region segmentation results on Electron Microscopy (EM) images than those generated by a network of the same architecture trained offline on exhaustive ground-truth labels.
Large-Scale Automatic Reconstruction of Neuronal Processes from Electron Microscopy Images
Mar 28, 2013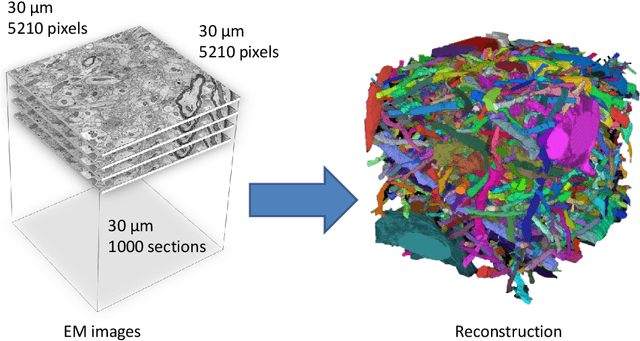
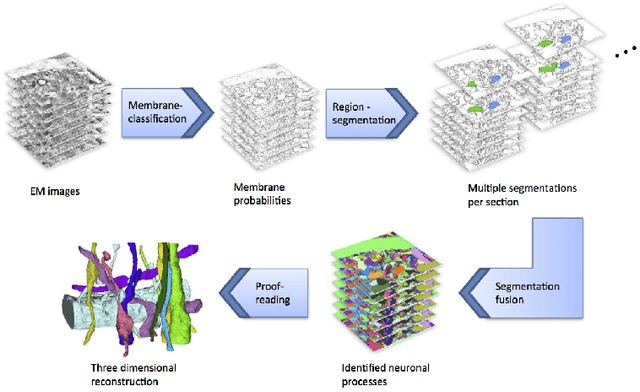
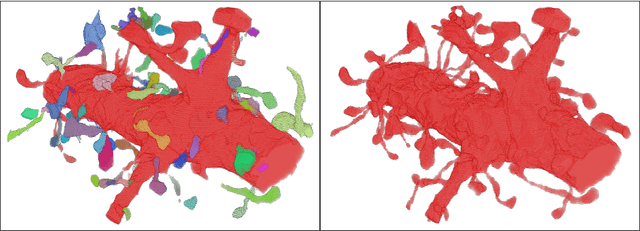
Abstract:Automated sample preparation and electron microscopy enables acquisition of very large image data sets. These technical advances are of special importance to the field of neuroanatomy, as 3D reconstructions of neuronal processes at the nm scale can provide new insight into the fine grained structure of the brain. Segmentation of large-scale electron microscopy data is the main bottleneck in the analysis of these data sets. In this paper we present a pipeline that provides state-of-the art reconstruction performance while scaling to data sets in the GB-TB range. First, we train a random forest classifier on interactive sparse user annotations. The classifier output is combined with an anisotropic smoothing prior in a Conditional Random Field framework to generate multiple segmentation hypotheses per image. These segmentations are then combined into geometrically consistent 3D objects by segmentation fusion. We provide qualitative and quantitative evaluation of the automatic segmentation and demonstrate large-scale 3D reconstructions of neuronal processes from a $\mathbf{27,000}$ $\mathbf{\mu m^3}$ volume of brain tissue over a cube of $\mathbf{30 \; \mu m}$ in each dimension corresponding to 1000 consecutive image sections. We also introduce Mojo, a proofreading tool including semi-automated correction of merge errors based on sparse user scribbles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge