Vítor Silva
Probabilistic Model Incorporating Auxiliary Covariates to Control FDR
Oct 06, 2022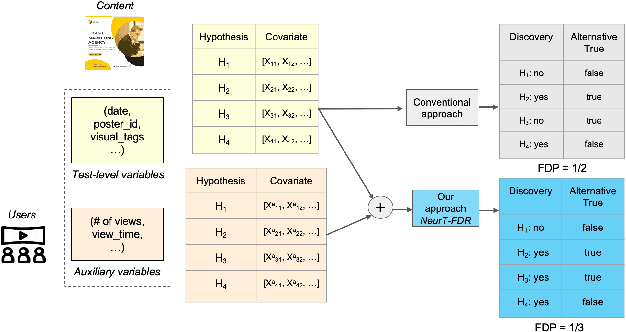
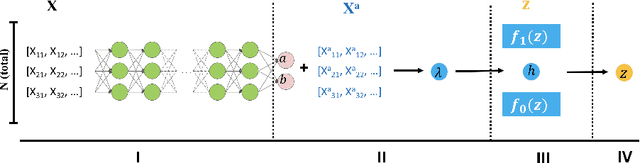
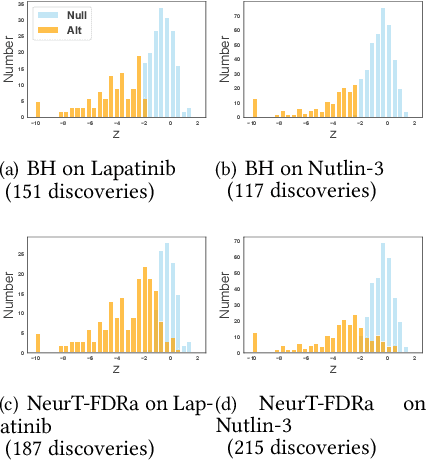
Abstract:Controlling False Discovery Rate (FDR) while leveraging the side information of multiple hypothesis testing is an emerging research topic in modern data science. Existing methods rely on the test-level covariates while ignoring metrics about test-level covariates. This strategy may not be optimal for complex large-scale problems, where indirect relations often exist among test-level covariates and auxiliary metrics or covariates. We incorporate auxiliary covariates among test-level covariates in a deep Black-Box framework controlling FDR (named as NeurT-FDR) which boosts statistical power and controls FDR for multiple-hypothesis testing. Our method parametrizes the test-level covariates as a neural network and adjusts the auxiliary covariates through a regression framework, which enables flexible handling of high-dimensional features as well as efficient end-to-end optimization. We show that NeurT-FDR makes substantially more discoveries in three real datasets compared to competitive baselines.
SemEval 2023 Task 9: Multilingual Tweet Intimacy Analysis
Oct 03, 2022



Abstract:We propose MINT, a new Multilingual INTimacy analysis dataset covering 13,384 tweets in 10 languages including English, French, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Korean, Dutch, Chinese, Hindi, and Arabic. We benchmarked a list of popular multilingual pre-trained language models. The dataset is released along with the SemEval 2023 Task 9: Multilingual Tweet Intimacy Analysis (https://sites.google.com/umich.edu/semeval-2023-tweet-intimacy).
Twitter Topic Classification
Sep 20, 2022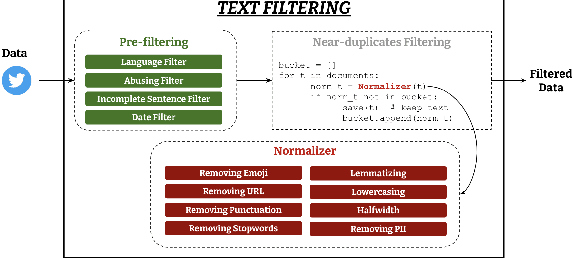


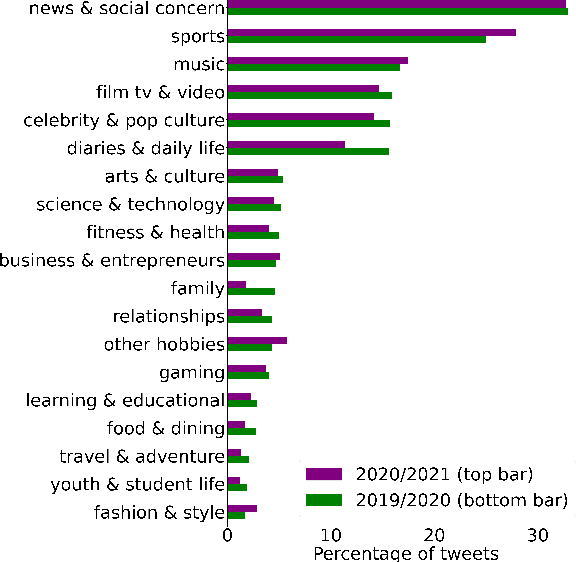
Abstract:Social media platforms host discussions about a wide variety of topics that arise everyday. Making sense of all the content and organising it into categories is an arduous task. A common way to deal with this issue is relying on topic modeling, but topics discovered using this technique are difficult to interpret and can differ from corpus to corpus. In this paper, we present a new task based on tweet topic classification and release two associated datasets. Given a wide range of topics covering the most important discussion points in social media, we provide training and testing data from recent time periods that can be used to evaluate tweet classification models. Moreover, we perform a quantitative evaluation and analysis of current general- and domain-specific language models on the task, which provide more insights on the challenges and nature of the task.
NeurT-FDR: Controlling FDR by Incorporating Feature Hierarchy
Jan 24, 2021

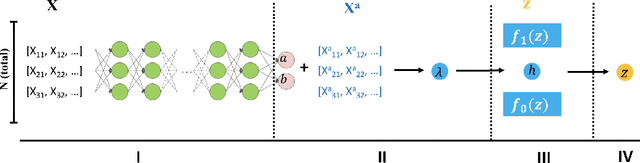

Abstract:Controlling false discovery rate (FDR) while leveraging the side information of multiple hypothesis testing is an emerging research topic in modern data science. Existing methods rely on the test-level covariates while ignoring possible hierarchy among the covariates. This strategy may not be optimal for complex large-scale problems, where hierarchical information often exists among those test-level covariates. We propose NeurT-FDR which boosts statistical power and controls FDR for multiple hypothesis testing while leveraging the hierarchy among test-level covariates. Our method parametrizes the test-level covariates as a neural network and adjusts the feature hierarchy through a regression framework, which enables flexible handling of high-dimensional features as well as efficient end-to-end optimization. We show that NeurT-FDR has strong FDR guarantees and makes substantially more discoveries in synthetic and real datasets compared to competitive baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge