Trong-Thang Pham
DuFal: Dual-Frequency-Aware Learning for High-Fidelity Extremely Sparse-view CBCT Reconstruction
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Sparse-view Cone-Beam Computed Tomography reconstruction from limited X-ray projections remains a challenging problem in medical imaging due to the inherent undersampling of fine-grained anatomical details, which correspond to high-frequency components. Conventional CNN-based methods often struggle to recover these fine structures, as they are typically biased toward learning low-frequency information. To address this challenge, this paper presents DuFal (Dual-Frequency-Aware Learning), a novel framework that integrates frequency-domain and spatial-domain processing via a dual-path architecture. The core innovation lies in our High-Local Factorized Fourier Neural Operator, which comprises two complementary branches: a Global High-Frequency Enhanced Fourier Neural Operator that captures global frequency patterns and a Local High-Frequency Enhanced Fourier Neural Operator that processes spatially partitioned patches to preserve spatial locality that might be lost in global frequency analysis. To improve efficiency, we design a Spectral-Channel Factorization scheme that reduces the Fourier Neural Operator parameter count. We also design a Cross-Attention Frequency Fusion module to integrate spatial and frequency features effectively. The fused features are then decoded through a Feature Decoder to produce projection representations, which are subsequently processed through an Intensity Field Decoding pipeline to reconstruct a final Computed Tomography volume. Experimental results on the LUNA16 and ToothFairy datasets demonstrate that DuFal significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in preserving high-frequency anatomical features, particularly under extremely sparse-view settings.
Interpreting Radiologist's Intention from Eye Movements in Chest X-ray Diagnosis
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Radiologists rely on eye movements to navigate and interpret medical images. A trained radiologist possesses knowledge about the potential diseases that may be present in the images and, when searching, follows a mental checklist to locate them using their gaze. This is a key observation, yet existing models fail to capture the underlying intent behind each fixation. In this paper, we introduce a deep learning-based approach, RadGazeIntent, designed to model this behavior: having an intention to find something and actively searching for it. Our transformer-based architecture processes both the temporal and spatial dimensions of gaze data, transforming fine-grained fixation features into coarse, meaningful representations of diagnostic intent to interpret radiologists' goals. To capture the nuances of radiologists' varied intention-driven behaviors, we process existing medical eye-tracking datasets to create three intention-labeled subsets: RadSeq (Systematic Sequential Search), RadExplore (Uncertainty-driven Exploration), and RadHybrid (Hybrid Pattern). Experimental results demonstrate RadGazeIntent's ability to predict which findings radiologists are examining at specific moments, outperforming baseline methods across all intention-labeled datasets.
Style Transfer for 2D Talking Head Animation
Mar 22, 2023



Abstract:Audio-driven talking head animation is a challenging research topic with many real-world applications. Recent works have focused on creating photo-realistic 2D animation, while learning different talking or singing styles remains an open problem. In this paper, we present a new method to generate talking head animation with learnable style references. Given a set of style reference frames, our framework can reconstruct 2D talking head animation based on a single input image and an audio stream. Our method first produces facial landmarks motion from the audio stream and constructs the intermediate style patterns from the style reference images. We then feed both outputs into a style-aware image generator to generate the photo-realistic and fidelity 2D animation. In practice, our framework can extract the style information of a specific character and transfer it to any new static image for talking head animation. The intensive experimental results show that our method achieves better results than recent state-of-the-art approaches qualitatively and quantitatively.
EmbryosFormer: Deformable Transformer and Collaborative Encoding-Decoding for Embryos Stage Development Classification
Oct 07, 2022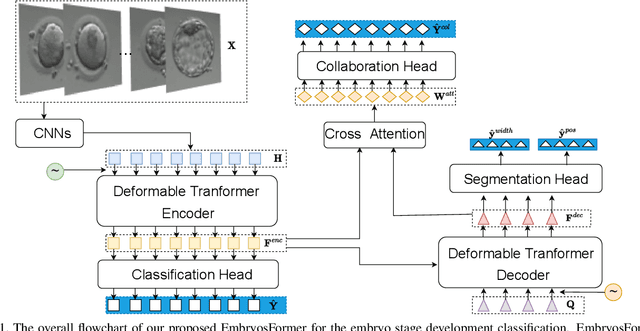
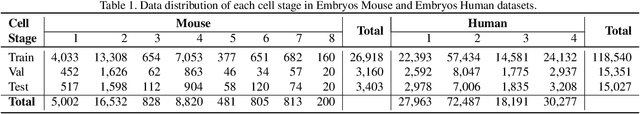
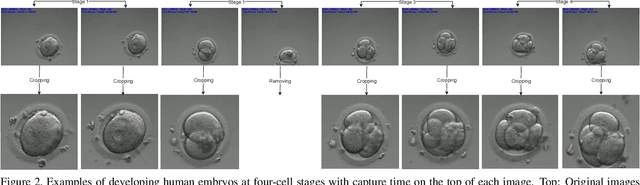
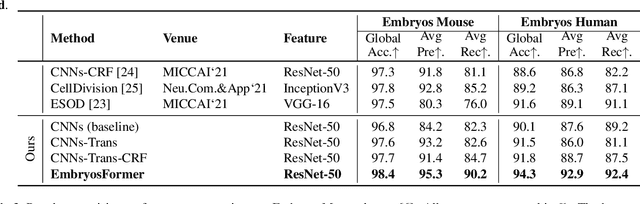
Abstract:The timing of cell divisions in early embryos during the In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF) process is a key predictor of embryo viability. However, observing cell divisions in Time-Lapse Monitoring (TLM) is a time-consuming process and highly depends on experts. In this paper, we propose EmbryosFormer, a computational model to automatically detect and classify cell divisions from original time-lapse images. Our proposed network is designed as an encoder-decoder deformable transformer with collaborative heads. The transformer contracting path predicts per-image labels and is optimized by a classification head. The transformer expanding path models the temporal coherency between embryo images to ensure monotonic non-decreasing constraint and is optimized by a segmentation head. Both contracting and expanding paths are synergetically learned by a collaboration head. We have benchmarked our proposed EmbryosFormer on two datasets: a public dataset with mouse embryos with 8-cell stage and an in-house dataset with human embryos with 4-cell stage. Source code: https://github.com/UARK-AICV/Embryos.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge