Tongyi Tang
Meta Lattice: Model Space Redesign for Cost-Effective Industry-Scale Ads Recommendations
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:The rapidly evolving landscape of products, surfaces, policies, and regulations poses significant challenges for deploying state-of-the-art recommendation models at industry scale, primarily due to data fragmentation across domains and escalating infrastructure costs that hinder sustained quality improvements. To address this challenge, we propose Lattice, a recommendation framework centered around model space redesign that extends Multi-Domain, Multi-Objective (MDMO) learning beyond models and learning objectives. Lattice addresses these challenges through a comprehensive model space redesign that combines cross-domain knowledge sharing, data consolidation, model unification, distillation, and system optimizations to achieve significant improvements in both quality and cost-efficiency. Our deployment of Lattice at Meta has resulted in 10% revenue-driving top-line metrics gain, 11.5% user satisfaction improvement, 6% boost in conversion rate, with 20% capacity saving.
External Large Foundation Model: How to Efficiently Serve Trillions of Parameters for Online Ads Recommendation
Feb 26, 2025



Abstract:Ads recommendation is a prominent service of online advertising systems and has been actively studied. Recent studies indicate that scaling-up and advanced design of the recommendation model can bring significant performance improvement. However, with a larger model scale, such prior studies have a significantly increasing gap from industry as they often neglect two fundamental challenges in industrial-scale applications. First, training and inference budgets are restricted for the model to be served, exceeding which may incur latency and impair user experience. Second, large-volume data arrive in a streaming mode with data distributions dynamically shifting, as new users/ads join and existing users/ads leave the system. We propose the External Large Foundation Model (ExFM) framework to address the overlooked challenges. Specifically, we develop external distillation and a data augmentation system (DAS) to control the computational cost of training/inference while maintaining high performance. We design the teacher in a way like a foundation model (FM) that can serve multiple students as vertical models (VMs) to amortize its building cost. We propose Auxiliary Head and Student Adapter to mitigate the data distribution gap between FM and VMs caused by the streaming data issue. Comprehensive experiments on internal industrial-scale applications and public datasets demonstrate significant performance gain by ExFM.
Personalized Interpolation: An Efficient Method to Tame Flexible Optimization Window Estimation
Jan 23, 2025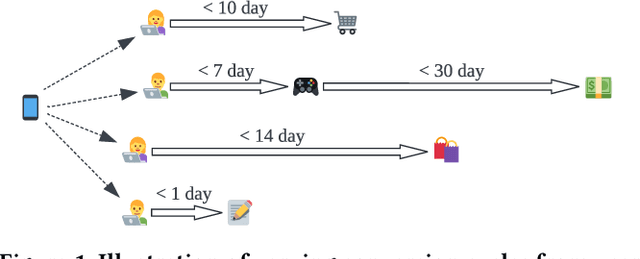
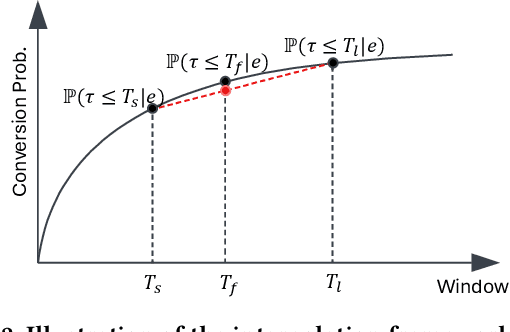
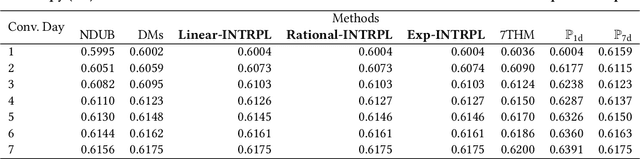
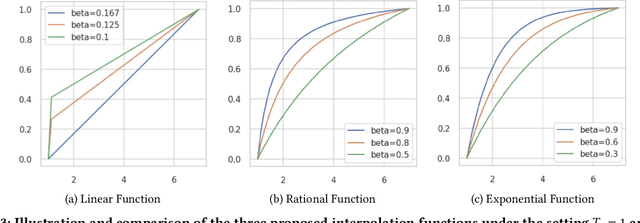
Abstract:In the realm of online advertising, optimizing conversions is crucial for delivering relevant products to users and enhancing business outcomes. Predicting conversion events is challenging due to variable delays between user interactions, such as impressions or clicks, and the actual conversions. These delays differ significantly across various advertisers and products, necessitating distinct optimization time windows for targeted conversions. To address this, we introduce a novel approach named the \textit{Personalized Interpolation} method, which innovatively builds upon existing fixed conversion window models to estimate flexible conversion windows. This method allows for the accurate estimation of conversions across a variety of delay ranges, thus meeting the diverse needs of advertisers without increasing system complexity. To validate the efficacy of our proposed method, we conducted comprehensive experiments using ads conversion model. Our experiments demonstrate that this method not only achieves high prediction accuracy but also does so more efficiently than other existing solutions. This validation underscores the potential of our Personalized Interpolation method to significantly enhance conversion optimization in real-world online advertising systems, promising improved targeting and effectiveness in advertising strategies.
Detecting Adversarial Examples with Bayesian Neural Network
May 28, 2021


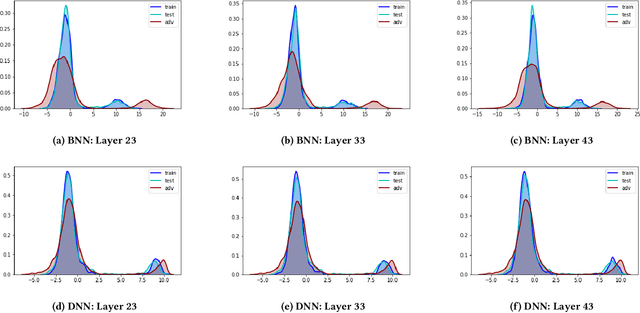
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new framework to detect adversarial examples motivated by the observations that random components can improve the smoothness of predictors and make it easier to simulate output distribution of deep neural network. With these observations, we propose a novel Bayesian adversarial example detector, short for BATer, to improve the performance of adversarial example detection. In specific, we study the distributional difference of hidden layer output between natural and adversarial examples, and propose to use the randomness of Bayesian neural network (BNN) to simulate hidden layer output distribution and leverage the distribution dispersion to detect adversarial examples. The advantage of BNN is that the output is stochastic while neural networks without random components do not have such characteristics. Empirical results on several benchmark datasets against popular attacks show that the proposed BATer outperforms the state-of-the-art detectors in adversarial example detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge