Tomaž Martinčič
Generative Model for Less-Resourced Language with 1 billion parameters
Oct 09, 2024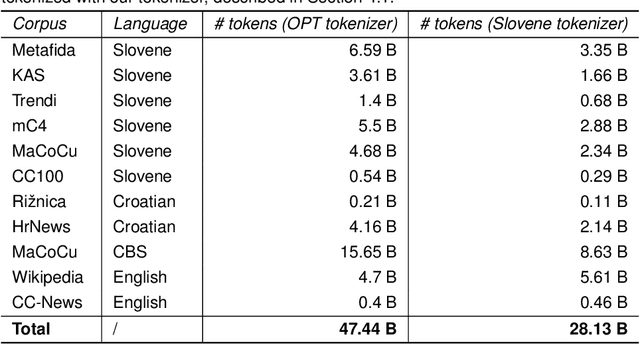
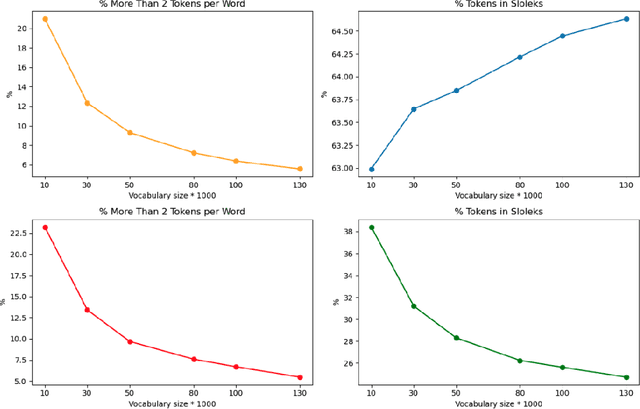
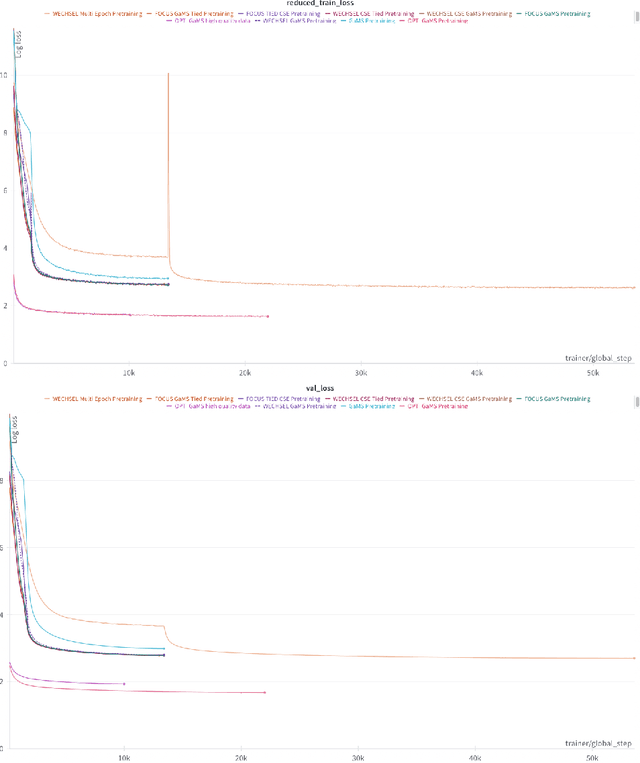
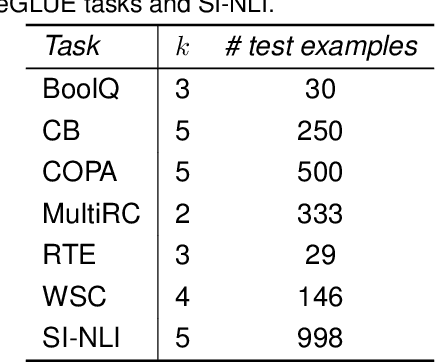
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are a basic infrastructure for modern natural language processing. Many commercial and open-source LLMs exist for English, e.g., ChatGPT, Llama, Falcon, and Mistral. As these models are trained on mostly English texts, their fluency and knowledge of low-resource languages and societies are superficial. We present the development of large generative language models for a less-resourced language. GaMS 1B - Generative Model for Slovene with 1 billion parameters was created by continuing pretraining of the existing English OPT model. We developed a new tokenizer adapted to Slovene, Croatian, and English languages and used embedding initialization methods FOCUS and WECHSEL to transfer the embeddings from the English OPT model. We evaluate our models on several classification datasets from the Slovene suite of benchmarks and generative sentence simplification task SENTA. We only used a few-shot in-context learning of our models, which are not yet instruction-tuned. For classification tasks, in this mode, the generative models lag behind the existing Slovene BERT-type models fine-tuned for specific tasks. On a sentence simplification task, the GaMS models achieve comparable or better performance than the GPT-3.5-Turbo model.
Why is the winner the best?
Mar 30, 2023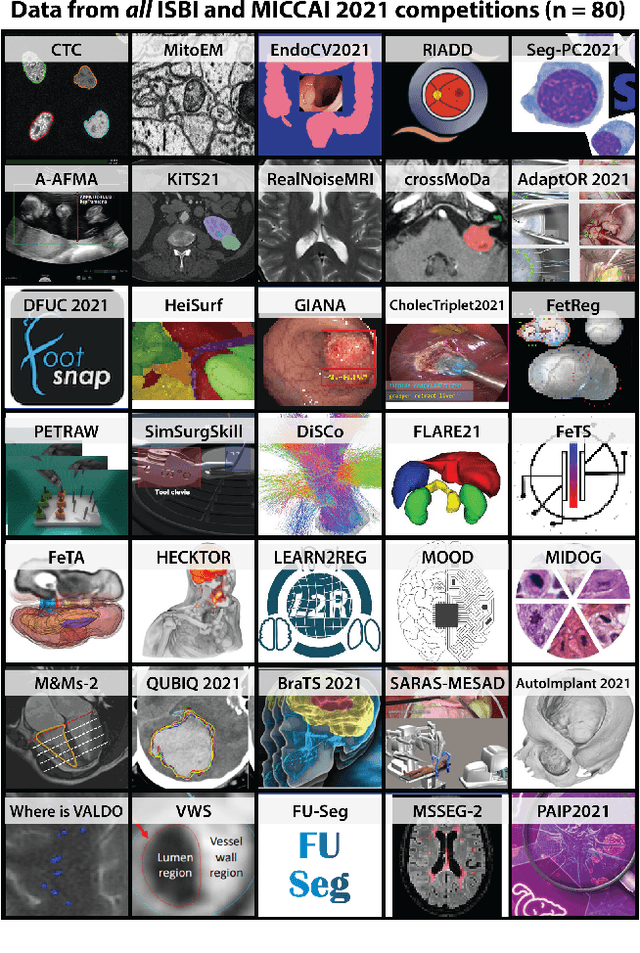
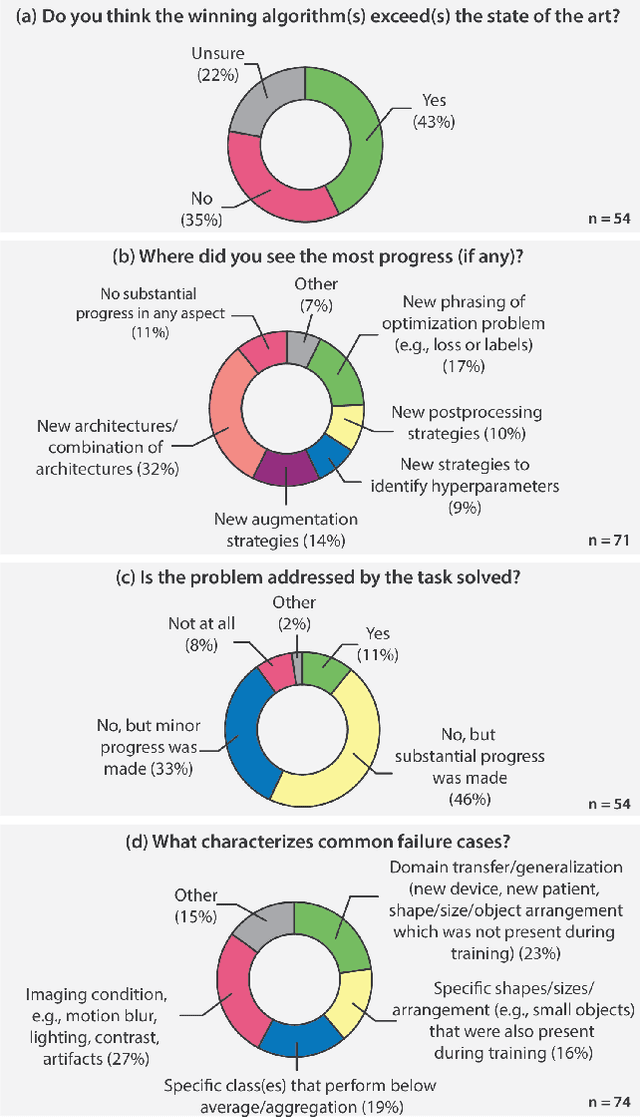
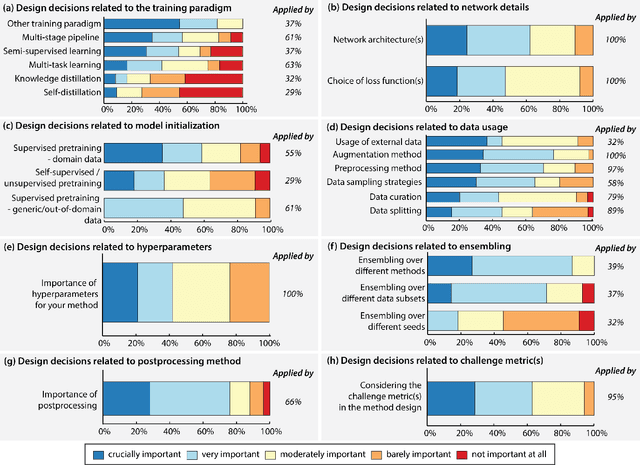
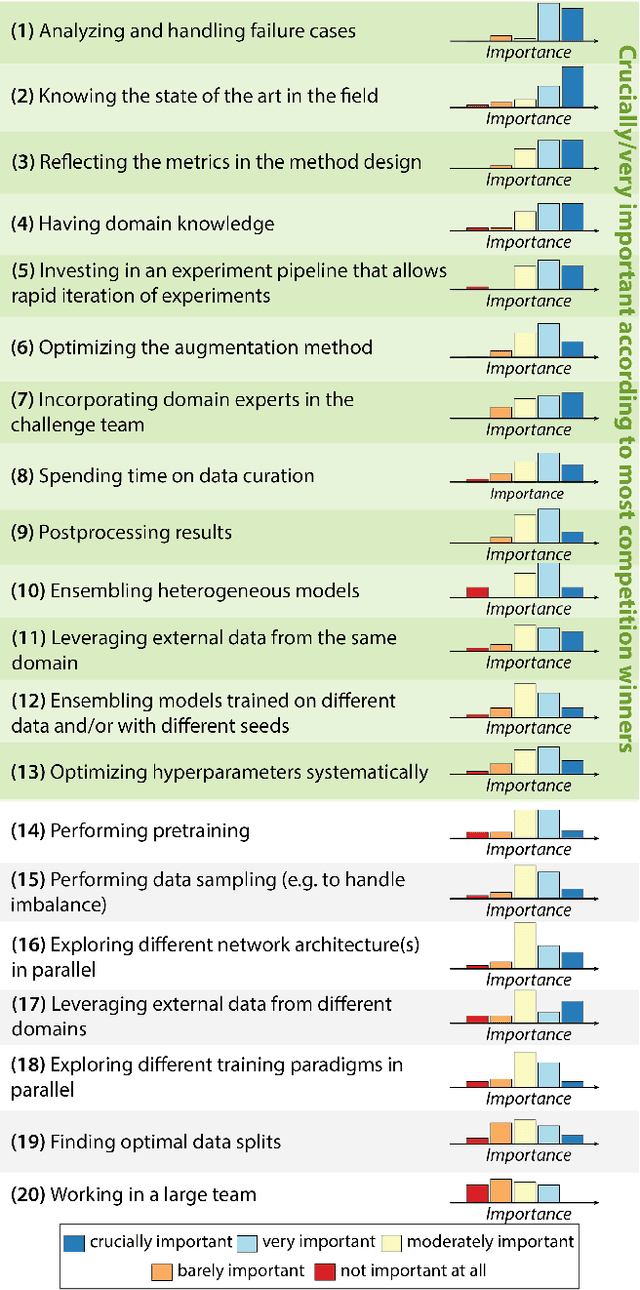
Abstract:International benchmarking competitions have become fundamental for the comparative performance assessment of image analysis methods. However, little attention has been given to investigating what can be learnt from these competitions. Do they really generate scientific progress? What are common and successful participation strategies? What makes a solution superior to a competing method? To address this gap in the literature, we performed a multi-center study with all 80 competitions that were conducted in the scope of IEEE ISBI 2021 and MICCAI 2021. Statistical analyses performed based on comprehensive descriptions of the submitted algorithms linked to their rank as well as the underlying participation strategies revealed common characteristics of winning solutions. These typically include the use of multi-task learning (63%) and/or multi-stage pipelines (61%), and a focus on augmentation (100%), image preprocessing (97%), data curation (79%), and postprocessing (66%). The "typical" lead of a winning team is a computer scientist with a doctoral degree, five years of experience in biomedical image analysis, and four years of experience in deep learning. Two core general development strategies stood out for highly-ranked teams: the reflection of the metrics in the method design and the focus on analyzing and handling failure cases. According to the organizers, 43% of the winning algorithms exceeded the state of the art but only 11% completely solved the respective domain problem. The insights of our study could help researchers (1) improve algorithm development strategies when approaching new problems, and (2) focus on open research questions revealed by this work.
Segmentation of Multiple Myeloma Plasma Cells in Microscopy Images with Noisy Labels
Nov 08, 2021



Abstract:A key component towards an improved and fast cancer diagnosis is the development of computer-assisted tools. In this article, we present the solution that won the SegPC-2021 competition for the segmentation of multiple myeloma plasma cells in microscopy images. The labels used in the competition dataset were generated semi-automatically and presented noise. To deal with it, a heavy image augmentation procedure was carried out and predictions from several models were combined using a custom ensemble strategy. State-of-the-art feature extractors and instance segmentation architectures were used, resulting in a mean Intersection-over-Union of 0.9389 on the SegPC-2021 final test set.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge