Tobias Pohlen
Reward learning from human preferences and demonstrations in Atari
Nov 15, 2018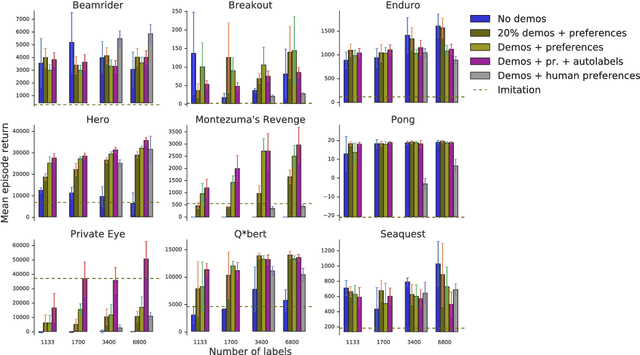
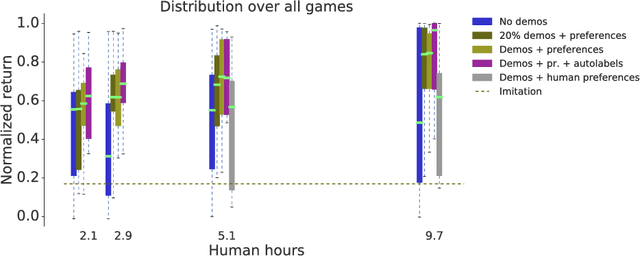
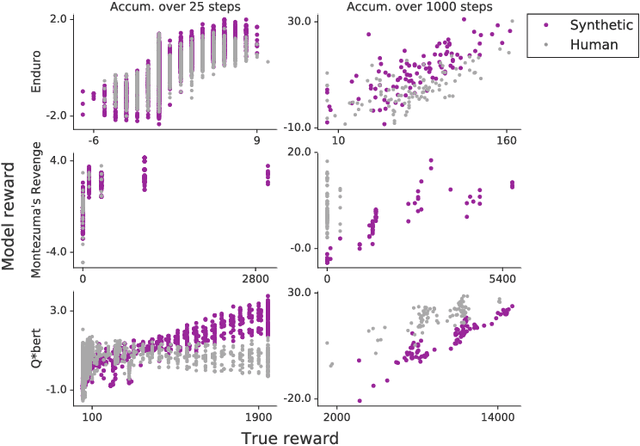
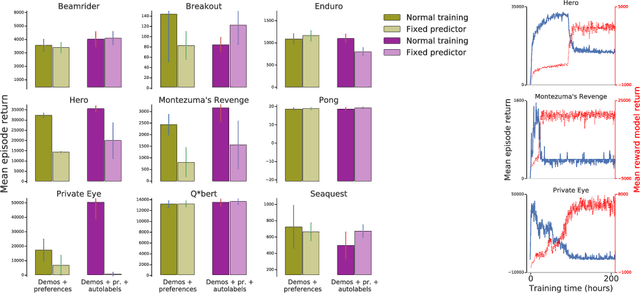
Abstract:To solve complex real-world problems with reinforcement learning, we cannot rely on manually specified reward functions. Instead, we can have humans communicate an objective to the agent directly. In this work, we combine two approaches to learning from human feedback: expert demonstrations and trajectory preferences. We train a deep neural network to model the reward function and use its predicted reward to train an DQN-based deep reinforcement learning agent on 9 Atari games. Our approach beats the imitation learning baseline in 7 games and achieves strictly superhuman performance on 2 games without using game rewards. Additionally, we investigate the goodness of fit of the reward model, present some reward hacking problems, and study the effects of noise in the human labels.
Observe and Look Further: Achieving Consistent Performance on Atari
May 29, 2018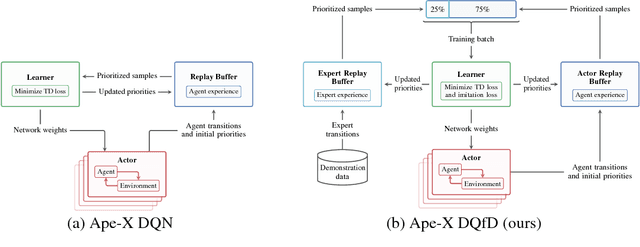
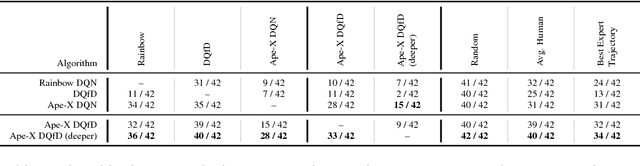
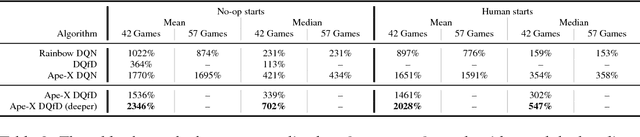
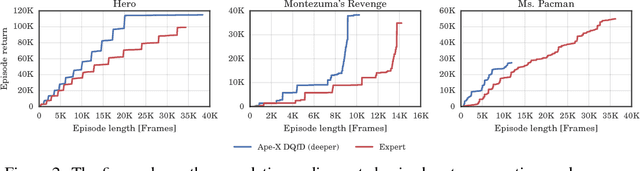
Abstract:Despite significant advances in the field of deep Reinforcement Learning (RL), today's algorithms still fail to learn human-level policies consistently over a set of diverse tasks such as Atari 2600 games. We identify three key challenges that any algorithm needs to master in order to perform well on all games: processing diverse reward distributions, reasoning over long time horizons, and exploring efficiently. In this paper, we propose an algorithm that addresses each of these challenges and is able to learn human-level policies on nearly all Atari games. A new transformed Bellman operator allows our algorithm to process rewards of varying densities and scales; an auxiliary temporal consistency loss allows us to train stably using a discount factor of $\gamma = 0.999$ (instead of $\gamma = 0.99$) extending the effective planning horizon by an order of magnitude; and we ease the exploration problem by using human demonstrations that guide the agent towards rewarding states. When tested on a set of 42 Atari games, our algorithm exceeds the performance of an average human on 40 games using a common set of hyper parameters. Furthermore, it is the first deep RL algorithm to solve the first level of Montezuma's Revenge.
Full-Resolution Residual Networks for Semantic Segmentation in Street Scenes
Dec 06, 2016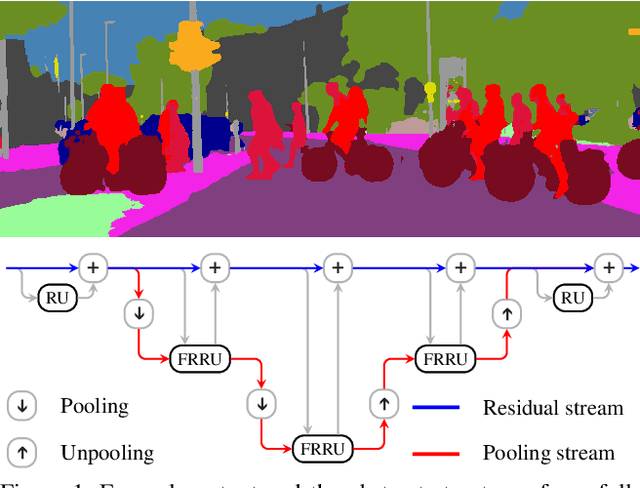

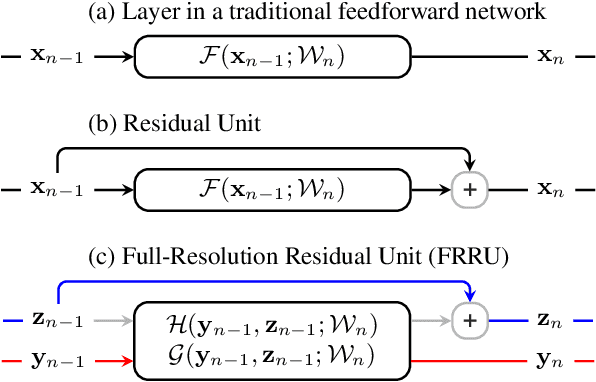

Abstract:Semantic image segmentation is an essential component of modern autonomous driving systems, as an accurate understanding of the surrounding scene is crucial to navigation and action planning. Current state-of-the-art approaches in semantic image segmentation rely on pre-trained networks that were initially developed for classifying images as a whole. While these networks exhibit outstanding recognition performance (i.e., what is visible?), they lack localization accuracy (i.e., where precisely is something located?). Therefore, additional processing steps have to be performed in order to obtain pixel-accurate segmentation masks at the full image resolution. To alleviate this problem we propose a novel ResNet-like architecture that exhibits strong localization and recognition performance. We combine multi-scale context with pixel-level accuracy by using two processing streams within our network: One stream carries information at the full image resolution, enabling precise adherence to segment boundaries. The other stream undergoes a sequence of pooling operations to obtain robust features for recognition. The two streams are coupled at the full image resolution using residuals. Without additional processing steps and without pre-training, our approach achieves an intersection-over-union score of 71.8% on the Cityscapes dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge