Tianjiao Zhao
Can Language Models Enable In-Context Database?
Nov 04, 2024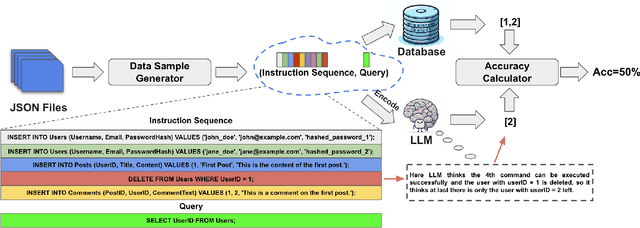
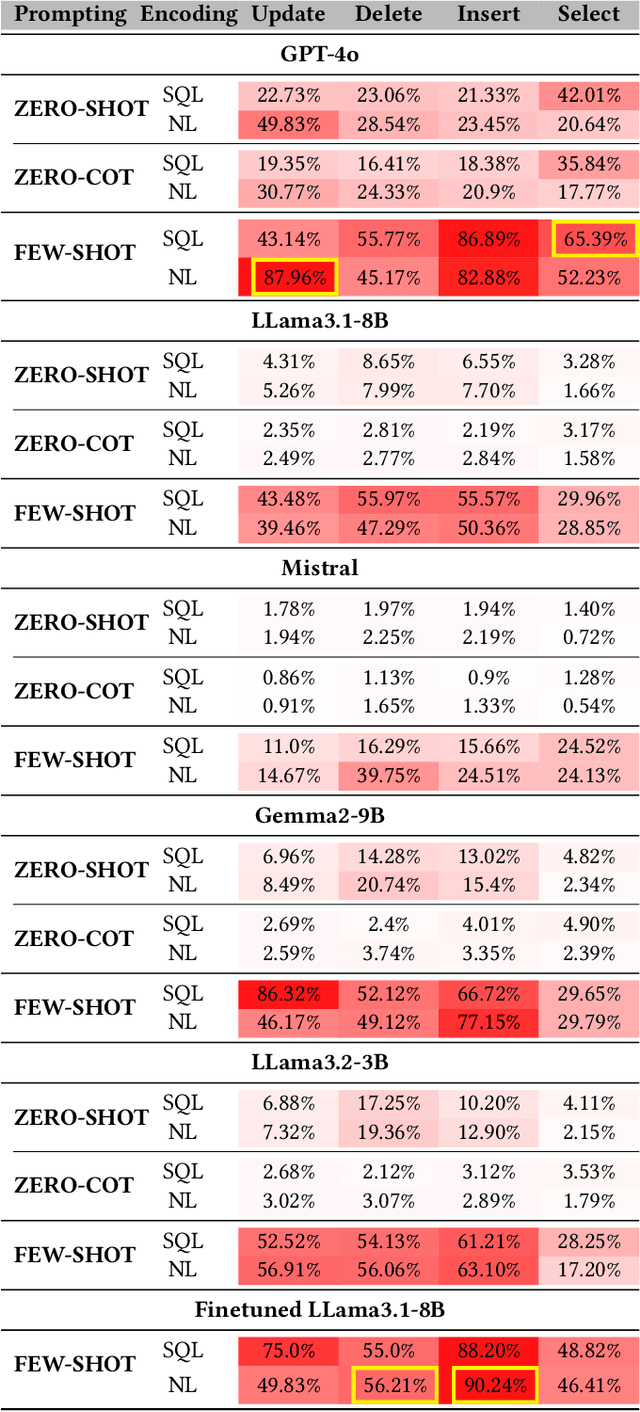
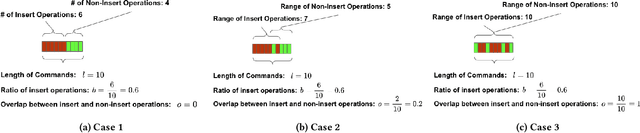
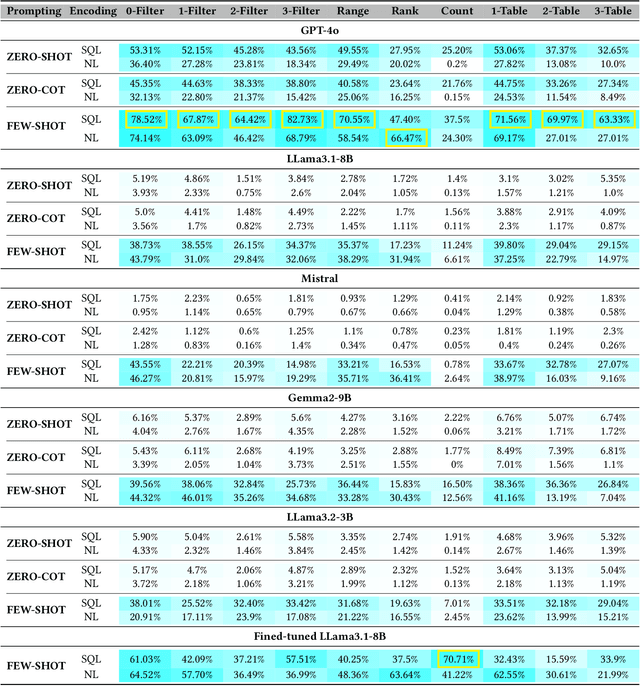
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are emerging as few-shot learners capable of handling a variety of tasks, including comprehension, planning, reasoning, question answering, arithmetic calculations, and more. At the core of these capabilities is LLMs' proficiency in representing and understanding structural or semi-structural data, such as tables and graphs. Numerous studies have demonstrated that reasoning on tabular data or graphs is not only feasible for LLMs but also gives a promising research direction which treats these data as in-context data. The lightweight and human readable characteristics of in-context database can potentially make it an alternative for the traditional database in typical RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) settings. However, almost all current work focuses on static in-context data, which does not allow dynamic update. In this paper, to enable dynamic database update, delta encoding of database is proposed. We explore how data stored in traditional RDBMS can be encoded as in-context text and evaluate LLMs' proficiency for CRUD (Create, Read, Update and Delete) operations on in-context databases. A benchmark named InConDB is presented and extensive experiments are conducted to show the performance of different language models in enabling in-context database by varying the database encoding method, prompting method, operation type and input data distribution, revealing both the proficiency and limitations.
Beyond One-Model-Fits-All: A Survey of Domain Specialization for Large Language Models
May 31, 2023



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have significantly advanced the field of natural language processing (NLP), providing a highly useful, task-agnostic foundation for a wide range of applications. The great promise of LLMs as general task solvers motivated people to extend their functionality largely beyond just a ``chatbot'', and use it as an assistant or even replacement for domain experts and tools in specific domains such as healthcare, finance, and education. However, directly applying LLMs to solve sophisticated problems in specific domains meets many hurdles, caused by the heterogeneity of domain data, the sophistication of domain knowledge, the uniqueness of domain objectives, and the diversity of the constraints (e.g., various social norms, cultural conformity, religious beliefs, and ethical standards in the domain applications). To fill such a gap, explosively-increase research, and practices have been conducted in very recent years on the domain specialization of LLMs, which, however, calls for a comprehensive and systematic review to better summarizes and guide this promising domain. In this survey paper, first, we propose a systematic taxonomy that categorizes the LLM domain-specialization techniques based on the accessibility to LLMs and summarizes the framework for all the subcategories as well as their relations and differences to each other. We also present a comprehensive taxonomy of critical application domains that can benefit from specialized LLMs, discussing their practical significance and open challenges. Furthermore, we offer insights into the current research status and future trends in this area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge