Tianci Luo
Embracing Collaboration Over Competition: Condensing Multiple Prompts for Visual In-Context Learning
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Visual In-Context Learning (VICL) enables adaptively solving vision tasks by leveraging pixel demonstrations, mimicking human-like task completion through analogy. Prompt selection is critical in VICL, but current methods assume the existence of a single "ideal" prompt in a pool of candidates, which in practice may not hold true. Multiple suitable prompts may exist, but individually they often fall short, leading to difficulties in selection and the exclusion of useful context. To address this, we propose a new perspective: prompt condensation. Rather than relying on a single prompt, candidate prompts collaborate to efficiently integrate informative contexts without sacrificing resolution. We devise Condenser, a lightweight external plugin that compresses relevant fine-grained context across multiple prompts. Optimized end-to-end with the backbone, Condenser ensures accurate integration of contextual cues. Experiments demonstrate Condenser outperforms state-of-the-arts across benchmark tasks, showing superior context compression, scalability with more prompts, and enhanced computational efficiency compared to ensemble methods, positioning it as a highly competitive solution for VICL. Code is open-sourced at https://github.com/gimpong/CVPR25-Condenser.
MambaVC: Learned Visual Compression with Selective State Spaces
May 28, 2024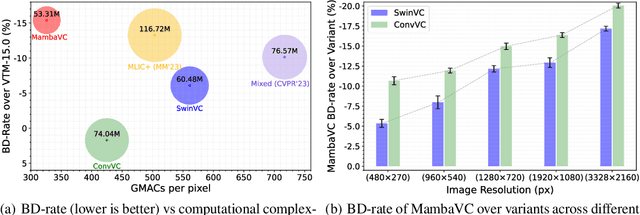
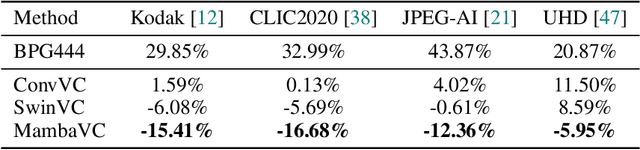
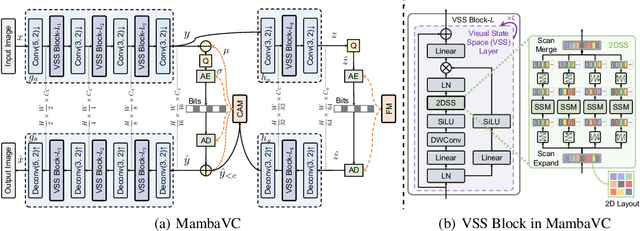
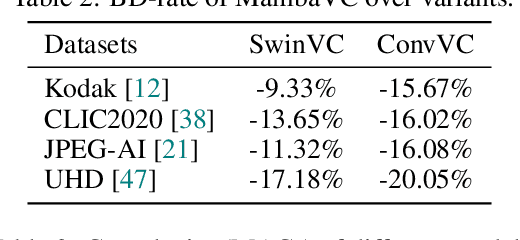
Abstract:Learned visual compression is an important and active task in multimedia. Existing approaches have explored various CNN- and Transformer-based designs to model content distribution and eliminate redundancy, where balancing efficacy (i.e., rate-distortion trade-off) and efficiency remains a challenge. Recently, state-space models (SSMs) have shown promise due to their long-range modeling capacity and efficiency. Inspired by this, we take the first step to explore SSMs for visual compression. We introduce MambaVC, a simple, strong and efficient compression network based on SSM. MambaVC develops a visual state space (VSS) block with a 2D selective scanning (2DSS) module as the nonlinear activation function after each downsampling, which helps to capture informative global contexts and enhances compression. On compression benchmark datasets, MambaVC achieves superior rate-distortion performance with lower computational and memory overheads. Specifically, it outperforms CNN and Transformer variants by 9.3% and 15.6% on Kodak, respectively, while reducing computation by 42% and 24%, and saving 12% and 71% of memory. MambaVC shows even greater improvements with high-resolution images, highlighting its potential and scalability in real-world applications. We also provide a comprehensive comparison of different network designs, underscoring MambaVC's advantages. Code is available at https://github.com/QinSY123/2024-MambaVC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge