Tao Yue
Learnable Burst-Encodable Time-of-Flight Imaging for High-Fidelity Long-Distance Depth Sensing
May 28, 2025Abstract:Long-distance depth imaging holds great promise for applications such as autonomous driving and robotics. Direct time-of-flight (dToF) imaging offers high-precision, long-distance depth sensing, yet demands ultra-short pulse light sources and high-resolution time-to-digital converters. In contrast, indirect time-of-flight (iToF) imaging often suffers from phase wrapping and low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) as the sensing distance increases. In this paper, we introduce a novel ToF imaging paradigm, termed Burst-Encodable Time-of-Flight (BE-ToF), which facilitates high-fidelity, long-distance depth imaging. Specifically, the BE-ToF system emits light pulses in burst mode and estimates the phase delay of the reflected signal over the entire burst period, thereby effectively avoiding the phase wrapping inherent to conventional iToF systems. Moreover, to address the low SNR caused by light attenuation over increasing distances, we propose an end-to-end learnable framework that jointly optimizes the coding functions and the depth reconstruction network. A specialized double well function and first-order difference term are incorporated into the framework to ensure the hardware implementability of the coding functions. The proposed approach is rigorously validated through comprehensive simulations and real-world prototype experiments, demonstrating its effectiveness and practical applicability.
A Machine Learning-Based Error Mitigation Approach For Reliable Software Development On IBM'S Quantum Computers
Apr 19, 2024



Abstract:Quantum computers have the potential to outperform classical computers for some complex computational problems. However, current quantum computers (e.g., from IBM and Google) have inherent noise that results in errors in the outputs of quantum software executing on the quantum computers, affecting the reliability of quantum software development. The industry is increasingly interested in machine learning (ML)--based error mitigation techniques, given their scalability and practicality. However, existing ML-based techniques have limitations, such as only targeting specific noise types or specific quantum circuits. This paper proposes a practical ML-based approach, called Q-LEAR, with a novel feature set, to mitigate noise errors in quantum software outputs. We evaluated Q-LEAR on eight quantum computers and their corresponding noisy simulators, all from IBM, and compared Q-LEAR with a state-of-the-art ML-based approach taken as baseline. Results show that, compared to the baseline, Q-LEAR achieved a 25% average improvement in error mitigation on both real quantum computers and simulators. We also discuss the implications and practicality of Q-LEAR, which, we believe, is valuable for practitioners.
EpiTESTER: Testing Autonomous Vehicles with Epigenetic Algorithm and Attention Mechanism
Nov 30, 2023Abstract:Testing autonomous vehicles (AVs) under various environmental scenarios that lead the vehicles to unsafe situations is known to be challenging. Given the infinite possible environmental scenarios, it is essential to find critical scenarios efficiently. To this end, we propose a novel testing method, named EpiTESTER, by taking inspiration from epigenetics, which enables species to adapt to sudden environmental changes. In particular, EpiTESTER adopts gene silencing as its epigenetic mechanism, which regulates gene expression to prevent the expression of a certain gene, and the probability of gene expression is dynamically computed as the environment changes. Given different data modalities (e.g., images, lidar point clouds) in the context of AV, EpiTESTER benefits from a multi-model fusion transformer to extract high-level feature representations from environmental factors and then calculates probabilities based on these features with the attention mechanism. To assess the cost-effectiveness of EpiTESTER, we compare it with a classical genetic algorithm (GA) (i.e., without any epigenetic mechanism implemented) and EpiTESTER with equal probability for each gene. We evaluate EpiTESTER with four initial environments from CARLA, an open-source simulator for autonomous driving research, and an end-to-end AV controller, Interfuser. Our results show that EpiTESTER achieved a promising performance in identifying critical scenarios compared to the baselines, showing that applying epigenetic mechanisms is a good option for solving practical problems.
C-Silicon-based metasurfaces for aperture-robust spectrometer/imaging with angle integration
Oct 31, 2023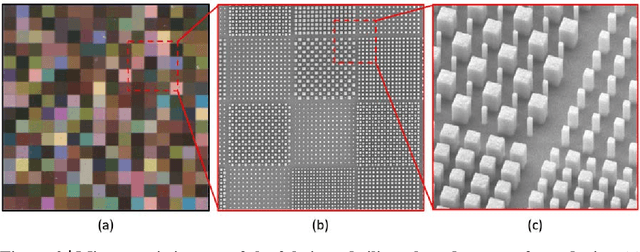
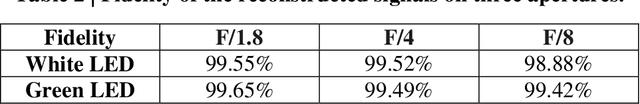
Abstract:Compared with conventional grating-based spectrometers, reconstructive spectrometers based on spectrally engineered filtering have the advantage of miniaturization because of the less demand for dispersive optics and free propagation space. However, available reconstructive spectrometers fail to balance the performance on operational bandwidth, spectral diversity and angular stability. In this work, we proposed a compact silicon metasurfaces based spectrometer/camera. After angle integration, the spectral response of the system is robust to angle/aperture within a wide working bandwidth from 400nm to 800nm. It is experimentally demonstrated that the proposed method could maintain the spectral consistency from F/1.8 to F/4 (The corresponding angle of incident light ranges from 7{\deg} to 16{\deg}) and the incident hyperspectral signal could be accurately reconstructed with a fidelity exceeding 99%. Additionally, a spectral imaging system with 400x400 pixels is also established in this work. The accurate reconstructed hyperspectral image indicates that the proposed aperture-robust spectrometer has the potential to be extended as a high-resolution broadband hyperspectral camera.
DeepQTest: Testing Autonomous Driving Systems with Reinforcement Learning and Real-world Weather Data
Oct 08, 2023Abstract:Autonomous driving systems (ADSs) are capable of sensing the environment and making driving decisions autonomously. These systems are safety-critical, and testing them is one of the important approaches to ensure their safety. However, due to the inherent complexity of ADSs and the high dimensionality of their operating environment, the number of possible test scenarios for ADSs is infinite. Besides, the operating environment of ADSs is dynamic, continuously evolving, and full of uncertainties, which requires a testing approach adaptive to the environment. In addition, existing ADS testing techniques have limited effectiveness in ensuring the realism of test scenarios, especially the realism of weather conditions and their changes over time. Recently, reinforcement learning (RL) has demonstrated great potential in addressing challenging problems, especially those requiring constant adaptations to dynamic environments. To this end, we present DeepQTest, a novel ADS testing approach that uses RL to learn environment configurations with a high chance of revealing abnormal ADS behaviors. Specifically, DeepQTest employs Deep Q-Learning and adopts three safety and comfort measures to construct the reward functions. To ensure the realism of generated scenarios, DeepQTest defines a set of realistic constraints and introduces real-world weather conditions into the simulated environment. We employed three comparison baselines, i.e., random, greedy, and a state-of-the-art RL-based approach DeepCOllision, for evaluating DeepQTest on an industrial-scale ADS. Evaluation results show that DeepQTest demonstrated significantly better effectiveness in terms of generating scenarios leading to collisions and ensuring scenario realism compared with the baselines. In addition, among the three reward functions implemented in DeepQTest, Time-To-Collision is recommended as the best design according to our study.
Digital Twin-based Anomaly Detection with Curriculum Learning in Cyber-physical Systems
Sep 27, 2023Abstract:Anomaly detection is critical to ensure the security of cyber-physical systems (CPS). However, due to the increasing complexity of attacks and CPS themselves, anomaly detection in CPS is becoming more and more challenging. In our previous work, we proposed a digital twin-based anomaly detection method, called ATTAIN, which takes advantage of both historical and real-time data of CPS. However, such data vary significantly in terms of difficulty. Therefore, similar to human learning processes, deep learning models (e.g., ATTAIN) can benefit from an easy-to-difficult curriculum. To this end, in this paper, we present a novel approach, named digitaL twin-based Anomaly deTecTion wIth Curriculum lEarning (LATTICE), which extends ATTAIN by introducing curriculum learning to optimize its learning paradigm. LATTICE attributes each sample with a difficulty score, before being fed into a training scheduler. The training scheduler samples batches of training data based on these difficulty scores such that learning from easy to difficult data can be performed. To evaluate LATTICE, we use five publicly available datasets collected from five real-world CPS testbeds. We compare LATTICE with ATTAIN and two other state-of-the-art anomaly detectors. Evaluation results show that LATTICE outperforms the three baselines and ATTAIN by 0.906%-2.367% in terms of the F1 score. LATTICE also, on average, reduces the training time of ATTAIN by 4.2% on the five datasets and is on par with the baselines in terms of detection delay time.
Knowledge Distillation-Empowered Digital Twin for Anomaly Detection
Sep 12, 2023



Abstract:Cyber-physical systems (CPSs), like train control and management systems (TCMS), are becoming ubiquitous in critical infrastructures. As safety-critical systems, ensuring their dependability during operation is crucial. Digital twins (DTs) have been increasingly studied for this purpose owing to their capability of runtime monitoring and warning, prediction and detection of anomalies, etc. However, constructing a DT for anomaly detection in TCMS necessitates sufficient training data and extracting both chronological and context features with high quality. Hence, in this paper, we propose a novel method named KDDT for TCMS anomaly detection. KDDT harnesses a language model (LM) and a long short-term memory (LSTM) network to extract contexts and chronological features, respectively. To enrich data volume, KDDT benefits from out-of-domain data with knowledge distillation (KD). We evaluated KDDT with two datasets from our industry partner Alstom and obtained the F1 scores of 0.931 and 0.915, respectively, demonstrating the effectiveness of KDDT. We also explored individual contributions of the DT model, LM, and KD to the overall performance of KDDT, via a comprehensive empirical study, and observed average F1 score improvements of 12.4%, 3%, and 6.05%, respectively.
EvoCLINICAL: Evolving Cyber-Cyber Digital Twin with Active Transfer Learning for Automated Cancer Registry System
Sep 06, 2023



Abstract:The Cancer Registry of Norway (CRN) collects information on cancer patients by receiving cancer messages from different medical entities (e.g., medical labs, and hospitals) in Norway. Such messages are validated by an automated cancer registry system: GURI. Its correct operation is crucial since it lays the foundation for cancer research and provides critical cancer-related statistics to its stakeholders. Constructing a cyber-cyber digital twin (CCDT) for GURI can facilitate various experiments and advanced analyses of the operational state of GURI without requiring intensive interactions with the real system. However, GURI constantly evolves due to novel medical diagnostics and treatment, technological advances, etc. Accordingly, CCDT should evolve as well to synchronize with GURI. A key challenge of achieving such synchronization is that evolving CCDT needs abundant data labelled by the new GURI. To tackle this challenge, we propose EvoCLINICAL, which considers the CCDT developed for the previous version of GURI as the pretrained model and fine-tunes it with the dataset labelled by querying a new GURI version. EvoCLINICAL employs a genetic algorithm to select an optimal subset of cancer messages from a candidate dataset and query GURI with it. We evaluate EvoCLINICAL on three evolution processes. The precision, recall, and F1 score are all greater than 91%, demonstrating the effectiveness of EvoCLINICAL. Furthermore, we replace the active learning part of EvoCLINICAL with random selection to study the contribution of transfer learning to the overall performance of EvoCLINICAL. Results show that employing active learning in EvoCLINICAL increases its performances consistently.
Adaptive and Cascaded Compressive Sensing
Mar 21, 2022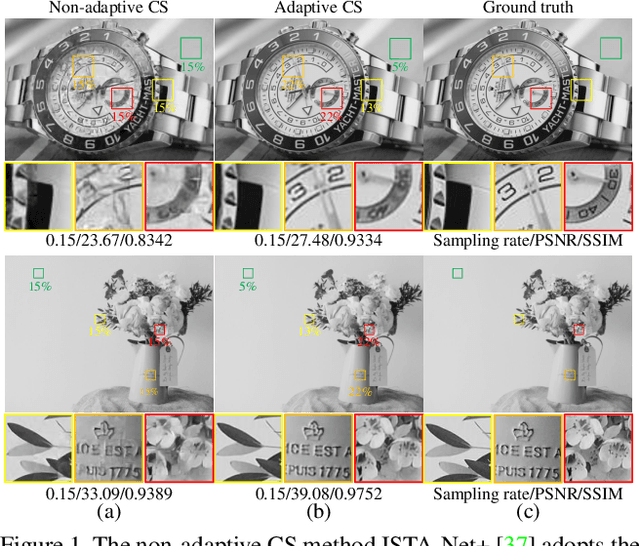
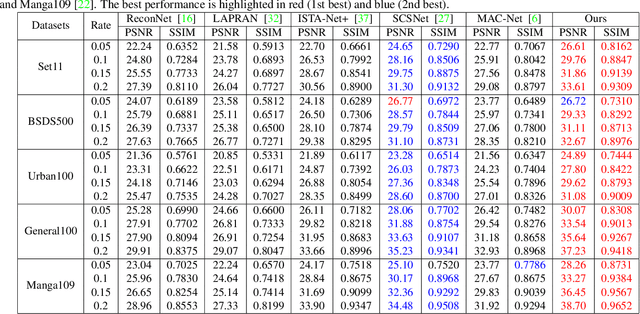
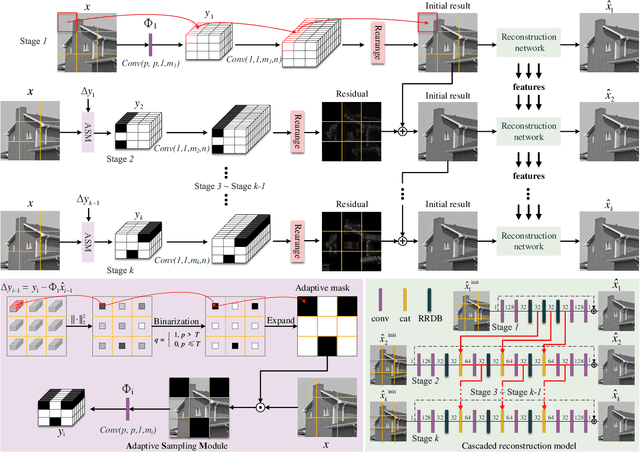
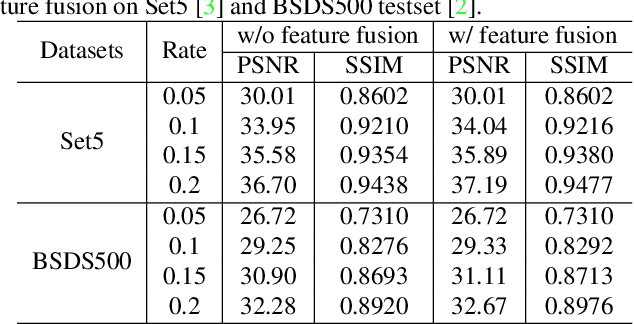
Abstract:Scene-dependent adaptive compressive sensing (CS) has been a long pursuing goal which has huge potential in significantly improving the performance of CS. However, without accessing to the ground truth image, how to design the scene-dependent adaptive strategy is still an open-problem and the improvement in sampling efficiency is still quite limited. In this paper, a restricted isometry property (RIP) condition based error clamping is proposed, which could directly predict the reconstruction error, i.e. the difference between the currently-stage reconstructed image and the ground truth image, and adaptively allocate samples to different regions at the successive sampling stage. Furthermore, we propose a cascaded feature fusion reconstruction network that could efficiently utilize the information derived from different adaptive sampling stages. The effectiveness of the proposed adaptive and cascaded CS method is demonstrated with extensive quantitative and qualitative results, compared with the state-of-the-art CS algorithms.
Prediction Surface Uncertainty Quantification in Object Detection Models for Autonomous Driving
Jul 11, 2021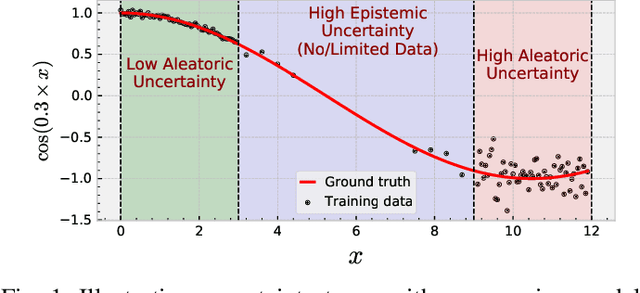
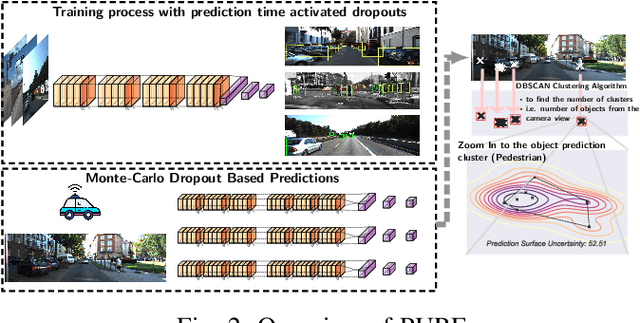
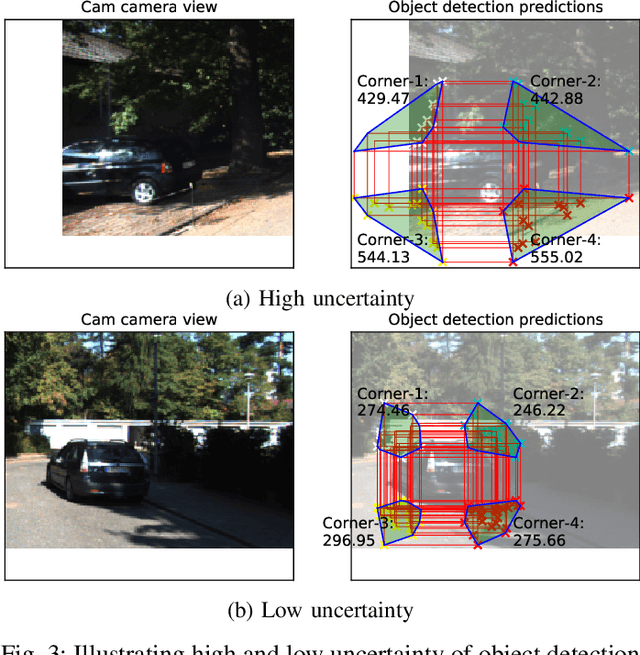
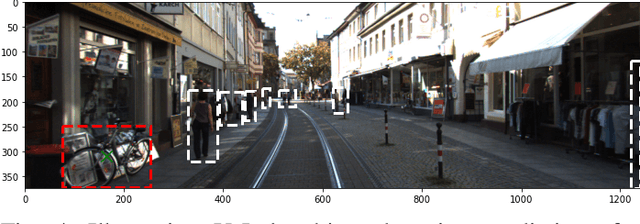
Abstract:Object detection in autonomous cars is commonly based on camera images and Lidar inputs, which are often used to train prediction models such as deep artificial neural networks for decision making for object recognition, adjusting speed, etc. A mistake in such decision making can be damaging; thus, it is vital to measure the reliability of decisions made by such prediction models via uncertainty measurement. Uncertainty, in deep learning models, is often measured for classification problems. However, deep learning models in autonomous driving are often multi-output regression models. Hence, we propose a novel method called PURE (Prediction sURface uncErtainty) for measuring prediction uncertainty of such regression models. We formulate the object recognition problem as a regression model with more than one outputs for finding object locations in a 2-dimensional camera view. For evaluation, we modified three widely-applied object recognition models (i.e., YoLo, SSD300 and SSD512) and used the KITTI, Stanford Cars, Berkeley DeepDrive, and NEXET datasets. Results showed the statistically significant negative correlation between prediction surface uncertainty and prediction accuracy suggesting that uncertainty significantly impacts the decisions made by autonomous driving.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge