Sushma Venkatesh
Empowering Morphing Attack Detection using Interpretable Image-Text Foundation Model
Aug 13, 2025Abstract:Morphing attack detection has become an essential component of face recognition systems for ensuring a reliable verification scenario. In this paper, we present a multimodal learning approach that can provide a textual description of morphing attack detection. We first show that zero-shot evaluation of the proposed framework using Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) can yield not only generalizable morphing attack detection, but also predict the most relevant text snippet. We present an extensive analysis of ten different textual prompts that include both short and long textual prompts. These prompts are engineered by considering the human understandable textual snippet. Extensive experiments were performed on a face morphing dataset that was developed using a publicly available face biometric dataset. We present an evaluation of SOTA pre-trained neural networks together with the proposed framework in the zero-shot evaluation of five different morphing generation techniques that are captured in three different mediums.
Towards Zero-Shot Differential Morphing Attack Detection with Multimodal Large Language Models
May 21, 2025Abstract:Leveraging the power of multimodal large language models (LLMs) offers a promising approach to enhancing the accuracy and interpretability of morphing attack detection (MAD), especially in real-world biometric applications. This work introduces the use of LLMs for differential morphing attack detection (D-MAD). To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to employ multimodal LLMs to D-MAD using real biometric data. To effectively utilize these models, we design Chain-of-Thought (CoT)-based prompts to reduce failure-to-answer rates and enhance the reasoning behind decisions. Our contributions include: (1) the first application of multimodal LLMs for D-MAD using real data subjects, (2) CoT-based prompt engineering to improve response reliability and explainability, (3) comprehensive qualitative and quantitative benchmarking of LLM performance using data from 54 individuals captured in passport enrollment scenarios, and (4) comparative analysis of two multimodal LLMs: ChatGPT-4o and Gemini providing insights into their morphing attack detection accuracy and decision transparency. Experimental results show that ChatGPT-4o outperforms Gemini in detection accuracy, especially against GAN-based morphs, though both models struggle under challenging conditions. While Gemini offers more consistent explanations, ChatGPT-4o is more resilient but prone to a higher failure-to-answer rate.
Biometrics in Extended Reality: A Review
Nov 14, 2024Abstract:In the domain of Extended Reality (XR), particularly Virtual Reality (VR), extensive research has been devoted to harnessing this transformative technology in various real-world applications. However, a critical challenge that must be addressed before unleashing the full potential of XR in practical scenarios is to ensure robust security and safeguard user privacy. This paper presents a systematic survey of the utility of biometric characteristics applied in the XR environment. To this end, we present a comprehensive overview of the different types of biometric modalities used for authentication and representation of users in a virtual environment. We discuss different biometric vulnerability gateways in general XR systems for the first time in the literature along with taxonomy. A comprehensive discussion on generating and authenticating biometric-based photorealistic avatars in XR environments is presented with a stringent taxonomy. We also discuss the availability of different datasets that are widely employed in evaluating biometric authentication in XR environments together with performance evaluation metrics. Finally, we discuss the open challenges and potential future work that need to be addressed in the field of biometrics in XR.
MorCode: Face Morphing Attack Generation using Generative Codebooks
Oct 10, 2024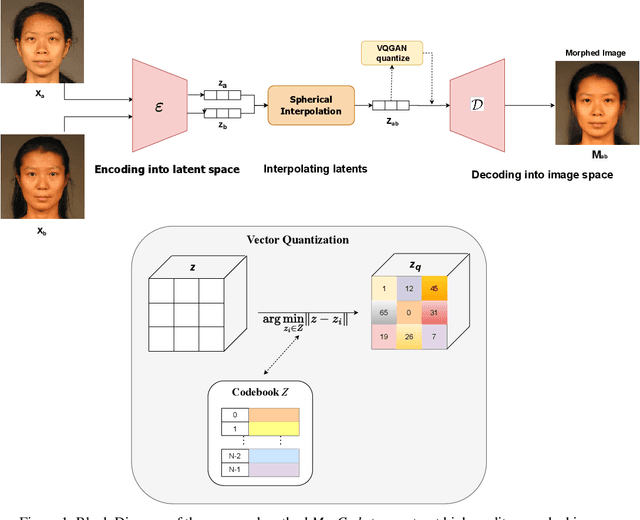
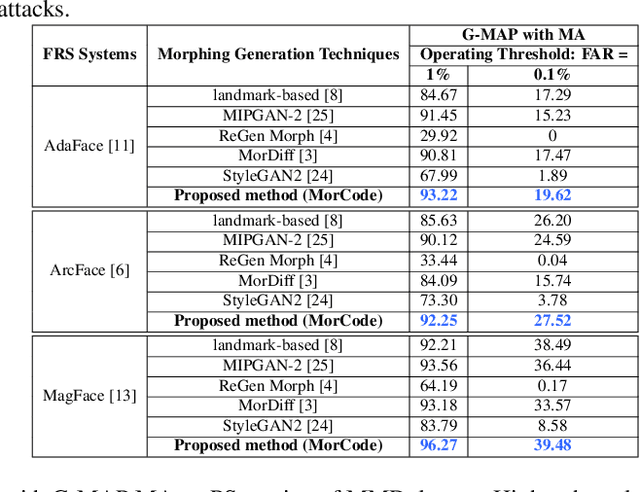

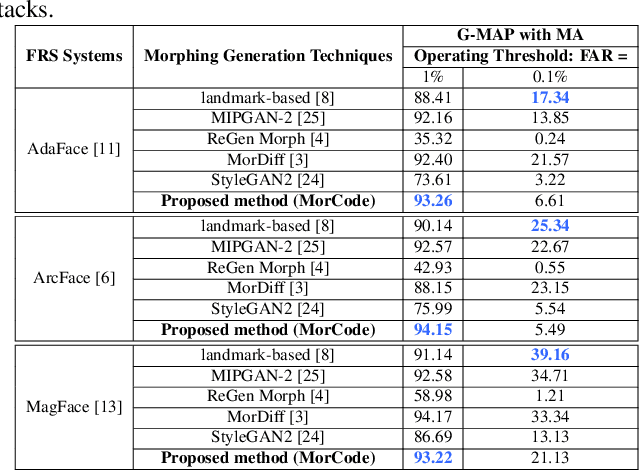
Abstract:Face recognition systems (FRS) can be compromised by face morphing attacks, which blend textural and geometric information from multiple facial images. The rapid evolution of generative AI, especially Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) or Diffusion models, where encoded images are interpolated to generate high-quality face morphing images. In this work, we present a novel method for the automatic face morphing generation method \textit{MorCode}, which leverages a contemporary encoder-decoder architecture conditioned on codebook learning to generate high-quality morphing images. Extensive experiments were performed on the newly constructed morphing dataset using five state-of-the-art morphing generation techniques using both digital and print-scan data. The attack potential of the proposed morphing generation technique, \textit{MorCode}, was benchmarked using three different face recognition systems. The obtained results indicate the highest attack potential of the proposed \textit{MorCode} when compared with five state-of-the-art morphing generation methods on both digital and print scan data.
VoxAtnNet: A 3D Point Clouds Convolutional Neural Network for Generalizable Face Presentation Attack Detection
Apr 19, 2024Abstract:Facial biometrics are an essential components of smartphones to ensure reliable and trustworthy authentication. However, face biometric systems are vulnerable to Presentation Attacks (PAs), and the availability of more sophisticated presentation attack instruments such as 3D silicone face masks will allow attackers to deceive face recognition systems easily. In this work, we propose a novel Presentation Attack Detection (PAD) algorithm based on 3D point clouds captured using the frontal camera of a smartphone to detect presentation attacks. The proposed PAD algorithm, VoxAtnNet, processes 3D point clouds to obtain voxelization to preserve the spatial structure. Then, the voxelized 3D samples were trained using the novel convolutional attention network to detect PAs on the smartphone. Extensive experiments were carried out on the newly constructed 3D face point cloud dataset comprising bona fide and two different 3D PAIs (3D silicone face mask and wrap photo mask), resulting in 3480 samples. The performance of the proposed method was compared with existing methods to benchmark the detection performance using three different evaluation protocols. The experimental results demonstrate the improved performance of the proposed method in detecting both known and unknown face presentation attacks.
Does complimentary information from multispectral imaging improve face presentation attack detection?
Nov 20, 2023Abstract:Presentation Attack Detection (PAD) has been extensively studied, particularly in the visible spectrum. With the advancement of sensing technology beyond the visible range, multispectral imaging has gained significant attention in this direction. We present PAD based on multispectral images constructed for eight different presentation artifacts resulted from three different artifact species. In this work, we introduce Face Presentation Attack Multispectral (FPAMS) database to demonstrate the significance of employing multispectral imaging. The goal of this work is to study complementary information that can be combined in two different ways (image fusion and score fusion) from multispectral imaging to improve the face PAD. The experimental evaluation results present an extensive qualitative analysis of 61650 sample multispectral images collected for bonafide and artifacts. The PAD based on the score fusion and image fusion method presents superior performance, demonstrating the significance of employing multispectral imaging to detect presentation artifacts.
Fingervein Verification using Convolutional Multi-Head Attention Network
Oct 25, 2023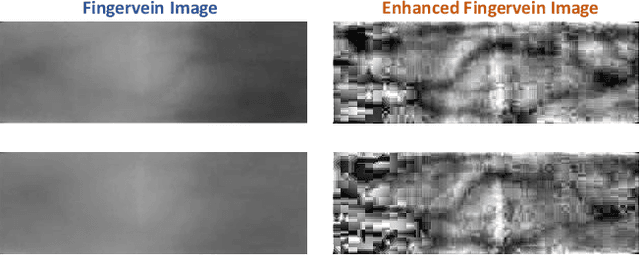
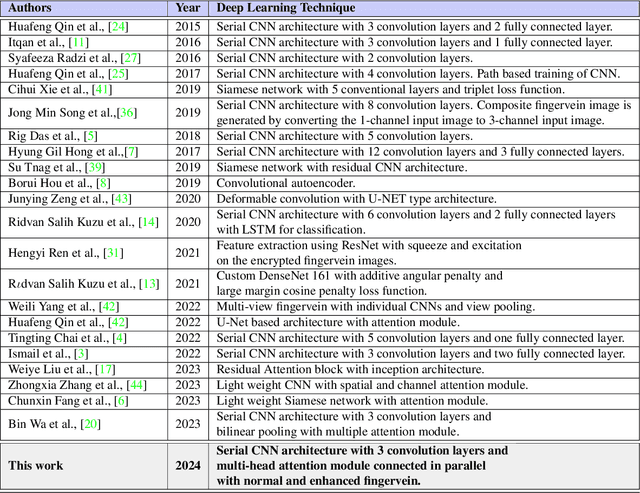
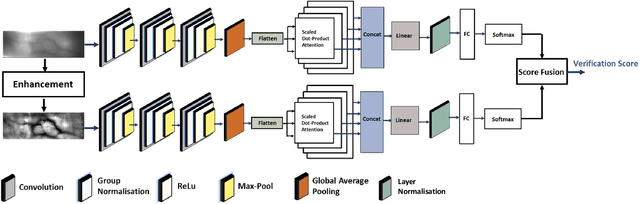
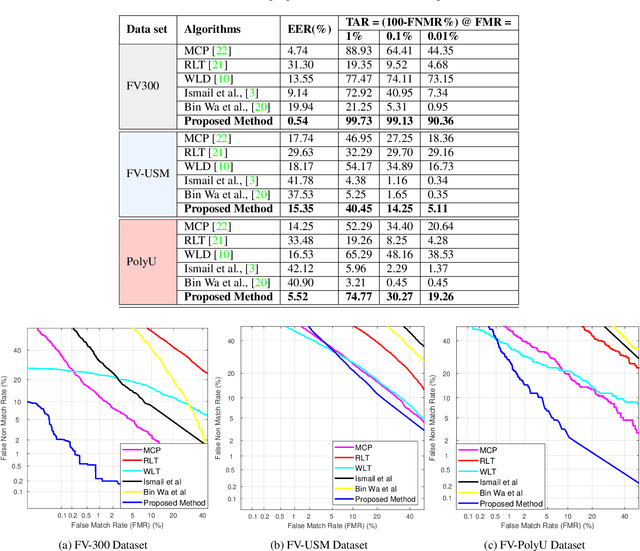
Abstract:Biometric verification systems are deployed in various security-based access-control applications that require user-friendly and reliable person verification. Among the different biometric characteristics, fingervein biometrics have been extensively studied owing to their reliable verification performance. Furthermore, fingervein patterns reside inside the skin and are not visible outside; therefore, they possess inherent resistance to presentation attacks and degradation due to external factors. In this paper, we introduce a novel fingervein verification technique using a convolutional multihead attention network called VeinAtnNet. The proposed VeinAtnNet is designed to achieve light weight with a smaller number of learnable parameters while extracting discriminant information from both normal and enhanced fingervein images. The proposed VeinAtnNet was trained on the newly constructed fingervein dataset with 300 unique fingervein patterns that were captured in multiple sessions to obtain 92 samples per unique fingervein. Extensive experiments were performed on the newly collected dataset FV-300 and the publicly available FV-USM and FV-PolyU fingervein dataset. The performance of the proposed method was compared with five state-of-the-art fingervein verification systems, indicating the efficacy of the proposed VeinAtnNet.
Sound-Print: Generalised Face Presentation Attack Detection using Deep Representation of Sound Echoes
Sep 24, 2023Abstract:Facial biometrics are widely deployed in smartphone-based applications because of their usability and increased verification accuracy in unconstrained scenarios. The evolving applications of smartphone-based facial recognition have also increased Presentation Attacks (PAs), where an attacker can present a Presentation Attack Instrument (PAI) to maliciously gain access to the application. Because the materials used to generate PAI are not deterministic, the detection of unknown presentation attacks is challenging. In this paper, we present an acoustic echo-based face Presentation Attack Detection (PAD) on a smartphone in which the PAs are detected based on the reflection profiles of the transmitted signal. We propose a novel transmission signal based on the wide pulse that allows us to model the background noise before transmitting the signal and increase the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR). The received signal reflections were processed to remove background noise and accurately represent reflection characteristics. The reflection profiles of the bona fide and PAs are different owing to the different reflection characteristics of the human skin and artefact materials. Extensive experiments are presented using the newly collected Acoustic Sound Echo Dataset (ASED) with 4807 samples captured from bona fide and four different types of PAIs, including print (two types), display, and silicone face-mask attacks. The obtained results indicate the robustness of the proposed method for detecting unknown face presentation attacks.
Differential Newborn Face Morphing Attack Detection using Wavelet Scatter Network
May 02, 2023



Abstract:Face Recognition System (FRS) are shown to be vulnerable to morphed images of newborns. Detecting morphing attacks stemming from face images of newborn is important to avoid unwanted consequences, both for security and society. In this paper, we present a new reference-based/Differential Morphing Attack Detection (MAD) method to detect newborn morphing images using Wavelet Scattering Network (WSN). We propose a two-layer WSN with 250 $\times$ 250 pixels and six rotations of wavelets per layer, resulting in 577 paths. The proposed approach is validated on a dataset of 852 bona fide images and 2460 morphing images constructed using face images of 42 unique newborns. The obtained results indicate a gain of over 10\% in detection accuracy over other existing D-MAD techniques.
Multispectral Imaging for Differential Face Morphing Attack Detection: A Preliminary Study
Apr 07, 2023



Abstract:Face morphing attack detection is emerging as an increasingly challenging problem owing to advancements in high-quality and realistic morphing attack generation. Reliable detection of morphing attacks is essential because these attacks are targeted for border control applications. This paper presents a multispectral framework for differential morphing-attack detection (D-MAD). The D-MAD methods are based on using two facial images that are captured from the ePassport (also called the reference image) and the trusted device (for example, Automatic Border Control (ABC) gates) to detect whether the face image presented in ePassport is morphed. The proposed multispectral D-MAD framework introduce a multispectral image captured as a trusted capture to capture seven different spectral bands to detect morphing attacks. Extensive experiments were conducted on the newly created datasets with 143 unique data subjects that were captured using both visible and multispectral cameras in multiple sessions. The results indicate the superior performance of the proposed multispectral framework compared to visible images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge