Aravinda Reddy PN
MorCode: Face Morphing Attack Generation using Generative Codebooks
Oct 10, 2024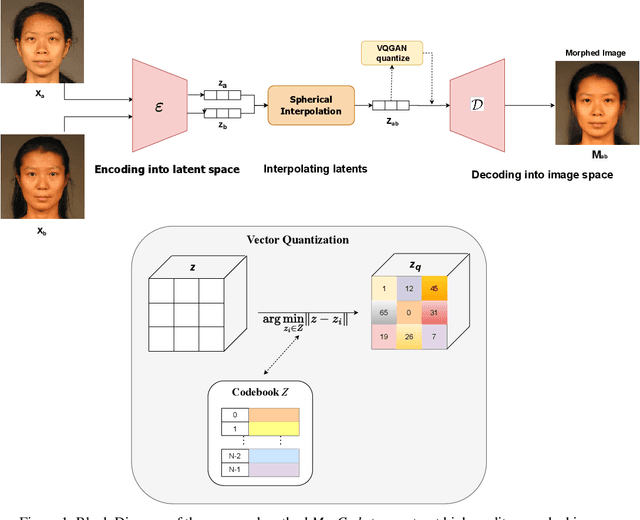
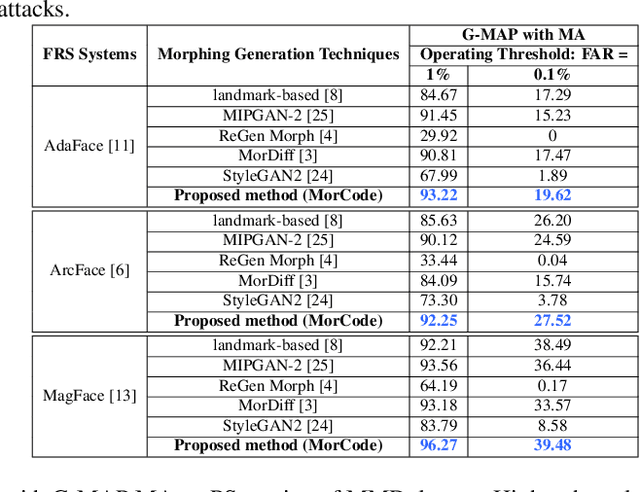

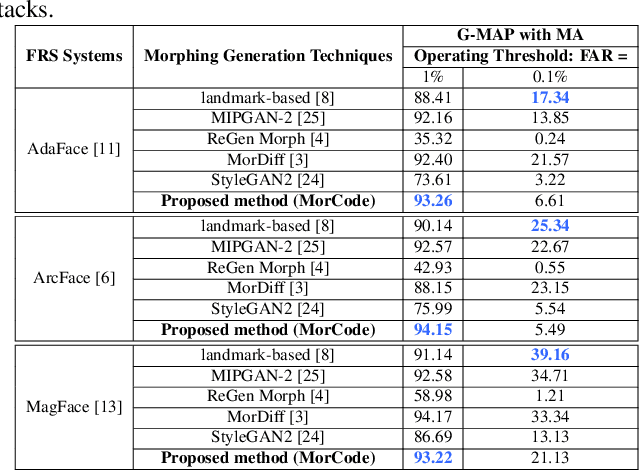
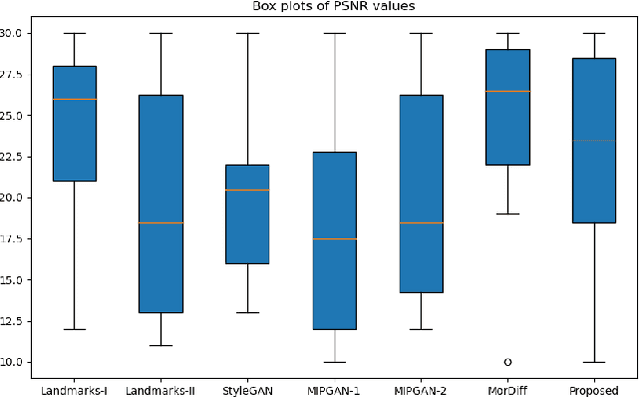
Abstract:Face recognition systems (FRS) can be compromised by face morphing attacks, which blend textural and geometric information from multiple facial images. The rapid evolution of generative AI, especially Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) or Diffusion models, where encoded images are interpolated to generate high-quality face morphing images. In this work, we present a novel method for the automatic face morphing generation method \textit{MorCode}, which leverages a contemporary encoder-decoder architecture conditioned on codebook learning to generate high-quality morphing images. Extensive experiments were performed on the newly constructed morphing dataset using five state-of-the-art morphing generation techniques using both digital and print-scan data. The attack potential of the proposed morphing generation technique, \textit{MorCode}, was benchmarked using three different face recognition systems. The obtained results indicate the highest attack potential of the proposed \textit{MorCode} when compared with five state-of-the-art morphing generation methods on both digital and print scan data.
Gumbel Rao Monte Carlo based Bi-Modal Neural Architecture Search for Audio-Visual Deepfake Detection
Oct 09, 2024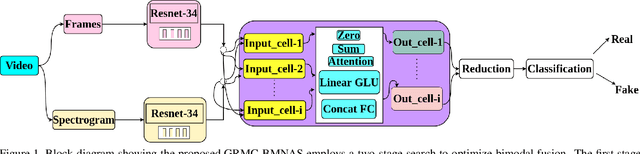
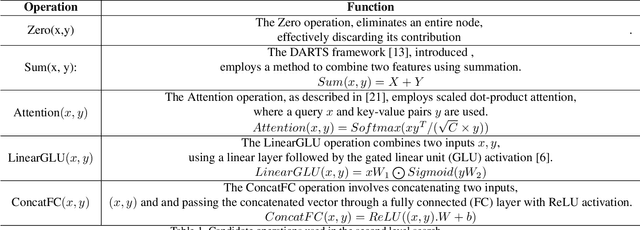
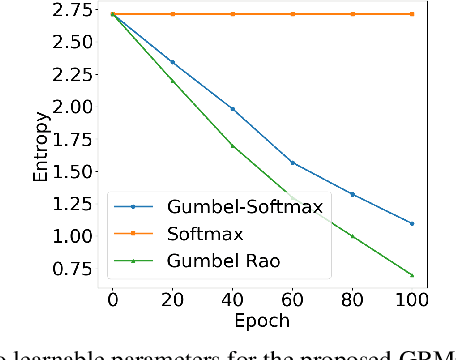
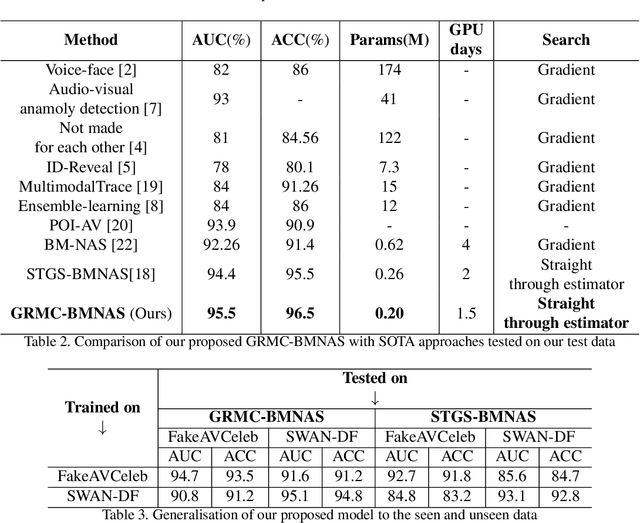
Abstract:Deepfakes pose a critical threat to biometric authentication systems by generating highly realistic synthetic media. Existing multimodal deepfake detectors often struggle to adapt to diverse data and rely on simple fusion methods. To address these challenges, we propose Gumbel-Rao Monte Carlo Bi-modal Neural Architecture Search (GRMC-BMNAS), a novel architecture search framework that employs Gumbel-Rao Monte Carlo sampling to optimize multimodal fusion. It refines the Straight through Gumbel Softmax (STGS) method by reducing variance with Rao-Blackwellization, stabilizing network training. Using a two-level search approach, the framework optimizes the network architecture, parameters, and performance. Crucial features are efficiently identified from backbone networks, while within the cell structure, a weighted fusion operation integrates information from various sources. By varying parameters such as temperature and number of Monte carlo samples yields an architecture that maximizes classification performance and better generalisation capability. Experimental results on the FakeAVCeleb and SWAN-DF datasets demonstrate an impressive AUC percentage of 95.4\%, achieved with minimal model parameters.
NeuralMultiling: A Novel Neural Architecture Search for Smartphone based Multilingual Speaker Verification
Aug 08, 2024



Abstract:Multilingual speaker verification introduces the challenge of verifying a speaker in multiple languages. Existing systems were built using i-vector/x-vector approaches along with Bi-LSTMs, which were trained to discriminate speakers, irrespective of the language. Instead of exploring the design space manually, we propose a neural architecture search for multilingual speaker verification suitable for mobile devices, called \textbf{NeuralMultiling}. First, our algorithm searches for an optimal operational combination of neural cells with different architectures for normal cells and reduction cells and then derives a CNN model by stacking neural cells. Using the derived architecture, we performed two different studies:1) language agnostic condition and 2) interoperability between languages and devices on the publicly available Multilingual Audio-Visual Smartphone (MAVS) dataset. The experimental results suggest that the derived architecture significantly outperforms the existing Autospeech method by a 5-6\% reduction in the Equal Error Rate (EER) with fewer model parameters.
Straight Through Gumbel Softmax Estimator based Bimodal Neural Architecture Search for Audio-Visual Deepfake Detection
Jun 19, 2024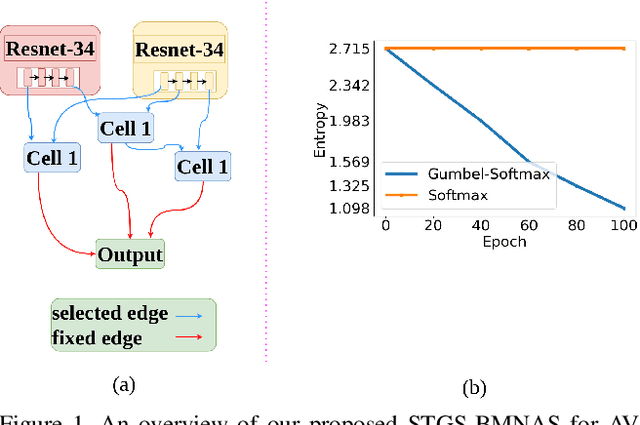
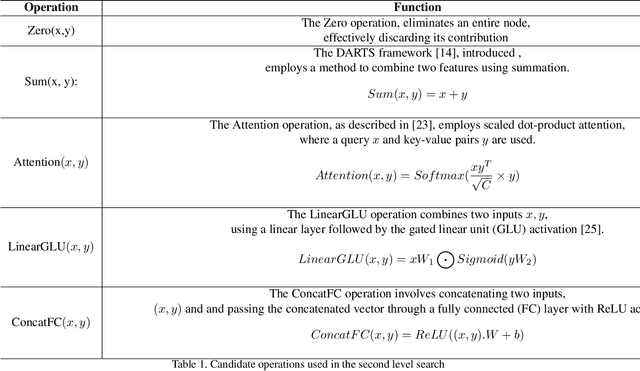
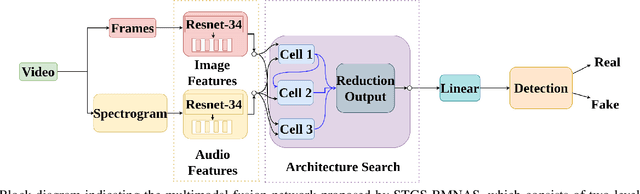
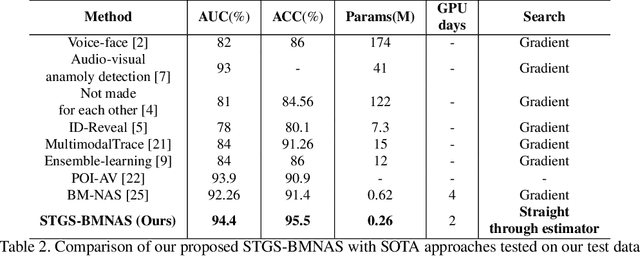
Abstract:Deepfakes are a major security risk for biometric authentication. This technology creates realistic fake videos that can impersonate real people, fooling systems that rely on facial features and voice patterns for identification. Existing multimodal deepfake detectors rely on conventional fusion methods, such as majority rule and ensemble voting, which often struggle to adapt to changing data characteristics and complex patterns. In this paper, we introduce the Straight-through Gumbel-Softmax (STGS) framework, offering a comprehensive approach to search multimodal fusion model architectures. Using a two-level search approach, the framework optimizes the network architecture, parameters, and performance. Initially, crucial features were efficiently identified from backbone networks, whereas within the cell structure, a weighted fusion operation integrated information from various sources. An architecture that maximizes the classification performance is derived by varying parameters such as temperature and sampling time. The experimental results on the FakeAVCeleb and SWAN-DF datasets demonstrated an impressive AUC value 94.4\% achieved with minimal model parameters.
MLSD-GAN -- Generating Strong High Quality Face Morphing Attacks using Latent Semantic Disentanglement
Apr 19, 2024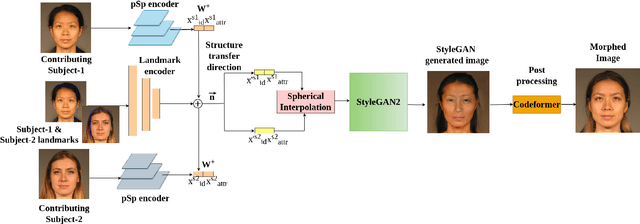

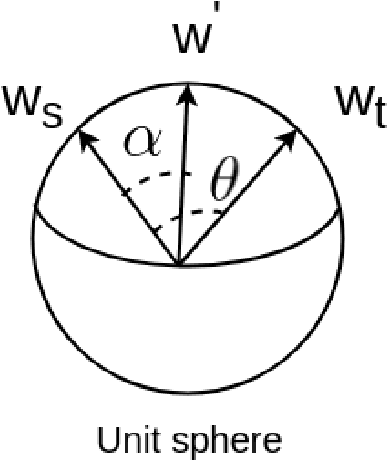
Abstract:Face-morphing attacks are a growing concern for biometric researchers, as they can be used to fool face recognition systems (FRS). These attacks can be generated at the image level (supervised) or representation level (unsupervised). Previous unsupervised morphing attacks have relied on generative adversarial networks (GANs). More recently, researchers have used linear interpolation of StyleGAN-encoded images to generate morphing attacks. In this paper, we propose a new method for generating high-quality morphing attacks using StyleGAN disentanglement. Our approach, called MLSD-GAN, spherically interpolates the disentangled latents to produce realistic and diverse morphing attacks. We evaluate the vulnerability of MLSD-GAN on two deep-learning-based FRS techniques. The results show that MLSD-GAN poses a significant threat to FRS, as it can generate morphing attacks that are highly effective at fooling these systems.
ExtSwap: Leveraging Extended Latent Mapper for Generating High Quality Face Swapping
Oct 19, 2023



Abstract:We present a novel face swapping method using the progressively growing structure of a pre-trained StyleGAN. Previous methods use different encoder decoder structures, embedding integration networks to produce high-quality results, but their quality suffers from entangled representation. We disentangle semantics by deriving identity and attribute features separately. By learning to map the concatenated features into the extended latent space, we leverage the state-of-the-art quality and its rich semantic extended latent space. Extensive experiments suggest that the proposed method successfully disentangles identity and attribute features and outperforms many state-of-the-art face swapping methods, both qualitatively and quantitatively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge