Stefan Walser
.Multi-Scale Robotics Lab, ETH Zürich, Switzerland
Non-invasive urinary bladder volume estimation with artefact-suppressed bio-impedance measurements
Mar 24, 2023



Abstract:Urine output is a vital parameter to gauge kidney health. Current monitoring methods include manually written records, invasive urinary catheterization or ultrasound measurements performed by highly skilled personnel. Catheterization bears high risks of infection while intermittent ultrasound measures and manual recording are time consuming and might miss early signs of kidney malfunction. Bioimpedance (BI) measurements may serve as a non-invasive alternative for measuring urine volume in vivo. However, limited robustness have prevented its clinical translation. Here, a deep learning-based algorithm is presented that processes the local BI of the lower abdomen and suppresses artefacts to measure the bladder volume quantitatively, non-invasively and without the continuous need for additional personnel. A tetrapolar BI wearable system called ANUVIS was used to collect continuous bladder volume data from three healthy subjects to demonstrate feasibility of operation, while clinical gold standards of urodynamic (n=6) and uroflowmetry tests (n=8) provided the ground truth. Optimized location for electrode placement and a model for the change in BI with changing bladder volume is deduced. The average error for full bladder volume estimation and for residual volume estimation was -29 +/-87.6 ml, thus, comparable to commercial portable ultrasound devices (Bland Altman analysis showed a bias of -5.2 ml with LoA between 119.7 ml to -130.1 ml), while providing the additional benefit of hands-free, non-invasive, and continuous bladder volume estimation. The combination of the wearable BI sensor node and the presented algorithm provides an attractive alternative to current standard of care with potential benefits in providing insights into kidney function.
Active Interaction Force Control for Omnidirectional Aerial Contact-Based Inspection
Apr 01, 2020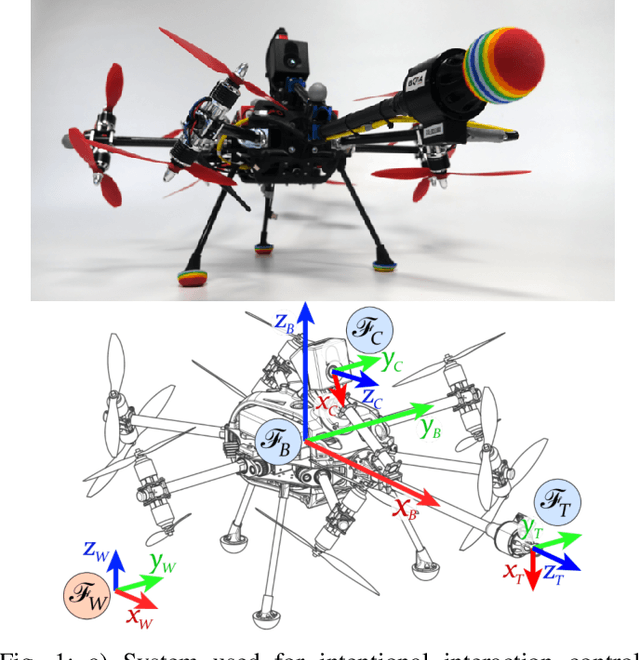
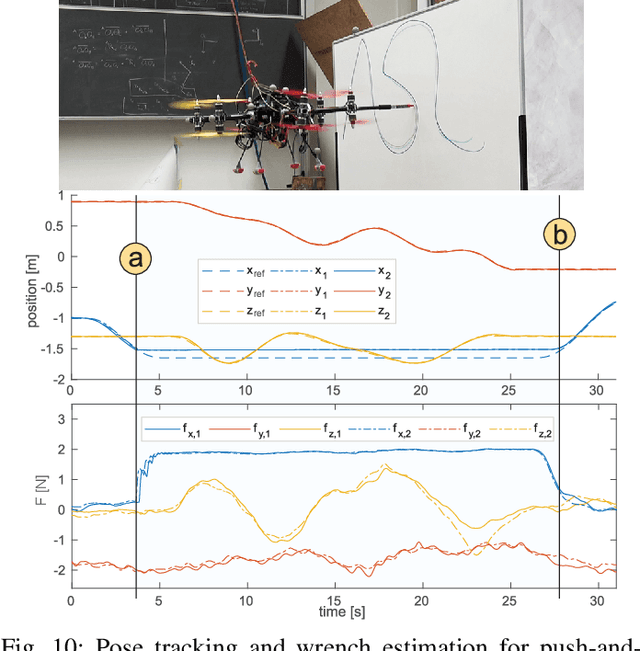
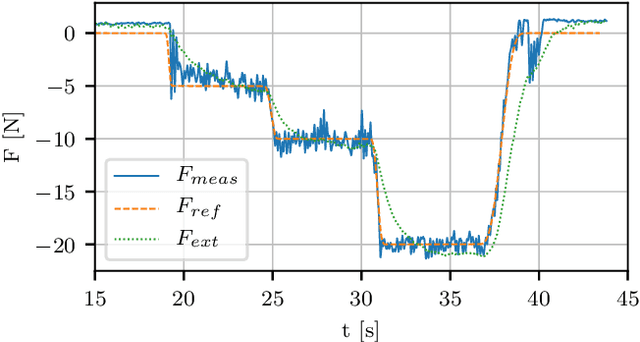
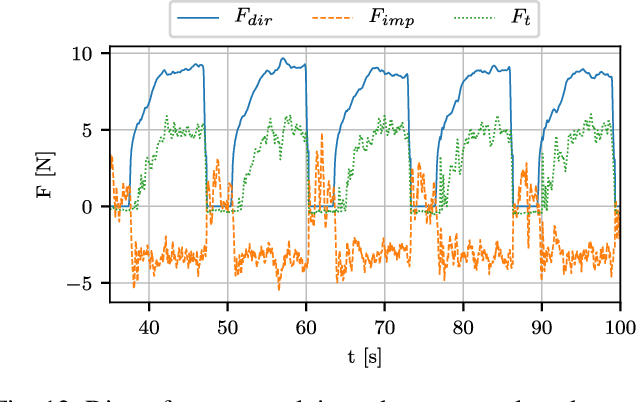
Abstract:This paper presents and validates two approaches for active interaction force control and planning for omnidirectional aerial manipulation platforms, with the goal of aerial contact inspection in unstructured environments. We extend upon an axis-selective impedance controller to present a variable axis-selective impedance control which integrates direct force control for intentional interaction, using feedback from an on-board force sensor. The control approaches aim to reject disturbances in free flight, while handling unintentional interaction, and actively controlling desired interaction forces. A fully actuated and omnidirectional tilt-rotor aerial system is used to show capabilities of the control and planning methods. Experiments demonstrate disturbance rejection, push-and-slide interaction, and force controlled interaction in different flight orientations. The system is validated as a tool for non-destructive testing of concrete infrastructure, and statistical results of interaction control performance are presented and discussed.
An Omnidirectional Aerial Manipulation Platform for Contact-Based Inspection
May 09, 2019
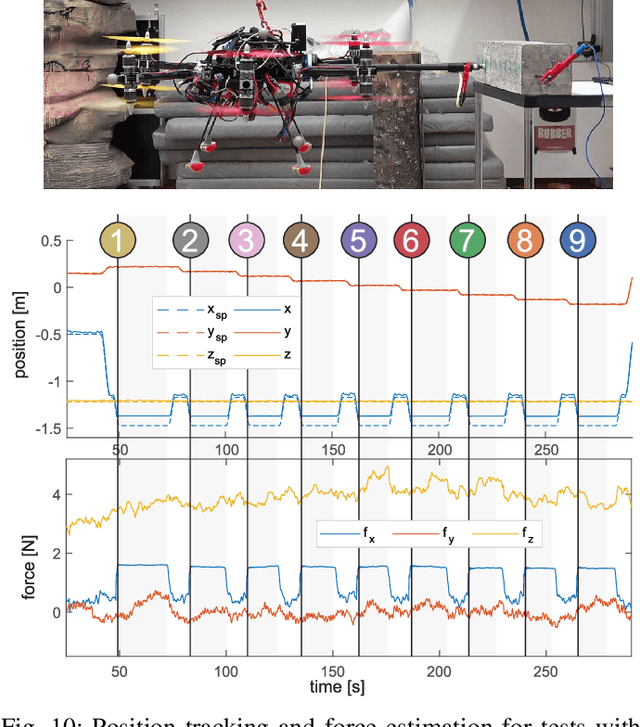
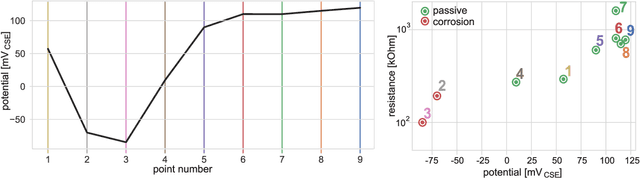
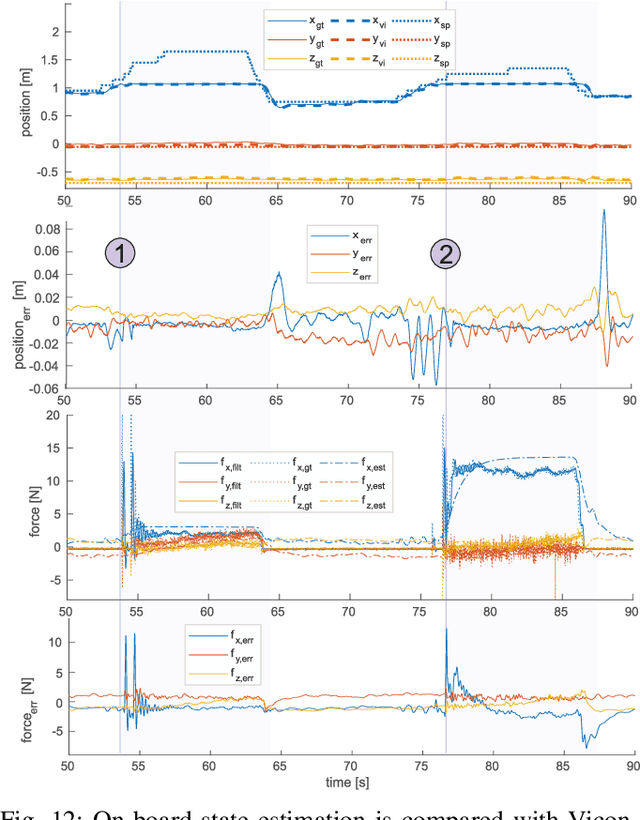
Abstract:This paper presents an omnidirectional aerial manipulation platform for robust and responsive interaction with unstructured environments, toward the goal of contact-based inspection. The fully actuated tilt-rotor aerial system is equipped with a rigidly mounted end-effector, and is able to exert a 6 degree of freedom force and torque, decoupling the system's translational and rotational dynamics, and enabling precise interaction with the environment while maintaining stability. An impedance controller with selective apparent inertia is formulated to permit compliance in certain degrees of freedom while achieving precise trajectory tracking and disturbance rejection in others. Experiments demonstrate disturbance rejection, push-and-slide interaction, and on-board state estimation with depth servoing to interact with local surfaces. The system is also validated as a tool for contact-based non-destructive testing of concrete infrastructure.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge