Sri Harsha Dumpala
Seeing Syntax: Uncovering Syntactic Learning Limitations in Vision-Language Models
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs), serve as foundation models for multi-modal applications such as image captioning and text-to-image generation. Recent studies have highlighted limitations in VLM text encoders, particularly in areas like compositionality and semantic understanding, though the underlying reasons for these limitations remain unclear. In this work, we aim to address this gap by analyzing the syntactic information, one of the fundamental linguistic properties, encoded by the text encoders of VLMs. We perform a thorough analysis comparing VLMs with different objective functions, parameter size and training data size, and with uni-modal language models (ULMs) in their ability to encode syntactic knowledge. Our findings suggest that ULM text encoders acquire syntactic information more effectively than those in VLMs. The syntactic information learned by VLM text encoders is shaped primarily by the pre-training objective, which plays a more crucial role than other factors such as model architecture, model size, or the volume of pre-training data. Models exhibit different layer-wise trends where CLIP performance dropped across layers while for other models, middle layers are rich in encoding syntactic knowledge.
Sensitivity of Generative VLMs to Semantically and Lexically Altered Prompts
Oct 16, 2024
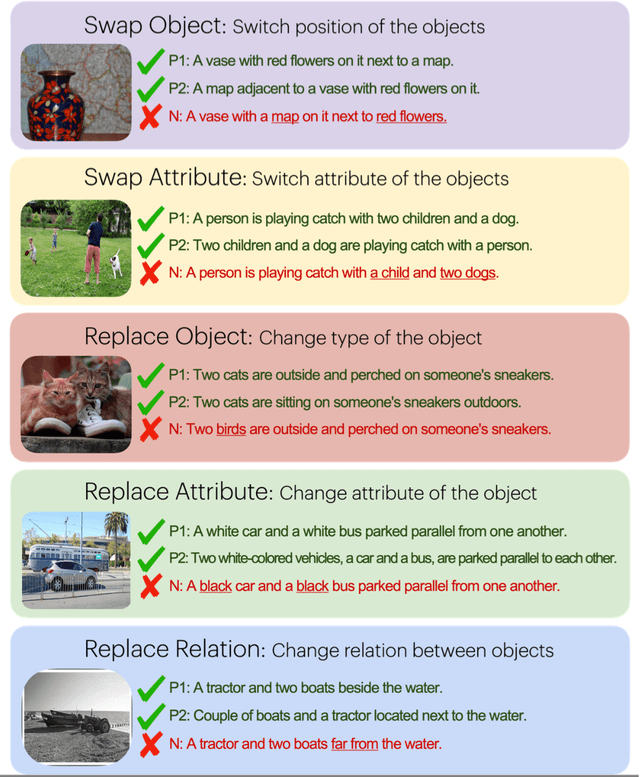
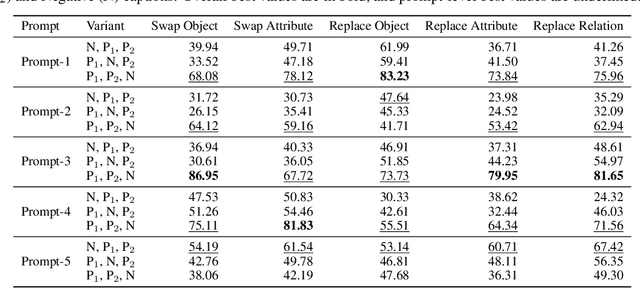
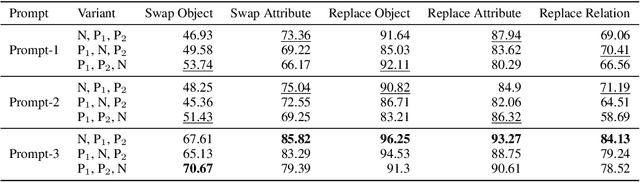
Abstract:Despite the significant influx of prompt-tuning techniques for generative vision-language models (VLMs), it remains unclear how sensitive these models are to lexical and semantic alterations in prompts. In this paper, we evaluate the ability of generative VLMs to understand lexical and semantic changes in text using the SugarCrepe++ dataset. We analyze the sensitivity of VLMs to lexical alterations in prompts without corresponding semantic changes. Our findings demonstrate that generative VLMs are highly sensitive to such alterations. Additionally, we show that this vulnerability affects the performance of techniques aimed at achieving consistency in their outputs.
XANE Background Acoustic Embeddings: Ablation and Clustering Analysis
Jul 08, 2024Abstract:We explore the recently proposed explainable acoustic neural embedding~(XANE) system that models the background acoustics of a speech signal in a non-intrusive manner. The XANE embeddings are used to estimate specific parameters related to the background acoustic properties of the signal which allows the embeddings to be explainable in terms of those parameters. We perform ablation studies on the XANE system and show that estimating all acoustic parameters jointly has an overall positive effect. Furthermore, we illustrate the value of XANE embeddings by performing clustering experiments on unseen test data and show that the proposed embeddings achieve a mean F1 score of 92\% for three different tasks, outperforming significantly the WavLM based signal embeddings and are complimentary to speaker embeddings.
Self-Supervised Embeddings for Detecting Individual Symptoms of Depression
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:Depression, a prevalent mental health disorder impacting millions globally, demands reliable assessment systems. Unlike previous studies that focus solely on either detecting depression or predicting its severity, our work identifies individual symptoms of depression while also predicting its severity using speech input. We leverage self-supervised learning (SSL)-based speech models to better utilize the small-sized datasets that are frequently encountered in this task. Our study demonstrates notable performance improvements by utilizing SSL embeddings compared to conventional speech features. We compare various types of SSL pretrained models to elucidate the type of speech information (semantic, speaker, or prosodic) that contributes the most in identifying different symptoms. Additionally, we evaluate the impact of combining multiple SSL embeddings on performance. Furthermore, we show the significance of multi-task learning for identifying depressive symptoms effectively.
Predicting Individual Depression Symptoms from Acoustic Features During Speech
Jun 23, 2024Abstract:Current automatic depression detection systems provide predictions directly without relying on the individual symptoms/items of depression as denoted in the clinical depression rating scales. In contrast, clinicians assess each item in the depression rating scale in a clinical setting, thus implicitly providing a more detailed rationale for a depression diagnosis. In this work, we make a first step towards using the acoustic features of speech to predict individual items of the depression rating scale before obtaining the final depression prediction. For this, we use convolutional (CNN) and recurrent (long short-term memory (LSTM)) neural networks. We consider different approaches to learning the temporal context of speech. Further, we analyze two variants of voting schemes for individual item prediction and depression detection. We also include an animated visualization that shows an example of item prediction over time as the speech progresses.
SUGARCREPE++ Dataset: Vision-Language Model Sensitivity to Semantic and Lexical Alterations
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:Despite their remarkable successes, state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs), including vision-and-language models (VLMs) and unimodal language models (ULMs), fail to understand precise semantics. For example, semantically equivalent sentences expressed using different lexical compositions elicit diverging representations. The degree of this divergence and its impact on encoded semantics is not very well understood. In this paper, we introduce the SUGARCREPE++ dataset to analyze the sensitivity of VLMs and ULMs to lexical and semantic alterations. Each sample in SUGARCREPE++ dataset consists of an image and a corresponding triplet of captions: a pair of semantically equivalent but lexically different positive captions and one hard negative caption. This poses a 3-way semantic (in)equivalence problem to the language models. We comprehensively evaluate VLMs and ULMs that differ in architecture, pre-training objectives and datasets to benchmark the performance of SUGARCREPE++ dataset. Experimental results highlight the difficulties of VLMs in distinguishing between lexical and semantic variations, particularly in object attributes and spatial relations. Although VLMs with larger pre-training datasets, model sizes, and multiple pre-training objectives achieve better performance on SUGARCREPE++, there is a significant opportunity for improvement. We show that all the models which achieve better performance on compositionality datasets need not perform equally well on SUGARCREPE++, signifying that compositionality alone may not be sufficient for understanding semantic and lexical alterations. Given the importance of the property that the SUGARCREPE++ dataset targets, it serves as a new challenge to the vision-and-language community.
XANE: eXplainable Acoustic Neural Embeddings
Jun 07, 2024Abstract:We present a novel method for extracting neural embeddings that model the background acoustics of a speech signal. The extracted embeddings are used to estimate specific parameters related to the background acoustic properties of the signal in a non-intrusive manner, which allows the embeddings to be explainable in terms of those parameters. We illustrate the value of these embeddings by performing clustering experiments on unseen test data and show that the proposed embeddings achieve a mean F1 score of 95.2\% for three different tasks, outperforming significantly the WavLM based signal embeddings. We also show that the proposed method can explain the embeddings by estimating 14 acoustic parameters characterizing the background acoustics, including reverberation and noise levels, overlapped speech detection, CODEC type detection and noise type detection with high accuracy and a real-time factor 17 times lower than an external baseline method.
VISLA Benchmark: Evaluating Embedding Sensitivity to Semantic and Lexical Alterations
Apr 25, 2024



Abstract:Despite their remarkable successes, state-of-the-art language models face challenges in grasping certain important semantic details. This paper introduces the VISLA (Variance and Invariance to Semantic and Lexical Alterations) benchmark, designed to evaluate the semantic and lexical understanding of language models. VISLA presents a 3-way semantic (in)equivalence task with a triplet of sentences associated with an image, to evaluate both vision-language models (VLMs) and unimodal language models (ULMs). An evaluation involving 34 VLMs and 20 ULMs reveals surprising difficulties in distinguishing between lexical and semantic variations. Spatial semantics encoded by language models also appear to be highly sensitive to lexical information. Notably, text encoders of VLMs demonstrate greater sensitivity to semantic and lexical variations than unimodal text encoders. Our contributions include the unification of image-to-text and text-to-text retrieval tasks, an off-the-shelf evaluation without fine-tuning, and assessing LMs' semantic (in)variance in the presence of lexical alterations. The results highlight strengths and weaknesses across diverse vision and unimodal language models, contributing to a deeper understanding of their capabilities. % VISLA enables a rigorous evaluation, shedding light on language models' capabilities in handling semantic and lexical nuances. Data and code will be made available at https://github.com/Sri-Harsha/visla_benchmark.
Test-Time Training for Depression Detection
Apr 07, 2024



Abstract:Previous works on depression detection use datasets collected in similar environments to train and test the models. In practice, however, the train and test distributions cannot be guaranteed to be identical. Distribution shifts can be introduced due to variations such as recording environment (e.g., background noise) and demographics (e.g., gender, age, etc). Such distributional shifts can surprisingly lead to severe performance degradation of the depression detection models. In this paper, we analyze the application of test-time training (TTT) to improve robustness of models trained for depression detection. When compared to regular testing of the models, we find TTT can significantly improve the robustness of the model under a variety of distributional shifts introduced due to: (a) background-noise, (b) gender-bias, and (c) data collection and curation procedure (i.e., train and test samples are from separate datasets).
Test-Time Training for Speech
Sep 28, 2023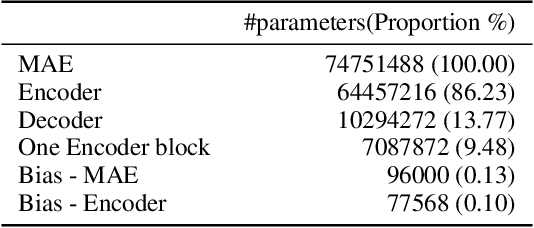
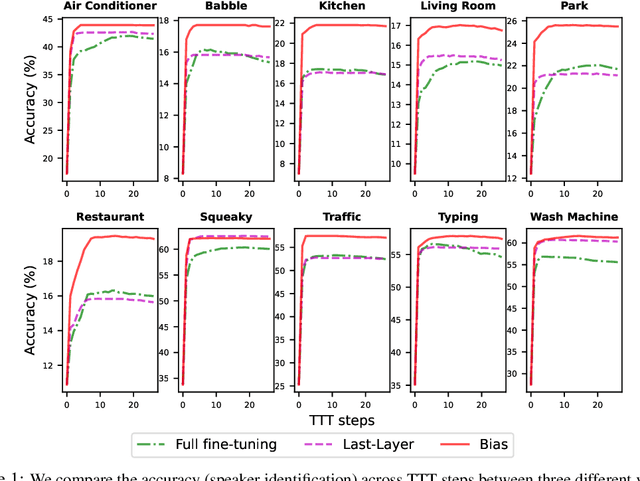
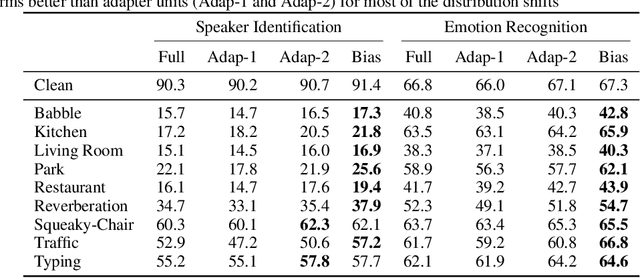
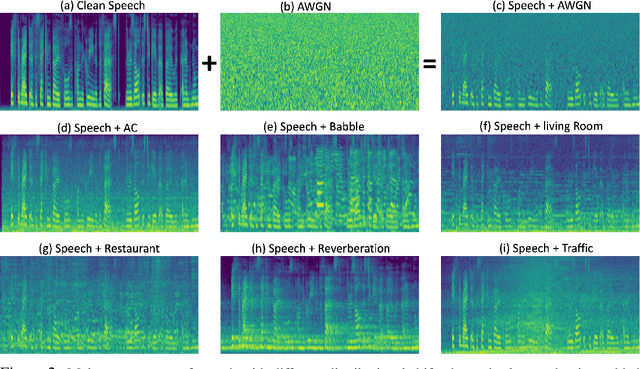
Abstract:In this paper, we study the application of Test-Time Training (TTT) as a solution to handling distribution shifts in speech applications. In particular, we introduce distribution-shifts to the test datasets of standard speech-classification tasks -- for example, speaker-identification and emotion-detection -- and explore how Test-Time Training (TTT) can help adjust to the distribution-shift. In our experiments that include distribution shifts due to background noise and natural variations in speech such as gender and age, we identify some key-challenges with TTT including sensitivity to optimization hyperparameters (e.g., number of optimization steps and subset of parameters chosen for TTT) and scalability (e.g., as each example gets its own set of parameters, TTT is not scalable). Finally, we propose using BitFit -- a parameter-efficient fine-tuning algorithm proposed for text applications that only considers the bias parameters for fine-tuning -- as a solution to the aforementioned challenges and demonstrate that it is consistently more stable than fine-tuning all the parameters of the model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge