Sheri Rempel
Predicting Individual Depression Symptoms from Acoustic Features During Speech
Jun 23, 2024Abstract:Current automatic depression detection systems provide predictions directly without relying on the individual symptoms/items of depression as denoted in the clinical depression rating scales. In contrast, clinicians assess each item in the depression rating scale in a clinical setting, thus implicitly providing a more detailed rationale for a depression diagnosis. In this work, we make a first step towards using the acoustic features of speech to predict individual items of the depression rating scale before obtaining the final depression prediction. For this, we use convolutional (CNN) and recurrent (long short-term memory (LSTM)) neural networks. We consider different approaches to learning the temporal context of speech. Further, we analyze two variants of voting schemes for individual item prediction and depression detection. We also include an animated visualization that shows an example of item prediction over time as the speech progresses.
Significance of Speaker Embeddings and Temporal Context for Depression Detection
Jul 24, 2021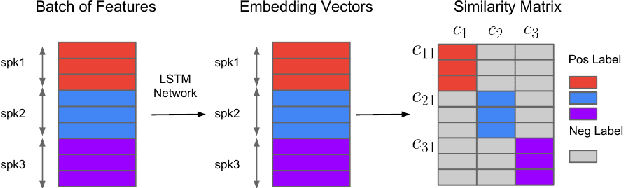
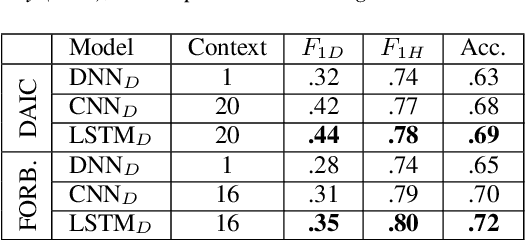
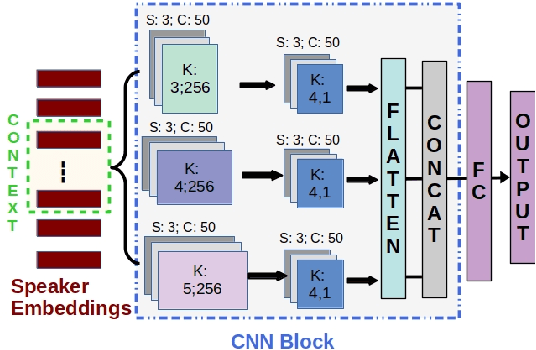
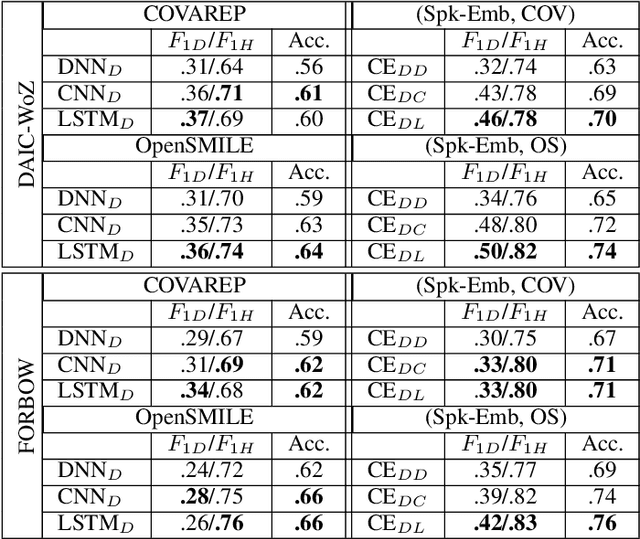
Abstract:Depression detection from speech has attracted a lot of attention in recent years. However, the significance of speaker-specific information in depression detection has not yet been explored. In this work, we analyze the significance of speaker embeddings for the task of depression detection from speech. Experimental results show that the speaker embeddings provide important cues to achieve state-of-the-art performance in depression detection. We also show that combining conventional OpenSMILE and COVAREP features, which carry complementary information, with speaker embeddings further improves the depression detection performance. The significance of temporal context in the training of deep learning models for depression detection is also analyzed in this paper.
Multimodal Deep Learning for Mental Disorders Prediction from Audio Speech Samples
Sep 12, 2019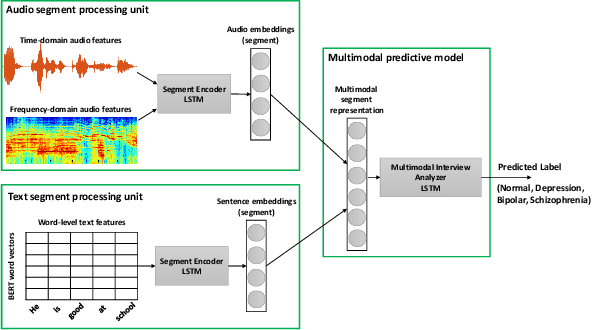
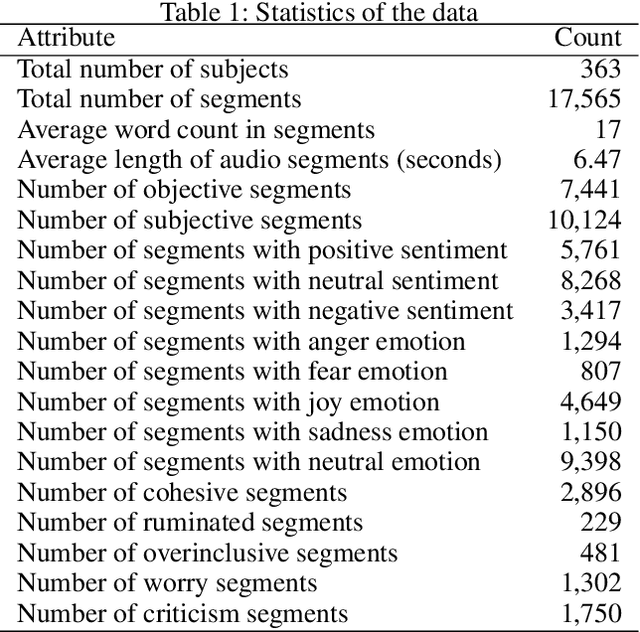
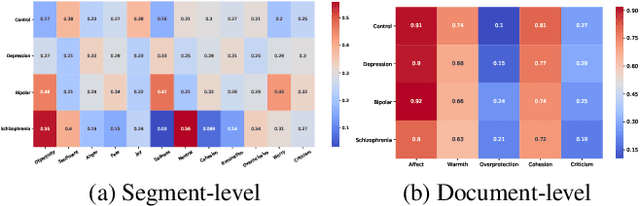
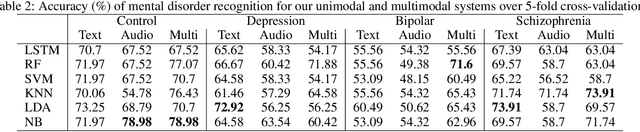
Abstract:Key features of mental illnesses are reflected in speech. Our research focuses on designing a multimodal deep learning structure that automatically extracts salient features from recorded speech samples for predicting various mental disorders including depression, bipolar, and schizophrenia. We adopt a variety of pre-trained models to extract embeddings from both audio and text segments. We use several state-of-the-art embedding techniques including BERT, FastText, and Doc2VecC for the text representation learning and WaveNet and VGG-ish models for audio encoding. We also leverage huge auxiliary emotion-labeled text and audio corpora to train emotion-specific embeddings and use transfer learning in order to address the problem of insufficient annotated multimodal data available. All these embeddings are then combined into a joint representation in a multimodal fusion layer and finally a recurrent neural network is used to predict the mental disorder. Our results show that mental disorders can be predicted with acceptable accuracy through multimodal analysis of clinical interviews.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge