Multimodal Deep Learning for Mental Disorders Prediction from Audio Speech Samples
Paper and Code
Sep 12, 2019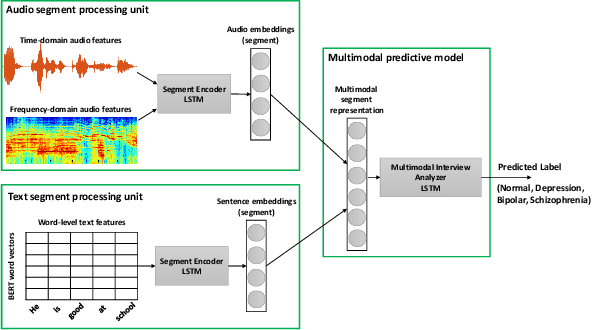
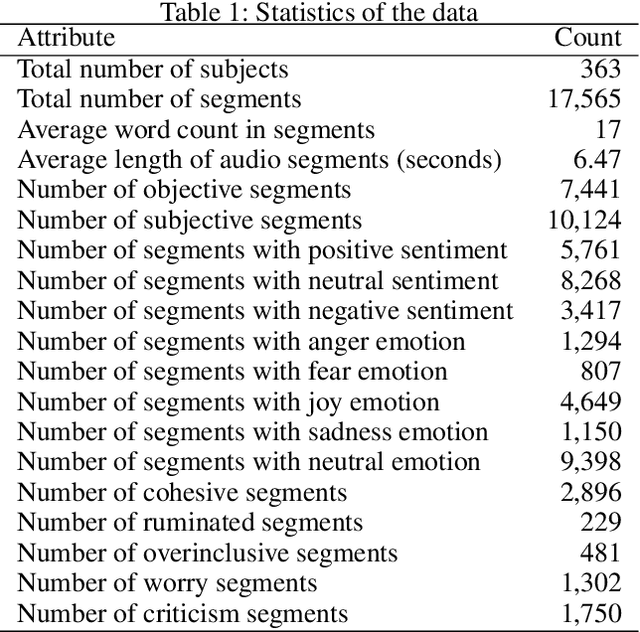
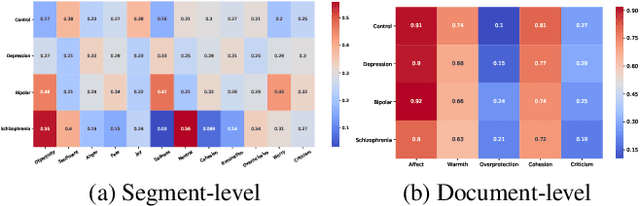
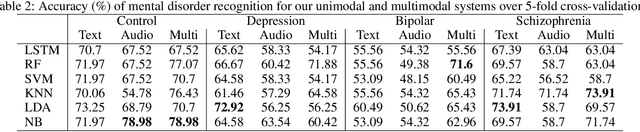
Key features of mental illnesses are reflected in speech. Our research focuses on designing a multimodal deep learning structure that automatically extracts salient features from recorded speech samples for predicting various mental disorders including depression, bipolar, and schizophrenia. We adopt a variety of pre-trained models to extract embeddings from both audio and text segments. We use several state-of-the-art embedding techniques including BERT, FastText, and Doc2VecC for the text representation learning and WaveNet and VGG-ish models for audio encoding. We also leverage huge auxiliary emotion-labeled text and audio corpora to train emotion-specific embeddings and use transfer learning in order to address the problem of insufficient annotated multimodal data available. All these embeddings are then combined into a joint representation in a multimodal fusion layer and finally a recurrent neural network is used to predict the mental disorder. Our results show that mental disorders can be predicted with acceptable accuracy through multimodal analysis of clinical interviews.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge