Evangelos Milios
Exploring the features used for summary evaluation by Human and GPT
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Summary assessment involves evaluating how well a generated summary reflects the key ideas and meaning of the source text, requiring a deep understanding of the content. Large Language Models (LLMs) have been used to automate this process, acting as judges to evaluate summaries with respect to the original text. While previous research investigated the alignment between LLMs and Human responses, it is not yet well understood what properties or features are exploited by them when asked to evaluate based on a particular quality dimension, and there has not been much attention towards mapping between evaluation scores and metrics. In this paper, we address this issue and discover features aligned with Human and Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPTs) responses by studying statistical and machine learning metrics. Furthermore, we show that instructing GPTs to employ metrics used by Human can improve their judgment and conforming them better with human responses.
Sensitivity of Generative VLMs to Semantically and Lexically Altered Prompts
Oct 16, 2024
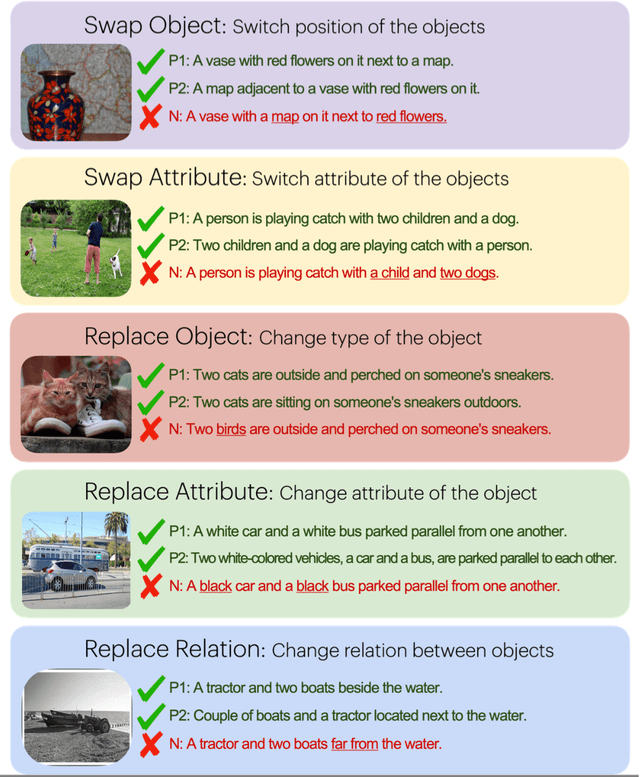
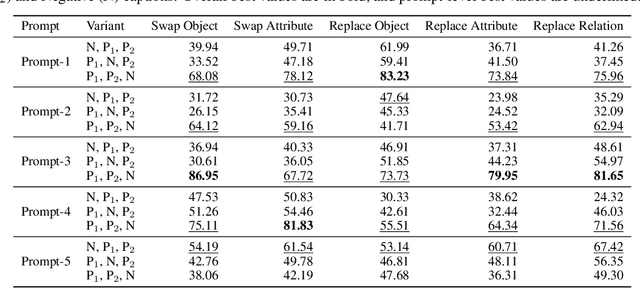
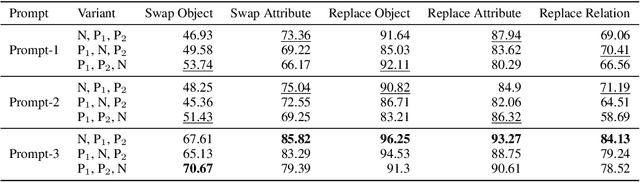
Abstract:Despite the significant influx of prompt-tuning techniques for generative vision-language models (VLMs), it remains unclear how sensitive these models are to lexical and semantic alterations in prompts. In this paper, we evaluate the ability of generative VLMs to understand lexical and semantic changes in text using the SugarCrepe++ dataset. We analyze the sensitivity of VLMs to lexical alterations in prompts without corresponding semantic changes. Our findings demonstrate that generative VLMs are highly sensitive to such alterations. Additionally, we show that this vulnerability affects the performance of techniques aimed at achieving consistency in their outputs.
SUGARCREPE++ Dataset: Vision-Language Model Sensitivity to Semantic and Lexical Alterations
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:Despite their remarkable successes, state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs), including vision-and-language models (VLMs) and unimodal language models (ULMs), fail to understand precise semantics. For example, semantically equivalent sentences expressed using different lexical compositions elicit diverging representations. The degree of this divergence and its impact on encoded semantics is not very well understood. In this paper, we introduce the SUGARCREPE++ dataset to analyze the sensitivity of VLMs and ULMs to lexical and semantic alterations. Each sample in SUGARCREPE++ dataset consists of an image and a corresponding triplet of captions: a pair of semantically equivalent but lexically different positive captions and one hard negative caption. This poses a 3-way semantic (in)equivalence problem to the language models. We comprehensively evaluate VLMs and ULMs that differ in architecture, pre-training objectives and datasets to benchmark the performance of SUGARCREPE++ dataset. Experimental results highlight the difficulties of VLMs in distinguishing between lexical and semantic variations, particularly in object attributes and spatial relations. Although VLMs with larger pre-training datasets, model sizes, and multiple pre-training objectives achieve better performance on SUGARCREPE++, there is a significant opportunity for improvement. We show that all the models which achieve better performance on compositionality datasets need not perform equally well on SUGARCREPE++, signifying that compositionality alone may not be sufficient for understanding semantic and lexical alterations. Given the importance of the property that the SUGARCREPE++ dataset targets, it serves as a new challenge to the vision-and-language community.
VISLA Benchmark: Evaluating Embedding Sensitivity to Semantic and Lexical Alterations
Apr 25, 2024



Abstract:Despite their remarkable successes, state-of-the-art language models face challenges in grasping certain important semantic details. This paper introduces the VISLA (Variance and Invariance to Semantic and Lexical Alterations) benchmark, designed to evaluate the semantic and lexical understanding of language models. VISLA presents a 3-way semantic (in)equivalence task with a triplet of sentences associated with an image, to evaluate both vision-language models (VLMs) and unimodal language models (ULMs). An evaluation involving 34 VLMs and 20 ULMs reveals surprising difficulties in distinguishing between lexical and semantic variations. Spatial semantics encoded by language models also appear to be highly sensitive to lexical information. Notably, text encoders of VLMs demonstrate greater sensitivity to semantic and lexical variations than unimodal text encoders. Our contributions include the unification of image-to-text and text-to-text retrieval tasks, an off-the-shelf evaluation without fine-tuning, and assessing LMs' semantic (in)variance in the presence of lexical alterations. The results highlight strengths and weaknesses across diverse vision and unimodal language models, contributing to a deeper understanding of their capabilities. % VISLA enables a rigorous evaluation, shedding light on language models' capabilities in handling semantic and lexical nuances. Data and code will be made available at https://github.com/Sri-Harsha/visla_benchmark.
Stance Reasoner: Zero-Shot Stance Detection on Social Media with Explicit Reasoning
Mar 22, 2024



Abstract:Social media platforms are rich sources of opinionated content. Stance detection allows the automatic extraction of users' opinions on various topics from such content. We focus on zero-shot stance detection, where the model's success relies on (a) having knowledge about the target topic; and (b) learning general reasoning strategies that can be employed for new topics. We present Stance Reasoner, an approach to zero-shot stance detection on social media that leverages explicit reasoning over background knowledge to guide the model's inference about the document's stance on a target. Specifically, our method uses a pre-trained language model as a source of world knowledge, with the chain-of-thought in-context learning approach to generate intermediate reasoning steps. Stance Reasoner outperforms the current state-of-the-art models on 3 Twitter datasets, including fully supervised models. It can better generalize across targets, while at the same time providing explicit and interpretable explanations for its predictions.
Empowering Air Travelers: A Chatbot for Canadian Air Passenger Rights
Mar 19, 2024Abstract:The Canadian air travel sector has seen a significant increase in flight delays, cancellations, and other issues concerning passenger rights. Recognizing this demand, we present a chatbot to assist passengers and educate them about their rights. Our system breaks a complex user input into simple queries which are used to retrieve information from a collection of documents detailing air travel regulations. The most relevant passages from these documents are presented along with links to the original documents and the generated queries, enabling users to dissect and leverage the information for their unique circumstances. The system successfully overcomes two predominant challenges: understanding complex user inputs, and delivering accurate answers, free of hallucinations, that passengers can rely on for making informed decisions. A user study comparing the chatbot to a Google search demonstrated the chatbot's usefulness and ease of use. Beyond the primary goal of providing accurate and timely information to air passengers regarding their rights, we hope that this system will also enable further research exploring the tradeoff between the user-friendly conversational interface of chatbots and the accuracy of retrieval systems.
Breaking the Token Barrier: Chunking and Convolution for Efficient Long Text Classification with BERT
Oct 31, 2023Abstract:Transformer-based models, specifically BERT, have propelled research in various NLP tasks. However, these models are limited to a maximum token limit of 512 tokens. Consequently, this makes it non-trivial to apply it in a practical setting with long input. Various complex methods have claimed to overcome this limit, but recent research questions the efficacy of these models across different classification tasks. These complex architectures evaluated on carefully curated long datasets perform at par or worse than simple baselines. In this work, we propose a relatively simple extension to vanilla BERT architecture called ChunkBERT that allows finetuning of any pretrained models to perform inference on arbitrarily long text. The proposed method is based on chunking token representations and CNN layers, making it compatible with any pre-trained BERT. We evaluate chunkBERT exclusively on a benchmark for comparing long-text classification models across a variety of tasks (including binary classification, multi-class classification, and multi-label classification). A BERT model finetuned using the ChunkBERT method performs consistently across long samples in the benchmark while utilizing only a fraction (6.25\%) of the original memory footprint. These findings suggest that efficient finetuning and inference can be achieved through simple modifications to pre-trained BERT models.
QuOTeS: Query-Oriented Technical Summarization
Jun 20, 2023Abstract:Abstract. When writing an academic paper, researchers often spend considerable time reviewing and summarizing papers to extract relevant citations and data to compose the Introduction and Related Work sections. To address this problem, we propose QuOTeS, an interactive system designed to retrieve sentences related to a summary of the research from a collection of potential references and hence assist in the composition of new papers. QuOTeS integrates techniques from Query-Focused Extractive Summarization and High-Recall Information Retrieval to provide Interactive Query-Focused Summarization of scientific documents. To measure the performance of our system, we carried out a comprehensive user study where participants uploaded papers related to their research and evaluated the system in terms of its usability and the quality of the summaries it produces. The results show that QuOTeS provides a positive user experience and consistently provides query-focused summaries that are relevant, concise, and complete. We share the code of our system and the novel Query-Focused Summarization dataset collected during our experiments at https://github.com/jarobyte91/quotes.
DimenFix: A novel meta-dimensionality reduction method for feature preservation
Nov 30, 2022Abstract:Dimensionality reduction has become an important research topic as demand for interpreting high-dimensional datasets has been increasing rapidly in recent years. There have been many dimensionality reduction methods with good performance in preserving the overall relationship among data points when mapping them to a lower-dimensional space. However, these existing methods fail to incorporate the difference in importance among features. To address this problem, we propose a novel meta-method, DimenFix, which can be operated upon any base dimensionality reduction method that involves a gradient-descent-like process. By allowing users to define the importance of different features, which is considered in dimensionality reduction, DimenFix creates new possibilities to visualize and understand a given dataset. Meanwhile, DimenFix does not increase the time cost or reduce the quality of dimensionality reduction with respect to the base dimensionality reduction used.
Post-OCR Document Correction with large Ensembles of Character Sequence Models
Sep 15, 2021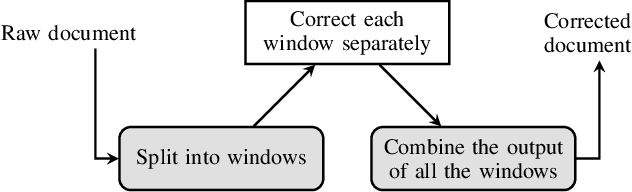
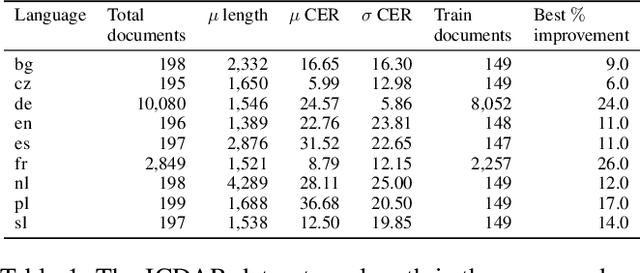
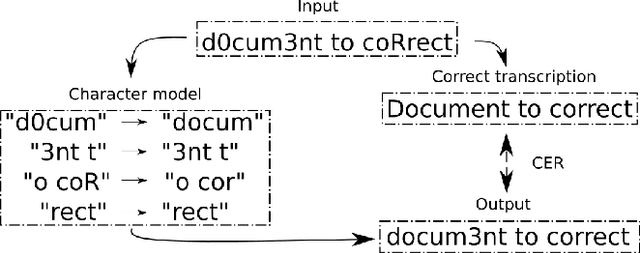
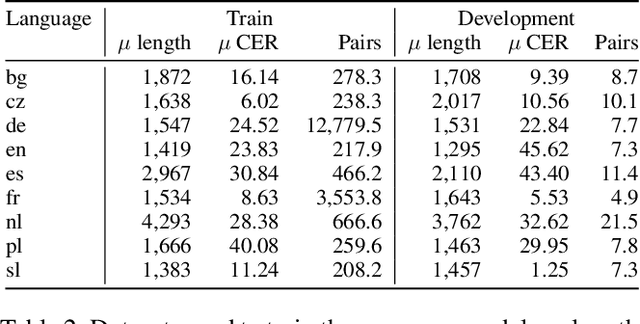
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel method based on character sequence-to-sequence models to correct documents already processed with Optical Character Recognition (OCR) systems. The main contribution of this paper is a set of strategies to accurately process strings much longer than the ones used to train the sequence model while being sample- and resource-efficient, supported by thorough experimentation. The strategy with the best performance involves splitting the input document in character n-grams and combining their individual corrections into the final output using a voting scheme that is equivalent to an ensemble of a large number of sequence models. We further investigate how to weigh the contributions from each one of the members of this ensemble. We test our method on nine languages of the ICDAR 2019 competition on post-OCR text correction and achieve a new state-of-the-art performance in five of them. Our code for post-OCR correction is shared at https://github.com/jarobyte91/post_ocr_correction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge