Sonia Castelo
ARTiST: Automated Text Simplification for Task Guidance in Augmented Reality
Feb 29, 2024
Abstract:Text presented in augmented reality provides in-situ, real-time information for users. However, this content can be challenging to apprehend quickly when engaging in cognitively demanding AR tasks, especially when it is presented on a head-mounted display. We propose ARTiST, an automatic text simplification system that uses a few-shot prompt and GPT-3 models to specifically optimize the text length and semantic content for augmented reality. Developed out of a formative study that included seven users and three experts, our system combines a customized error calibration model with a few-shot prompt to integrate the syntactic, lexical, elaborative, and content simplification techniques, and generate simplified AR text for head-worn displays. Results from a 16-user empirical study showed that ARTiST lightens the cognitive load and improves performance significantly over both unmodified text and text modified via traditional methods. Our work constitutes a step towards automating the optimization of batch text data for readability and performance in augmented reality.
A Visual Mining Approach to Improved Multiple-Instance Learning
Dec 14, 2020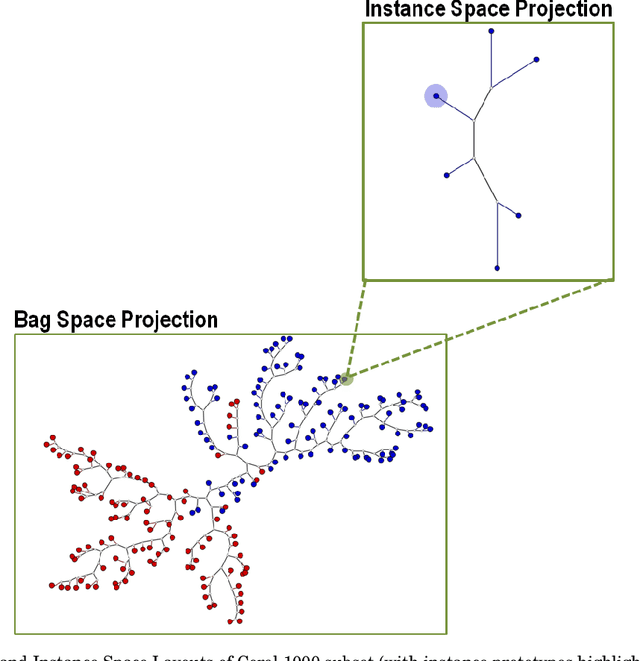
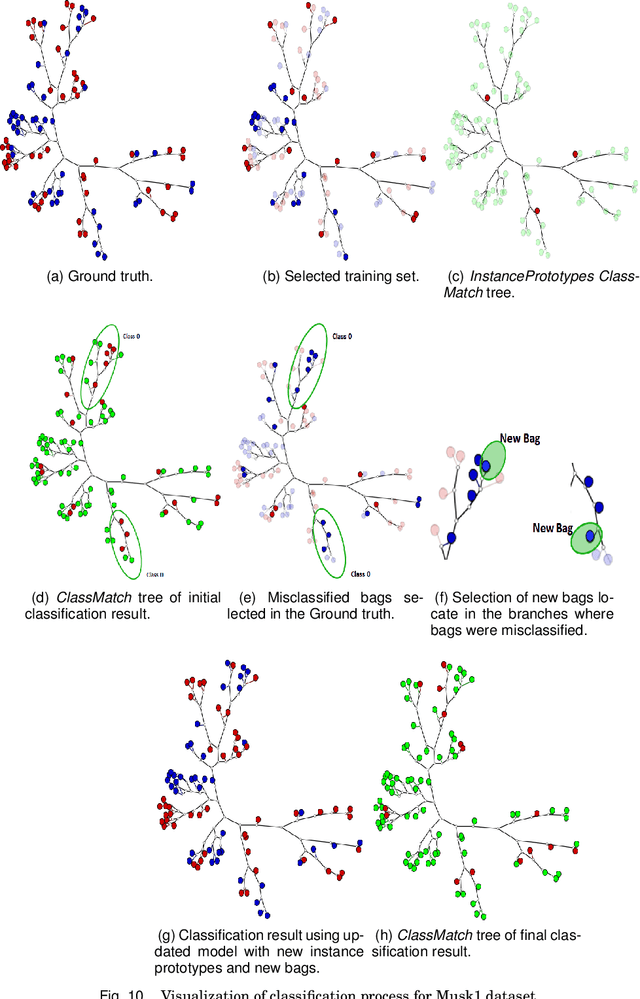

Abstract:Multiple-instance learning (MIL) is a paradigm of machine learning that aims to classify a set (bag) of objects (instances), assigning labels only to the bags. This problem is often addressed by selecting an instance to represent each bag, transforming a MIL problem into a standard supervised learning. Visualization can be a useful tool to assess learning scenarios by incorporating the users' knowledge into the classification process. Considering that multiple-instance learning is a paradigm that cannot be handled by current visualization techniques, we propose a multiscale tree-based visualization to support MIL. The first level of the tree represents the bags, and the second level represents the instances belonging to each bag, allowing the user to understand the data in an intuitive way. In addition, we propose two new instance selection methods for MIL, which help the user to improve the model even further. Our methods are also able to handle both binary and multiclass scenarios. In our experiments, SVM was used to build the classifiers. With support of the MILTree layout, the initial classification model was updated by changing the training set - composed by the prototype instances. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of our approach, showing that visual mining by MILTree can help users in exploring and improving models in MIL scenarios, and that our instance selection methods over-perform current available alternatives in most cases.
Visus: An Interactive System for Automatic Machine Learning Model Building and Curation
Jul 05, 2019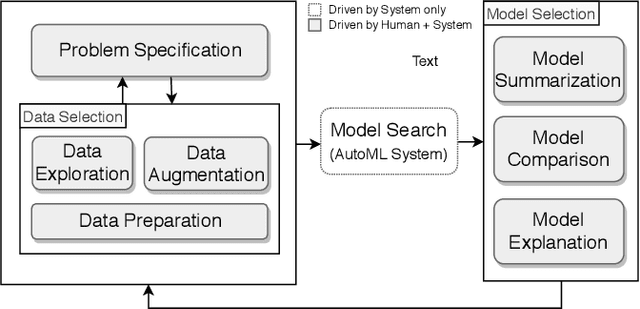
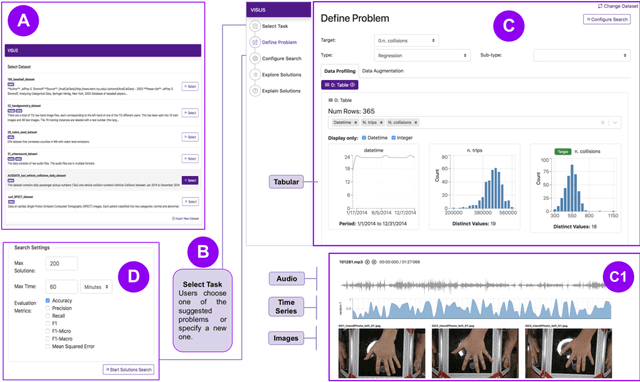
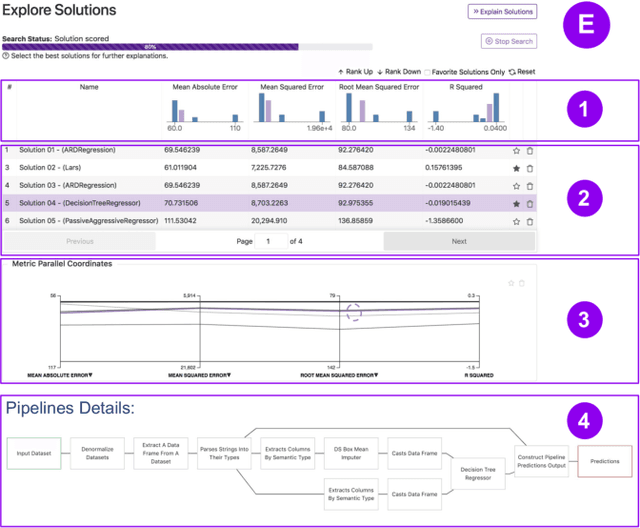
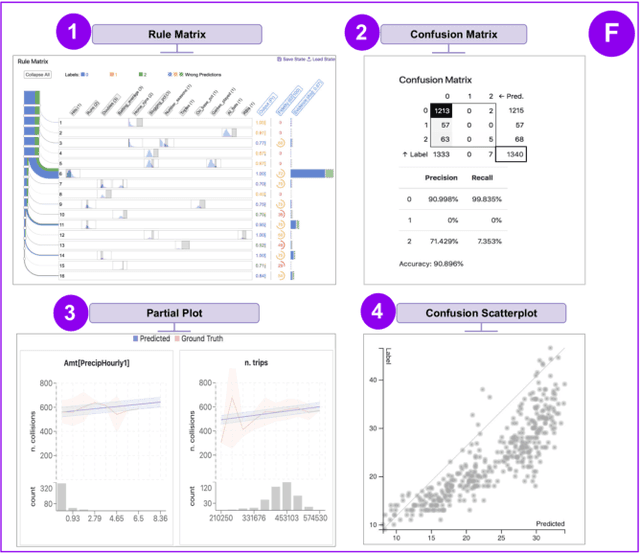
Abstract:While the demand for machine learning (ML) applications is booming, there is a scarcity of data scientists capable of building such models. Automatic machine learning (AutoML) approaches have been proposed that help with this problem by synthesizing end-to-end ML data processing pipelines. However, these follow a best-effort approach and a user in the loop is necessary to curate and refine the derived pipelines. Since domain experts often have little or no expertise in machine learning, easy-to-use interactive interfaces that guide them throughout the model building process are necessary. In this paper, we present Visus, a system designed to support the model building process and curation of ML data processing pipelines generated by AutoML systems. We describe the framework used to ground our design choices and a usage scenario enabled by Visus. Finally, we discuss the feedback received in user testing sessions with domain experts.
A Topic-Agnostic Approach for Identifying Fake News Pages
May 02, 2019



Abstract:Fake news and misinformation have been increasingly used to manipulate popular opinion and influence political processes. To better understand fake news, how they are propagated, and how to counter their effect, it is necessary to first identify them. Recently, approaches have been proposed to automatically classify articles as fake based on their content. An important challenge for these approaches comes from the dynamic nature of news: as new political events are covered, topics and discourse constantly change and thus, a classifier trained using content from articles published at a given time is likely to become ineffective in the future. To address this challenge, we propose a topic-agnostic (TAG) classification strategy that uses linguistic and web-markup features to identify fake news pages. We report experimental results using multiple data sets which show that our approach attains high accuracy in the identification of fake news, even as topics evolve over time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge