Songjiang Li
Neighbor2Neighbor: Self-Supervised Denoising from Single Noisy Images
Jan 11, 2021



Abstract:In the last few years, image denoising has benefited a lot from the fast development of neural networks. However, the requirement of large amounts of noisy-clean image pairs for supervision limits the wide use of these models. Although there have been a few attempts in training an image denoising model with only single noisy images, existing self-supervised denoising approaches suffer from inefficient network training, loss of useful information, or dependence on noise modeling. In this paper, we present a very simple yet effective method named Neighbor2Neighbor to train an effective image denoising model with only noisy images. Firstly, a random neighbor down-sampler is proposed for the generation of training image pairs. In detail, input and target used to train a network are images down-sampled from the same noisy image, satisfying the requirement that paired pixels of paired images are neighbors and have very similar appearance with each other. Secondly, a denoising network is trained on down-sampled training pairs generated in the first stage, with a proposed regularizer as additional loss for better performance. The proposed Neighbor2Neighbor framework is able to enjoy the progress of state-of-the-art supervised denoising networks in network architecture design. Moreover, it avoids heavy dependence on the assumption of the noise distribution. We explain our approach from a theoretical perspective and further validate it through extensive experiments, including synthetic experiments with different noise distributions in sRGB space and real-world experiments on a denoising benchmark dataset in raw-RGB space.
Video Super-Resolution with Recurrent Structure-Detail Network
Aug 02, 2020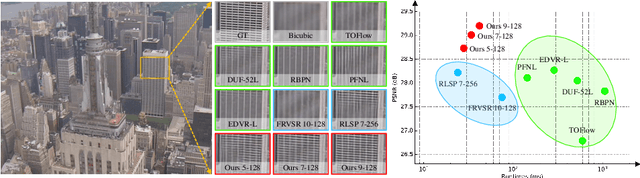
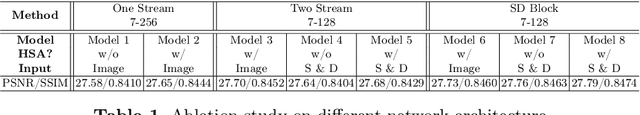


Abstract:Most video super-resolution methods super-resolve a single reference frame with the help of neighboring frames in a temporal sliding window. They are less efficient compared to the recurrent-based methods. In this work, we propose a novel recurrent video super-resolution method which is both effective and efficient in exploiting previous frames to super-resolve the current frame. It divides the input into structure and detail components which are fed to a recurrent unit composed of several proposed two-stream structure-detail blocks. In addition, a hidden state adaptation module that allows the current frame to selectively use information from hidden state is introduced to enhance its robustness to appearance change and error accumulation. Extensive ablation study validate the effectiveness of the proposed modules. Experiments on several benchmark datasets demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed method compared to state-of-the-art methods on video super-resolution.
Video Super-resolution with Temporal Group Attention
Jul 21, 2020
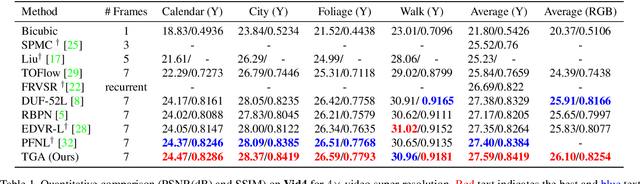

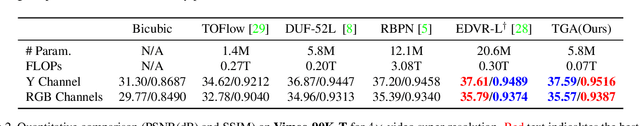
Abstract:Video super-resolution, which aims at producing a high-resolution video from its corresponding low-resolution version, has recently drawn increasing attention. In this work, we propose a novel method that can effectively incorporate temporal information in a hierarchical way. The input sequence is divided into several groups, with each one corresponding to a kind of frame rate. These groups provide complementary information to recover missing details in the reference frame, which is further integrated with an attention module and a deep intra-group fusion module. In addition, a fast spatial alignment is proposed to handle videos with large motion. Extensive results demonstrate the capability of the proposed model in handling videos with various motion. It achieves favorable performance against state-of-the-art methods on several benchmark datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge