Simar Kareer
Emergence of Human to Robot Transfer in Vision-Language-Action Models
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:Vision-language-action (VLA) models can enable broad open world generalization, but require large and diverse datasets. It is appealing to consider whether some of this data can come from human videos, which cover diverse real-world situations and are easy to obtain. However, it is difficult to train VLAs with human videos alone, and establishing a mapping between humans and robots requires manual engineering and presents a major research challenge. Drawing inspiration from advances in large language models, where the ability to learn from diverse supervision emerges with scale, we ask whether a similar phenomenon holds for VLAs that incorporate human video data. We introduce a simple co-training recipe, and find that human-to-robot transfer emerges once the VLA is pre-trained on sufficient scenes, tasks, and embodiments. Our analysis suggests that this emergent capability arises because diverse pretraining produces embodiment-agnostic representations for human and robot data. We validate these findings through a series of experiments probing human to robot skill transfer and find that with sufficiently diverse robot pre-training our method can nearly double the performance on generalization settings seen only in human data.
EMMA: Scaling Mobile Manipulation via Egocentric Human Data
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Scaling mobile manipulation imitation learning is bottlenecked by expensive mobile robot teleoperation. We present Egocentric Mobile MAnipulation (EMMA), an end-to-end framework training mobile manipulation policies from human mobile manipulation data with static robot data, sidestepping mobile teleoperation. To accomplish this, we co-train human full-body motion data with static robot data. In our experiments across three real-world tasks, EMMA demonstrates comparable performance to baselines trained on teleoperated mobile robot data (Mobile ALOHA), achieving higher or equivalent task performance in full task success. We find that EMMA is able to generalize to new spatial configurations and scenes, and we observe positive performance scaling as we increase the hours of human data, opening new avenues for scalable robotic learning in real-world environments. Details of this project can be found at https://ego-moma.github.io/.
EgoMimic: Scaling Imitation Learning via Egocentric Video
Oct 31, 2024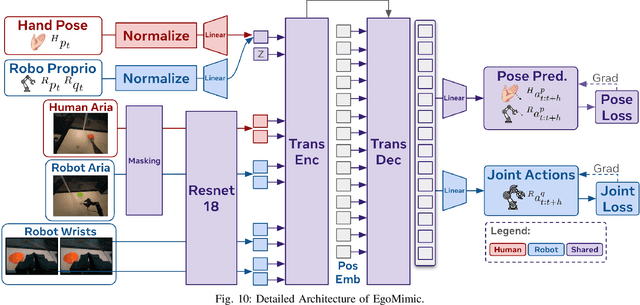
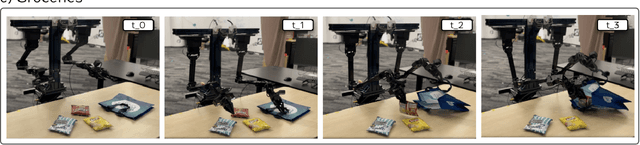

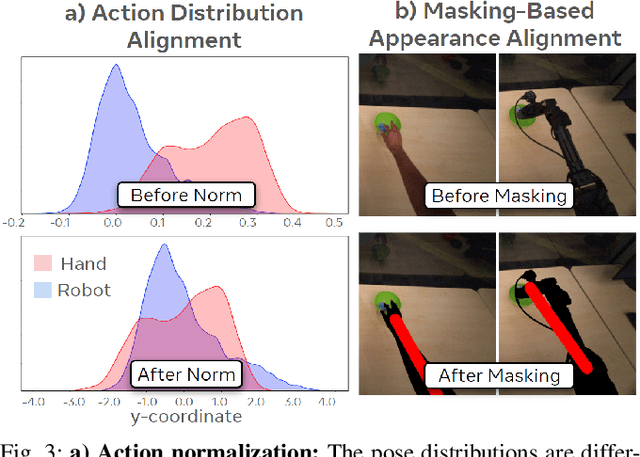
Abstract:The scale and diversity of demonstration data required for imitation learning is a significant challenge. We present EgoMimic, a full-stack framework which scales manipulation via human embodiment data, specifically egocentric human videos paired with 3D hand tracking. EgoMimic achieves this through: (1) a system to capture human embodiment data using the ergonomic Project Aria glasses, (2) a low-cost bimanual manipulator that minimizes the kinematic gap to human data, (3) cross-domain data alignment techniques, and (4) an imitation learning architecture that co-trains on human and robot data. Compared to prior works that only extract high-level intent from human videos, our approach treats human and robot data equally as embodied demonstration data and learns a unified policy from both data sources. EgoMimic achieves significant improvement on a diverse set of long-horizon, single-arm and bimanual manipulation tasks over state-of-the-art imitation learning methods and enables generalization to entirely new scenes. Finally, we show a favorable scaling trend for EgoMimic, where adding 1 hour of additional hand data is significantly more valuable than 1 hour of additional robot data. Videos and additional information can be found at https://egomimic.github.io/
We're Not Using Videos Effectively: An Updated Domain Adaptive Video Segmentation Baseline
Feb 06, 2024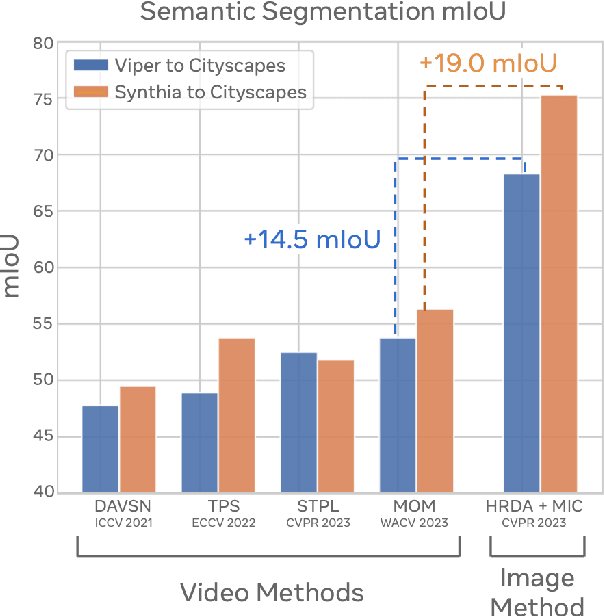

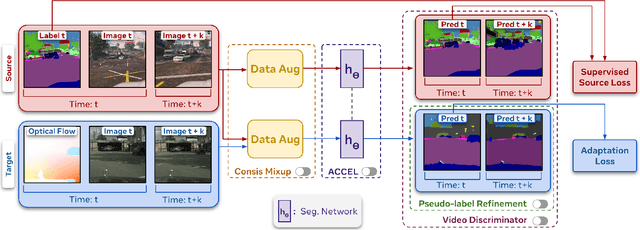
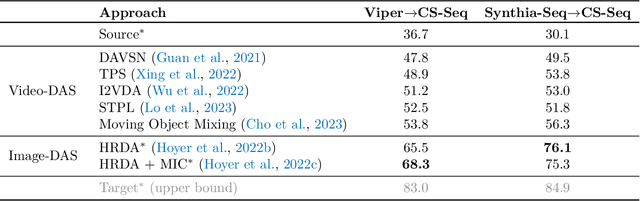
Abstract:There has been abundant work in unsupervised domain adaptation for semantic segmentation (DAS) seeking to adapt a model trained on images from a labeled source domain to an unlabeled target domain. While the vast majority of prior work has studied this as a frame-level Image-DAS problem, a few Video-DAS works have sought to additionally leverage the temporal signal present in adjacent frames. However, Video-DAS works have historically studied a distinct set of benchmarks from Image-DAS, with minimal cross-benchmarking. In this work, we address this gap. Surprisingly, we find that (1) even after carefully controlling for data and model architecture, state-of-the-art Image-DAS methods (HRDA and HRDA+MIC) outperform Video-DAS methods on established Video-DAS benchmarks (+14.5 mIoU on Viper$\rightarrow$CityscapesSeq, +19.0 mIoU on Synthia$\rightarrow$CityscapesSeq), and (2) naive combinations of Image-DAS and Video-DAS techniques only lead to marginal improvements across datasets. To avoid siloed progress between Image-DAS and Video-DAS, we open-source our codebase with support for a comprehensive set of Video-DAS and Image-DAS methods on a common benchmark. Code available at https://github.com/SimarKareer/UnifiedVideoDA
ViNL: Visual Navigation and Locomotion Over Obstacles
Oct 26, 2022Abstract:We present Visual Navigation and Locomotion over obstacles (ViNL), which enables a quadrupedal robot to navigate unseen apartments while stepping over small obstacles that lie in its path (e.g., shoes, toys, cables), similar to how humans and pets lift their feet over objects as they walk. ViNL consists of: (1) a visual navigation policy that outputs linear and angular velocity commands that guides the robot to a goal coordinate in unfamiliar indoor environments; and (2) a visual locomotion policy that controls the robot's joints to avoid stepping on obstacles while following provided velocity commands. Both the policies are entirely "model-free", i.e. sensors-to-actions neural networks trained end-to-end. The two are trained independently in two entirely different simulators and then seamlessly co-deployed by feeding the velocity commands from the navigator to the locomotor, entirely "zero-shot" (without any co-training). While prior works have developed learning methods for visual navigation or visual locomotion, to the best of our knowledge, this is the first fully learned approach that leverages vision to accomplish both (1) intelligent navigation in new environments, and (2) intelligent visual locomotion that aims to traverse cluttered environments without disrupting obstacles. On the task of navigation to distant goals in unknown environments, ViNL using just egocentric vision significantly outperforms prior work on robust locomotion using privileged terrain maps (+32.8% success and -4.42 collisions per meter). Additionally, we ablate our locomotion policy to show that each aspect of our approach helps reduce obstacle collisions. Videos and code at http://www.joannetruong.com/projects/vinl.html
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge