Sicheng Zuo
DVGT: Driving Visual Geometry Transformer
Dec 18, 2025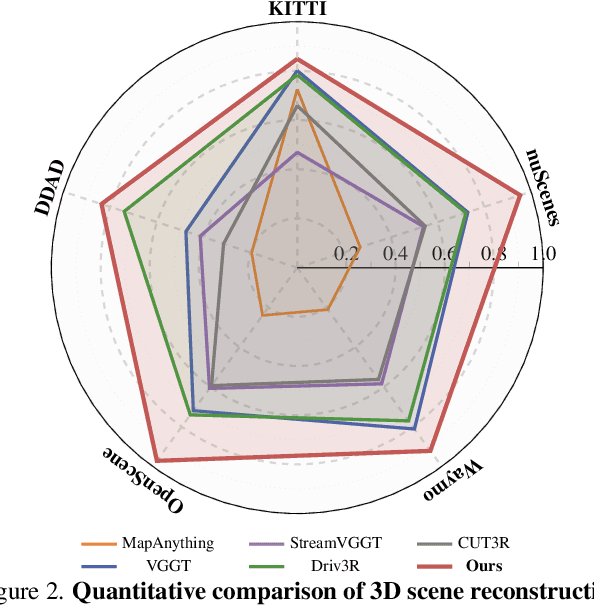
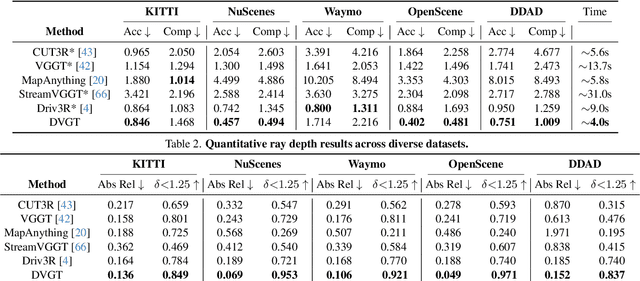
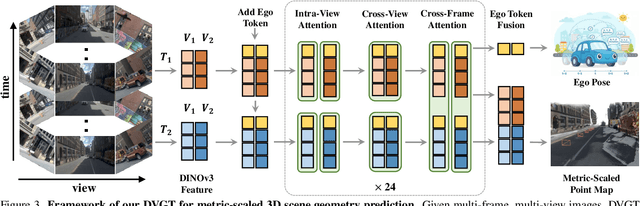
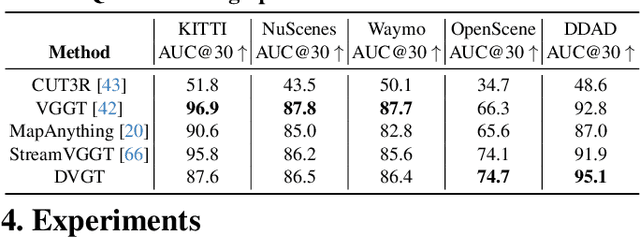
Abstract:Perceiving and reconstructing 3D scene geometry from visual inputs is crucial for autonomous driving. However, there still lacks a driving-targeted dense geometry perception model that can adapt to different scenarios and camera configurations. To bridge this gap, we propose a Driving Visual Geometry Transformer (DVGT), which reconstructs a global dense 3D point map from a sequence of unposed multi-view visual inputs. We first extract visual features for each image using a DINO backbone, and employ alternating intra-view local attention, cross-view spatial attention, and cross-frame temporal attention to infer geometric relations across images. We then use multiple heads to decode a global point map in the ego coordinate of the first frame and the ego poses for each frame. Unlike conventional methods that rely on precise camera parameters, DVGT is free of explicit 3D geometric priors, enabling flexible processing of arbitrary camera configurations. DVGT directly predicts metric-scaled geometry from image sequences, eliminating the need for post-alignment with external sensors. Trained on a large mixture of driving datasets including nuScenes, OpenScene, Waymo, KITTI, and DDAD, DVGT significantly outperforms existing models on various scenarios. Code is available at https://github.com/wzzheng/DVGT.
QuadricFormer: Scene as Superquadrics for 3D Semantic Occupancy Prediction
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:3D occupancy prediction is crucial for robust autonomous driving systems as it enables comprehensive perception of environmental structures and semantics. Most existing methods employ dense voxel-based scene representations, ignoring the sparsity of driving scenes and resulting in inefficiency. Recent works explore object-centric representations based on sparse Gaussians, but their ellipsoidal shape prior limits the modeling of diverse structures. In real-world driving scenes, objects exhibit rich geometries (e.g., cuboids, cylinders, and irregular shapes), necessitating excessive ellipsoidal Gaussians densely packed for accurate modeling, which leads to inefficient representations. To address this, we propose to use geometrically expressive superquadrics as scene primitives, enabling efficient representation of complex structures with fewer primitives through their inherent shape diversity. We develop a probabilistic superquadric mixture model, which interprets each superquadric as an occupancy probability distribution with a corresponding geometry prior, and calculates semantics through probabilistic mixture. Building on this, we present QuadricFormer, a superquadric-based model for efficient 3D occupancy prediction, and introduce a pruning-and-splitting module to further enhance modeling efficiency by concentrating superquadrics in occupied regions. Extensive experiments on the nuScenes dataset demonstrate that QuadricFormer achieves state-of-the-art performance while maintaining superior efficiency.
GaussianWorld: Gaussian World Model for Streaming 3D Occupancy Prediction
Dec 13, 2024


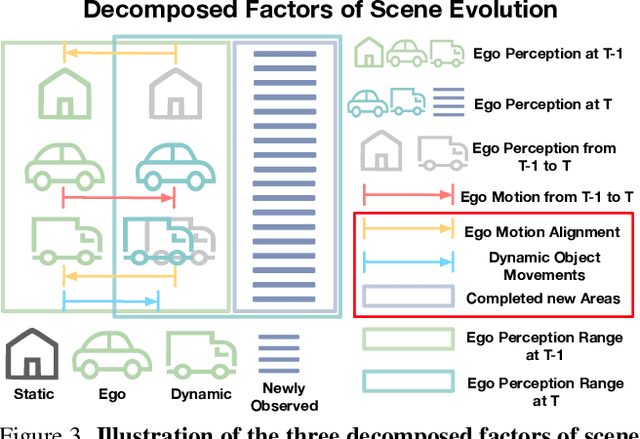
Abstract:3D occupancy prediction is important for autonomous driving due to its comprehensive perception of the surroundings. To incorporate sequential inputs, most existing methods fuse representations from previous frames to infer the current 3D occupancy. However, they fail to consider the continuity of driving scenarios and ignore the strong prior provided by the evolution of 3D scenes (e.g., only dynamic objects move). In this paper, we propose a world-model-based framework to exploit the scene evolution for perception. We reformulate 3D occupancy prediction as a 4D occupancy forecasting problem conditioned on the current sensor input. We decompose the scene evolution into three factors: 1) ego motion alignment of static scenes; 2) local movements of dynamic objects; and 3) completion of newly-observed scenes. We then employ a Gaussian world model (GaussianWorld) to explicitly exploit these priors and infer the scene evolution in the 3D Gaussian space considering the current RGB observation. We evaluate the effectiveness of our framework on the widely used nuScenes dataset. Our GaussianWorld improves the performance of the single-frame counterpart by over 2% in mIoU without introducing additional computations. Code: https://github.com/zuosc19/GaussianWorld.
GaussianAD: Gaussian-Centric End-to-End Autonomous Driving
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Vision-based autonomous driving shows great potential due to its satisfactory performance and low costs. Most existing methods adopt dense representations (e.g., bird's eye view) or sparse representations (e.g., instance boxes) for decision-making, which suffer from the trade-off between comprehensiveness and efficiency. This paper explores a Gaussian-centric end-to-end autonomous driving (GaussianAD) framework and exploits 3D semantic Gaussians to extensively yet sparsely describe the scene. We initialize the scene with uniform 3D Gaussians and use surrounding-view images to progressively refine them to obtain the 3D Gaussian scene representation. We then use sparse convolutions to efficiently perform 3D perception (e.g., 3D detection, semantic map construction). We predict 3D flows for the Gaussians with dynamic semantics and plan the ego trajectory accordingly with an objective of future scene forecasting. Our GaussianAD can be trained in an end-to-end manner with optional perception labels when available. Extensive experiments on the widely used nuScenes dataset verify the effectiveness of our end-to-end GaussianAD on various tasks including motion planning, 3D occupancy prediction, and 4D occupancy forecasting. Code: https://github.com/wzzheng/GaussianAD.
Doe-1: Closed-Loop Autonomous Driving with Large World Model
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:End-to-end autonomous driving has received increasing attention due to its potential to learn from large amounts of data. However, most existing methods are still open-loop and suffer from weak scalability, lack of high-order interactions, and inefficient decision-making. In this paper, we explore a closed-loop framework for autonomous driving and propose a large Driving wOrld modEl (Doe-1) for unified perception, prediction, and planning. We formulate autonomous driving as a next-token generation problem and use multi-modal tokens to accomplish different tasks. Specifically, we use free-form texts (i.e., scene descriptions) for perception and generate future predictions directly in the RGB space with image tokens. For planning, we employ a position-aware tokenizer to effectively encode action into discrete tokens. We train a multi-modal transformer to autoregressively generate perception, prediction, and planning tokens in an end-to-end and unified manner. Experiments on the widely used nuScenes dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of Doe-1 in various tasks including visual question-answering, action-conditioned video generation, and motion planning. Code: https://github.com/wzzheng/Doe.
GPD-1: Generative Pre-training for Driving
Dec 11, 2024



Abstract:Modeling the evolutions of driving scenarios is important for the evaluation and decision-making of autonomous driving systems. Most existing methods focus on one aspect of scene evolution such as map generation, motion prediction, and trajectory planning. In this paper, we propose a unified Generative Pre-training for Driving (GPD-1) model to accomplish all these tasks altogether without additional fine-tuning. We represent each scene with ego, agent, and map tokens and formulate autonomous driving as a unified token generation problem. We adopt the autoregressive transformer architecture and use a scene-level attention mask to enable intra-scene bi-directional interactions. For the ego and agent tokens, we propose a hierarchical positional tokenizer to effectively encode both 2D positions and headings. For the map tokens, we train a map vector-quantized autoencoder to efficiently compress ego-centric semantic maps into discrete tokens. We pre-train our GPD-1 on the large-scale nuPlan dataset and conduct extensive experiments to evaluate its effectiveness. With different prompts, our GPD-1 successfully generalizes to various tasks without finetuning, including scene generation, traffic simulation, closed-loop simulation, map prediction, and motion planning. Code: https://github.com/wzzheng/GPD.
EmbodiedOcc: Embodied 3D Occupancy Prediction for Vision-based Online Scene Understanding
Dec 05, 2024Abstract:3D occupancy prediction provides a comprehensive description of the surrounding scenes and has become an essential task for 3D perception. Most existing methods focus on offline perception from one or a few views and cannot be applied to embodied agents which demands to gradually perceive the scene through progressive embodied exploration. In this paper, we formulate an embodied 3D occupancy prediction task to target this practical scenario and propose a Gaussian-based EmbodiedOcc framework to accomplish it. We initialize the global scene with uniform 3D semantic Gaussians and progressively update local regions observed by the embodied agent. For each update, we extract semantic and structural features from the observed image and efficiently incorporate them via deformable cross-attention to refine the regional Gaussians. Finally, we employ Gaussian-to-voxel splatting to obtain the global 3D occupancy from the updated 3D Gaussians. Our EmbodiedOcc assumes an unknown (i.e., uniformly distributed) environment and maintains an explicit global memory of it with 3D Gaussians. It gradually gains knowledge through local refinement of regional Gaussians, which is consistent with how humans understand new scenes through embodied exploration. We reorganize an EmbodiedOcc-ScanNet benchmark based on local annotations to facilitate the evaluation of the embodied 3D occupancy prediction task. Experiments demonstrate that our EmbodiedOcc outperforms existing local prediction methods and accomplishes the embodied occupancy prediction with high accuracy and strong expandability. Our code is available at: https://github.com/YkiWu/EmbodiedOcc.
PointOcc: Cylindrical Tri-Perspective View for Point-based 3D Semantic Occupancy Prediction
Aug 31, 2023



Abstract:Semantic segmentation in autonomous driving has been undergoing an evolution from sparse point segmentation to dense voxel segmentation, where the objective is to predict the semantic occupancy of each voxel in the concerned 3D space. The dense nature of the prediction space has rendered existing efficient 2D-projection-based methods (e.g., bird's eye view, range view, etc.) ineffective, as they can only describe a subspace of the 3D scene. To address this, we propose a cylindrical tri-perspective view to represent point clouds effectively and comprehensively and a PointOcc model to process them efficiently. Considering the distance distribution of LiDAR point clouds, we construct the tri-perspective view in the cylindrical coordinate system for more fine-grained modeling of nearer areas. We employ spatial group pooling to maintain structural details during projection and adopt 2D backbones to efficiently process each TPV plane. Finally, we obtain the features of each point by aggregating its projected features on each of the processed TPV planes without the need for any post-processing. Extensive experiments on both 3D occupancy prediction and LiDAR segmentation benchmarks demonstrate that the proposed PointOcc achieves state-of-the-art performance with much faster speed. Specifically, despite only using LiDAR, PointOcc significantly outperforms all other methods, including multi-modal methods, with a large margin on the OpenOccupancy benchmark. Code: https://github.com/wzzheng/PointOcc.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge