Si Shi
SceneRAG: Scene-level Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Video Understanding
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:Despite recent advances in retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) for video understanding, effectively understanding long-form video content remains underexplored due to the vast scale and high complexity of video data. Current RAG approaches typically segment videos into fixed-length chunks, which often disrupts the continuity of contextual information and fails to capture authentic scene boundaries. Inspired by the human ability to naturally organize continuous experiences into coherent scenes, we present SceneRAG, a unified framework that leverages large language models to segment videos into narrative-consistent scenes by processing ASR transcripts alongside temporal metadata. SceneRAG further sharpens these initial boundaries through lightweight heuristics and iterative correction. For each scene, the framework fuses information from both visual and textual modalities to extract entity relations and dynamically builds a knowledge graph, enabling robust multi-hop retrieval and generation that account for long-range dependencies. Experiments on the LongerVideos benchmark, featuring over 134 hours of diverse content, confirm that SceneRAG substantially outperforms prior baselines, achieving a win rate of up to 72.5 percent on generation tasks.
Foodfusion: A Novel Approach for Food Image Composition via Diffusion Models
Aug 26, 2024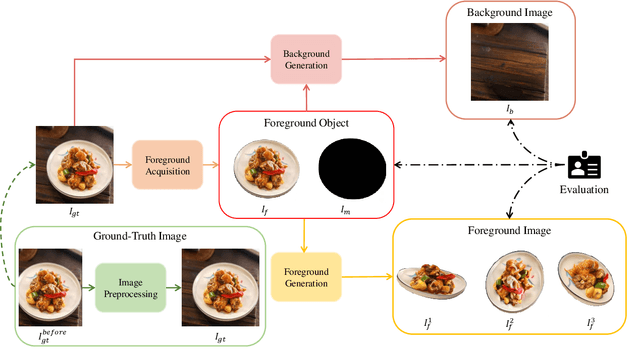
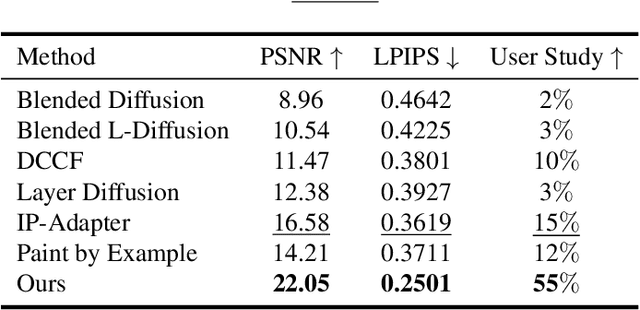

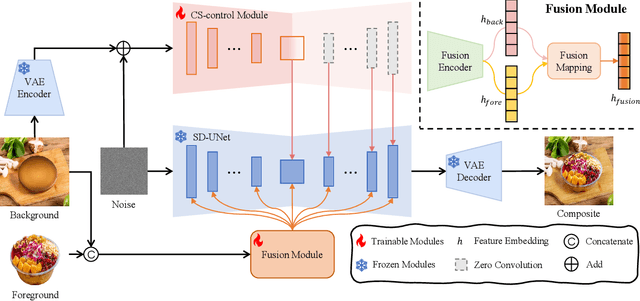
Abstract:Food image composition requires the use of existing dish images and background images to synthesize a natural new image, while diffusion models have made significant advancements in image generation, enabling the construction of end-to-end architectures that yield promising results. However, existing diffusion models face challenges in processing and fusing information from multiple images and lack access to high-quality publicly available datasets, which prevents the application of diffusion models in food image composition. In this paper, we introduce a large-scale, high-quality food image composite dataset, FC22k, which comprises 22,000 foreground, background, and ground truth ternary image pairs. Additionally, we propose a novel food image composition method, Foodfusion, which leverages the capabilities of the pre-trained diffusion models and incorporates a Fusion Module for processing and integrating foreground and background information. This fused information aligns the foreground features with the background structure by merging the global structural information at the cross-attention layer of the denoising UNet. To further enhance the content and structure of the background, we also integrate a Content-Structure Control Module. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and scalability of our proposed method.
DualVAE: Dual Disentangled Variational AutoEncoder for Recommendation
Jan 10, 2024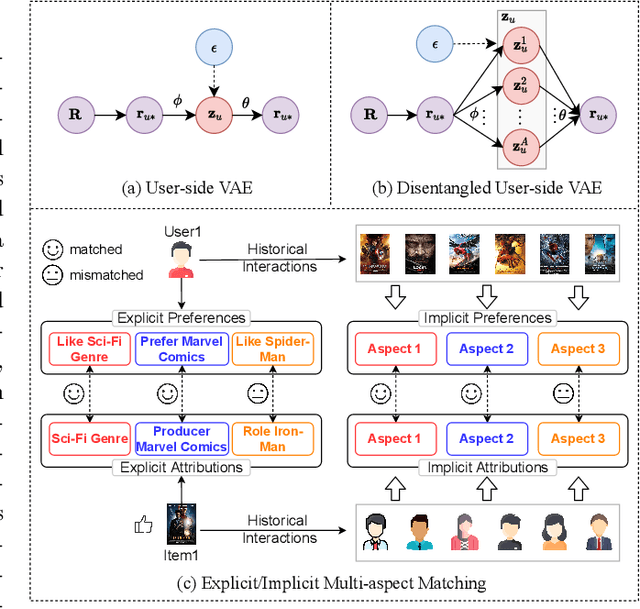

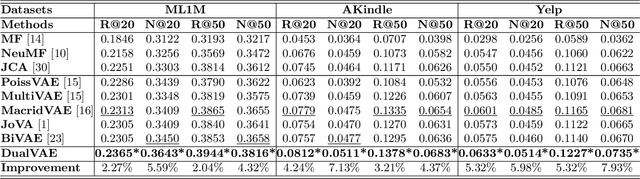
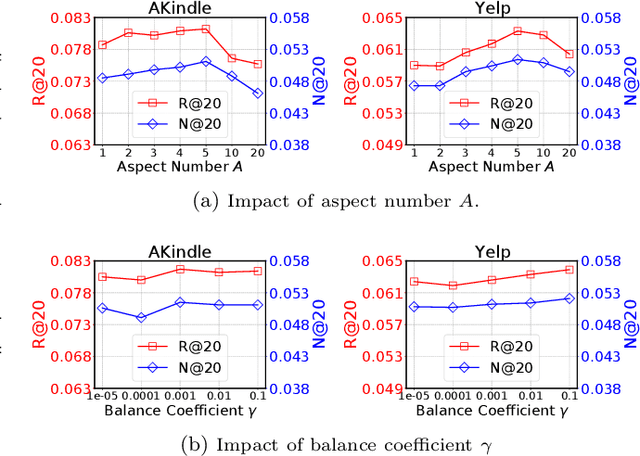
Abstract:Learning precise representations of users and items to fit observed interaction data is the fundamental task of collaborative filtering. Existing studies usually infer entangled representations to fit such interaction data, neglecting to model the diverse matching relationships between users and items behind their interactions, leading to limited performance and weak interpretability. To address this problem, we propose a Dual Disentangled Variational AutoEncoder (DualVAE) for collaborative recommendation, which combines disentangled representation learning with variational inference to facilitate the generation of implicit interaction data. Specifically, we first implement the disentangling concept by unifying an attention-aware dual disentanglement and disentangled variational autoencoder to infer the disentangled latent representations of users and items. Further, to encourage the correspondence and independence of disentangled representations of users and items, we design a neighborhood-enhanced representation constraint with a customized contrastive mechanism to improve the representation quality. Extensive experiments on three real-world benchmarks show that our proposed model significantly outperforms several recent state-of-the-art baselines. Further empirical experimental results also illustrate the interpretability of the disentangled representations learned by DualVAE.
LGMRec: Local and Global Graph Learning for Multimodal Recommendation
Dec 27, 2023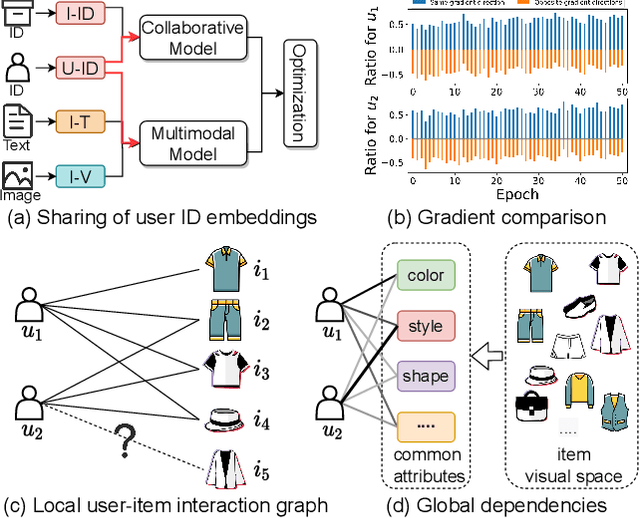
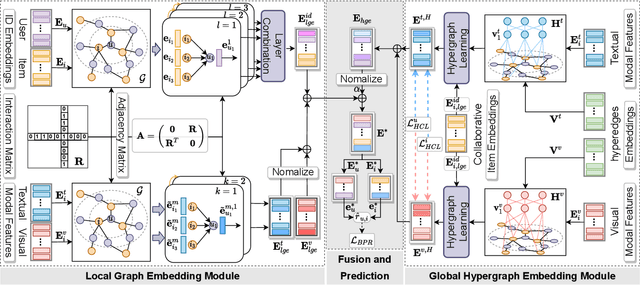
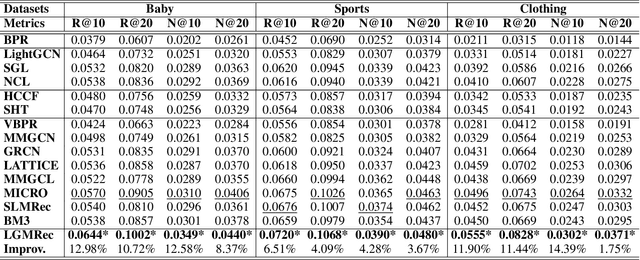
Abstract:The multimodal recommendation has gradually become the infrastructure of online media platforms, enabling them to provide personalized service to users through a joint modeling of user historical behaviors (e.g., purchases, clicks) and item various modalities (e.g., visual and textual). The majority of existing studies typically focus on utilizing modal features or modal-related graph structure to learn user local interests. Nevertheless, these approaches encounter two limitations: (1) Shared updates of user ID embeddings result in the consequential coupling between collaboration and multimodal signals; (2) Lack of exploration into robust global user interests to alleviate the sparse interaction problems faced by local interest modeling. To address these issues, we propose a novel Local and Global Graph Learning-guided Multimodal Recommender (LGMRec), which jointly models local and global user interests. Specifically, we present a local graph embedding module to independently learn collaborative-related and modality-related embeddings of users and items with local topological relations. Moreover, a global hypergraph embedding module is designed to capture global user and item embeddings by modeling insightful global dependency relations. The global embeddings acquired within the hypergraph embedding space can then be combined with two decoupled local embeddings to improve the accuracy and robustness of recommendations. Extensive experiments conducted on three benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of our LGMRec over various state-of-the-art recommendation baselines, showcasing its effectiveness in modeling both local and global user interests.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge