Shuxian Bi
Proactive Recommendation in Social Networks: Steering User Interest via Neighbor Influence
Sep 13, 2024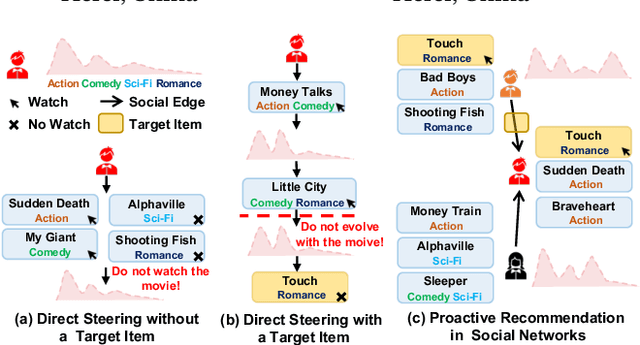
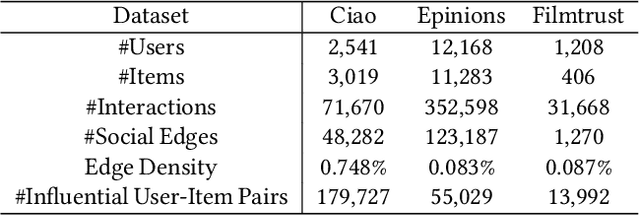
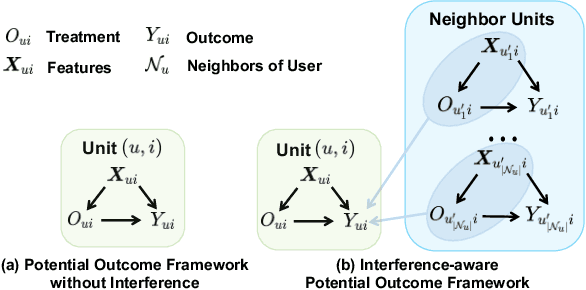
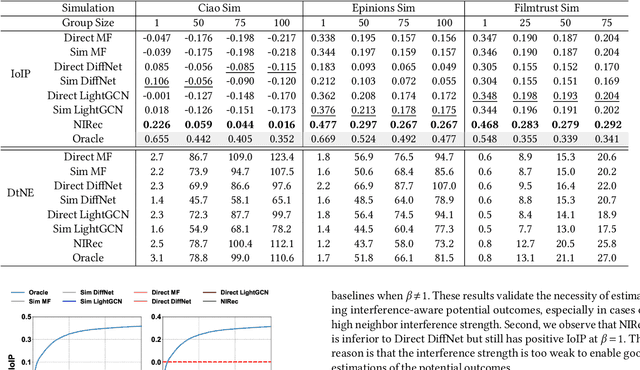
Abstract:Recommending items solely catering to users' historical interests narrows users' horizons. Recent works have considered steering target users beyond their historical interests by directly adjusting items exposed to them. However, the recommended items for direct steering might not align perfectly with users' interests evolution, detrimentally affecting target users' experience. To avoid this issue, we propose a new task named Proactive Recommendation in Social Networks (PRSN) that indirectly steers users' interest by utilizing the influence of social neighbors, i.e., indirect steering by adjusting the exposure of a target item to target users' neighbors. The key to PRSN lies in answering an interventional question: what would a target user's feedback be on a target item if the item is exposed to the user's different neighbors? To answer this question, we resort to causal inference and formalize PRSN as: (1) estimating the potential feedback of a user on an item, under the network interference by the item's exposure to the user's neighbors; and (2) adjusting the exposure of a target item to target users' neighbors to trade off steering performance and the damage to the neighbors' experience. To this end, we propose a Neighbor Interference Recommendation (NIRec) framework with two key modules: (1)an interference representation-based estimation module for modeling potential feedback; and (2) a post-learning-based optimization module for optimizing a target item's exposure to trade off steering performance and the neighbors' experience by greedy search. We conduct extensive semi-simulation experiments based on three real-world datasets, validating the steering effectiveness of NIRec.
Incorporate LLMs with Influential Recommender System
Sep 07, 2024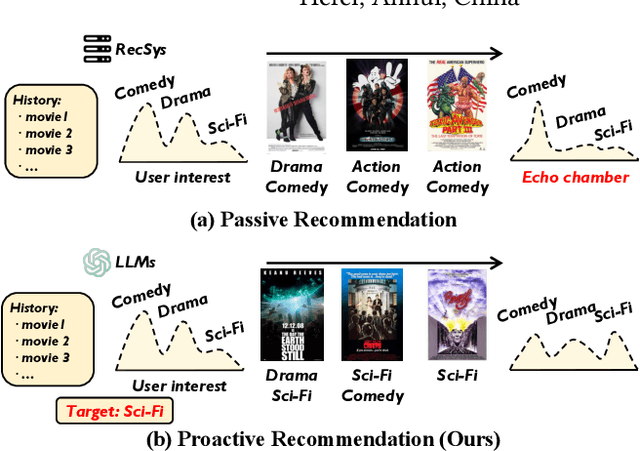
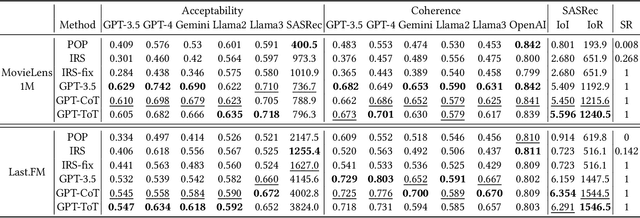
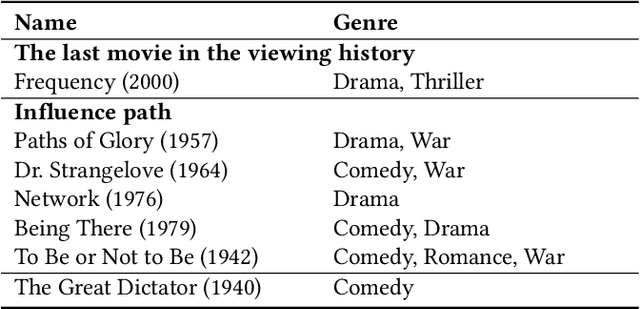
Abstract:Recommender systems have achieved increasing accuracy over the years. However, this precision often leads users to narrow their interests, resulting in issues such as limited diversity and the creation of echo chambers. Current research addresses these challenges through proactive recommender systems by recommending a sequence of items (called influence path) to guide user interest in the target item. However, existing methods struggle to construct a coherent influence path that builds up with items the user is likely to enjoy. In this paper, we leverage the Large Language Model's (LLMs) exceptional ability for path planning and instruction following, introducing a novel approach named LLM-based Influence Path Planning (LLM-IPP). Our approach maintains coherence between consecutive recommendations and enhances user acceptability of the recommended items. To evaluate LLM-IPP, we implement various user simulators and metrics to measure user acceptability and path coherence. Experimental results demonstrate that LLM-IPP significantly outperforms traditional proactive recommender systems. This study pioneers the integration of LLMs into proactive recommender systems, offering a reliable and user-engaging methodology for future recommendation technologies.
Proactive Recommendation with Iterative Preference Guidance
Mar 12, 2024Abstract:Recommender systems mainly tailor personalized recommendations according to user interests learned from user feedback. However, such recommender systems passively cater to user interests and even reinforce existing interests in the feedback loop, leading to problems like filter bubbles and opinion polarization. To counteract this, proactive recommendation actively steers users towards developing new interests in a target item or topic by strategically modulating recommendation sequences. Existing work for proactive recommendation faces significant hurdles: 1) overlooking the user feedback in the guidance process; 2) lacking explicit modeling of the guiding objective; and 3) insufficient flexibility for integration into existing industrial recommender systems. To address these issues, we introduce an Iterative Preference Guidance (IPG) framework. IPG performs proactive recommendation in a flexible post-processing manner by ranking items according to their IPG scores that consider both interaction probability and guiding value. These scores are explicitly estimated with iteratively updated user representation that considers the most recent user interactions. Extensive experiments validate that IPG can effectively guide user interests toward target interests with a reasonable trade-off in recommender accuracy. The code is available at https://github.com/GabyUSTC/IPG-Rec.
On the Equivalence of Decoupled Graph Convolution Network and Label Propagation
Oct 23, 2020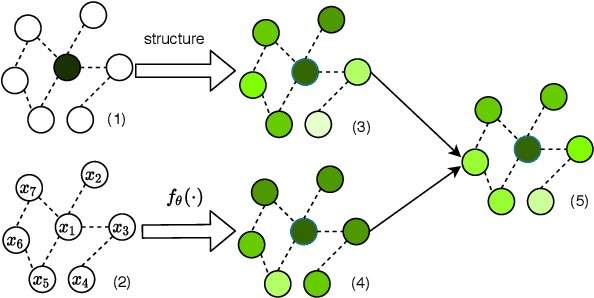
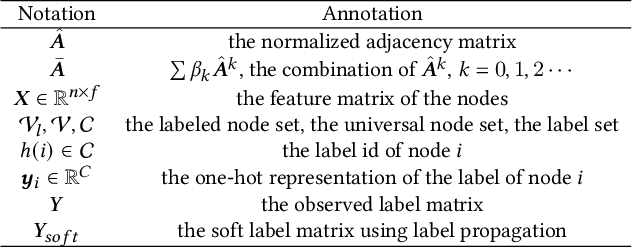
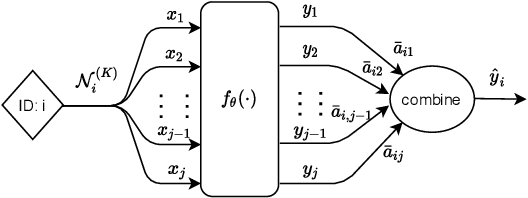
Abstract:The original design of Graph Convolution Network (GCN) couples feature transformation and neighborhood aggregation for node representation learning. Recently, some work shows that coupling is inferior to decoupling, which supports deep graph propagation and has become the latest paradigm of GCN (e.g., APPNP and SGCN). Despite effectiveness, the working mechanisms of the decoupled GCN are not well understood. In this paper, we explore the decoupled GCN for semi-supervised node classification from a novel and fundamental perspective -- label propagation. We conduct thorough theoretical analyses, proving that the decoupled GCN is essentially the same as the two-step label propagation: first, propagating the known labels along the graph to generate pseudo-labels for the unlabeled nodes, and second, training normal neural network classifiers on the augmented pseudo-labeled data. More interestingly, we reveal the effectiveness of decoupled GCN: going beyond the conventional label propagation, it could automatically assign structure- and model- aware weights to the pseudo-label data. This explains why the decoupled GCN is relatively robust to the structure noise and over-smoothing, but sensitive to the label noise and model initialization. Based on this insight, we propose a new label propagation method named Propagation then Training Adaptively (PTA), which overcomes the flaws of the decoupled GCN with a dynamic and adaptive weighting strategy. Our PTA is simple yet more effective and robust than decoupled GCN. We empirically validate our findings on four benchmark datasets, demonstrating the advantages of our method.
Data Augmentation View on Graph Convolutional Network and the Proposal of Monte Carlo Graph Learning
Jun 23, 2020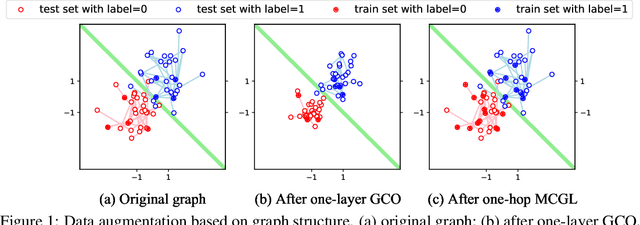
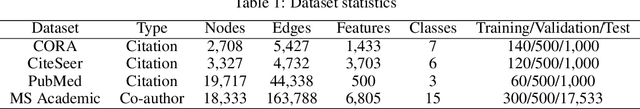
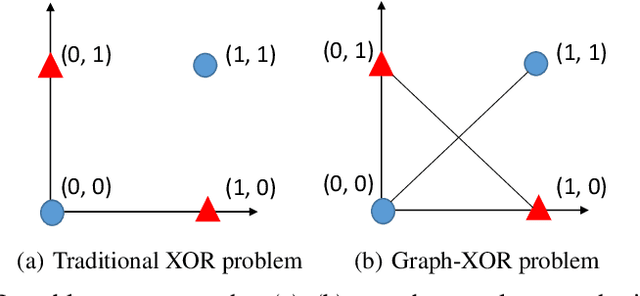
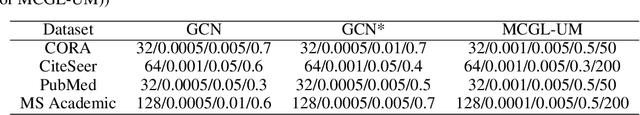
Abstract:Today, there are two major understandings for graph convolutional networks, i.e., in the spectral and spatial domain. But both lack transparency. In this work, we introduce a new understanding for it -- data augmentation, which is more transparent than the previous understandings. Inspired by it, we propose a new graph learning paradigm -- Monte Carlo Graph Learning (MCGL). The core idea of MCGL contains: (1) Data augmentation: propagate the labels of the training set through the graph structure and expand the training set; (2) Model training: use the expanded training set to train traditional classifiers. We use synthetic datasets to compare the strengths of MCGL and graph convolutional operation on clean graphs. In addition, we show that MCGL's tolerance to graph structure noise is weaker than GCN on noisy graphs (four real-world datasets). Moreover, inspired by MCGL, we re-analyze the reasons why the performance of GCN becomes worse when deepened too much: rather than the mainstream view of over-smoothing, we argue that the main reason is the graph structure noise, and experimentally verify our view. The code is available at https://github.com/DongHande/MCGL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge