Shuochen Liu
VIGIL: Defending LLM Agents Against Tool Stream Injection via Verify-Before-Commit
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:LLM agents operating in open environments face escalating risks from indirect prompt injection, particularly within the tool stream where manipulated metadata and runtime feedback hijack execution flow. Existing defenses encounter a critical dilemma as advanced models prioritize injected rules due to strict alignment while static protection mechanisms sever the feedback loop required for adaptive reasoning. To reconcile this conflict, we propose \textbf{VIGIL}, a framework that shifts the paradigm from restrictive isolation to a verify-before-commit protocol. By facilitating speculative hypothesis generation and enforcing safety through intent-grounded verification, \textbf{VIGIL} preserves reasoning flexibility while ensuring robust control. We further introduce \textbf{SIREN}, a benchmark comprising 959 tool stream injection cases designed to simulate pervasive threats characterized by dynamic dependencies. Extensive experiments demonstrate that \textbf{VIGIL} outperforms state-of-the-art dynamic defenses by reducing the attack success rate by over 22\% while more than doubling the utility under attack compared to static baselines, thereby achieving an optimal balance between security and utility. Code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/VIGIL-378B/.
Look As You Think: Unifying Reasoning and Visual Evidence Attribution for Verifiable Document RAG via Reinforcement Learning
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:Aiming to identify precise evidence sources from visual documents, visual evidence attribution for visual document retrieval-augmented generation (VD-RAG) ensures reliable and verifiable predictions from vision-language models (VLMs) in multimodal question answering. Most existing methods adopt end-to-end training to facilitate intuitive answer verification. However, they lack fine-grained supervision and progressive traceability throughout the reasoning process. In this paper, we introduce the Chain-of-Evidence (CoE) paradigm for VD-RAG. CoE unifies Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning and visual evidence attribution by grounding reference elements in reasoning steps to specific regions with bounding boxes and page indexes. To enable VLMs to generate such evidence-grounded reasoning, we propose Look As You Think (LAT), a reinforcement learning framework that trains models to produce verifiable reasoning paths with consistent attribution. During training, LAT evaluates the attribution consistency of each evidence region and provides rewards only when the CoE trajectory yields correct answers, encouraging process-level self-verification. Experiments on vanilla Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct with Paper- and Wiki-VISA benchmarks show that LAT consistently improves the vanilla model in both single- and multi-image settings, yielding average gains of 8.23% in soft exact match (EM) and 47.0% in IoU@0.5. Meanwhile, LAT not only outperforms the supervised fine-tuning baseline, which is trained to directly produce answers with attribution, but also exhibits stronger generalization across domains.
TeaRAG: A Token-Efficient Agentic Retrieval-Augmented Generation Framework
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) utilizes external knowledge to augment Large Language Models' (LLMs) reliability. For flexibility, agentic RAG employs autonomous, multi-round retrieval and reasoning to resolve queries. Although recent agentic RAG has improved via reinforcement learning, they often incur substantial token overhead from search and reasoning processes. This trade-off prioritizes accuracy over efficiency. To address this issue, this work proposes TeaRAG, a token-efficient agentic RAG framework capable of compressing both retrieval content and reasoning steps. 1) First, the retrieved content is compressed by augmenting chunk-based semantic retrieval with a graph retrieval using concise triplets. A knowledge association graph is then built from semantic similarity and co-occurrence. Finally, Personalized PageRank is leveraged to highlight key knowledge within this graph, reducing the number of tokens per retrieval. 2) Besides, to reduce reasoning steps, Iterative Process-aware Direct Preference Optimization (IP-DPO) is proposed. Specifically, our reward function evaluates the knowledge sufficiency by a knowledge matching mechanism, while penalizing excessive reasoning steps. This design can produce high-quality preference-pair datasets, supporting iterative DPO to improve reasoning conciseness. Across six datasets, TeaRAG improves the average Exact Match by 4% and 2% while reducing output tokens by 61% and 59% on Llama3-8B-Instruct and Qwen2.5-14B-Instruct, respectively. Code is available at https://github.com/Applied-Machine-Learning-Lab/TeaRAG.
Xiangqi-R1: Enhancing Spatial Strategic Reasoning in LLMs for Chinese Chess via Reinforcement Learning
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Game playing has long served as a fundamental benchmark for evaluating Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities in general reasoning, their effectiveness in spatial strategic reasoning, which is critical for complex and fully observable board games, remains insufficiently explored. In this work, we adopt Chinese Chess (Xiangqi) as a challenging and rich testbed due to its intricate rules and spatial complexity. To advance LLMs' strategic competence in such environments, we propose a training framework tailored to Xiangqi, built upon a large-scale dataset of five million board-move pairs enhanced with expert annotations and engine evaluations. Building on this foundation, we introduce Xiangqi-R1, a 7B-parameter model trained in multi-stage manner: (1) fine-tuning for legal move prediction to capture basic spatial rules, (2) incorporating strategic annotations to improve decision-making, and (3) applying reinforcement learning via Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) with multi-dimensional reward signals to enhance reasoning stability. Our Experimental results indicate that, despite their size and power, general-purpose LLMs struggle to achieve satisfactory performance in these tasks. Compared to general-purpose LLMs, Xiangqi-R1 greatly advances with an 18% rise in move legality and a 22% boost in analysis accuracy. Our results point to a promising path for creating general strategic intelligence in spatially complex areas.
Prompt Transfer for Dual-Aspect Cross Domain Cognitive Diagnosis
Dec 06, 2024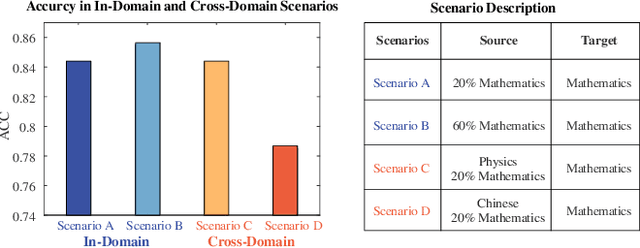
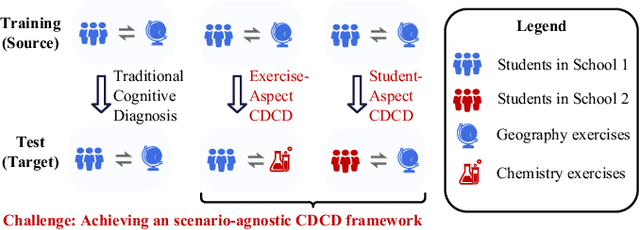
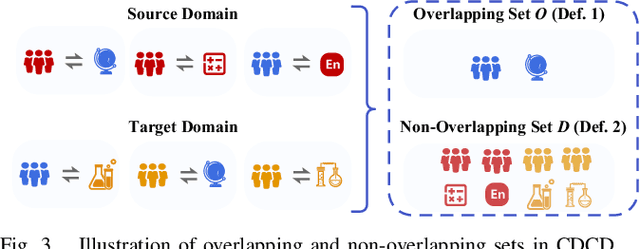
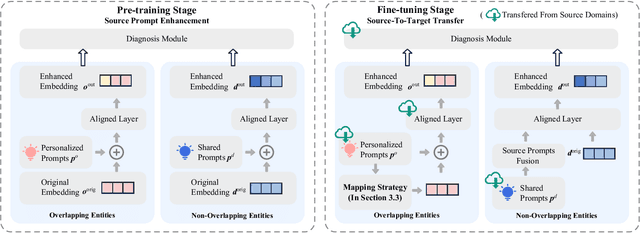
Abstract:Cognitive Diagnosis (CD) aims to evaluate students' cognitive states based on their interaction data, enabling downstream applications such as exercise recommendation and personalized learning guidance. However, existing methods often struggle with accuracy drops in cross-domain cognitive diagnosis (CDCD), a practical yet challenging task. While some efforts have explored exercise-aspect CDCD, such as crosssubject scenarios, they fail to address the broader dual-aspect nature of CDCD, encompassing both student- and exerciseaspect variations. This diversity creates significant challenges in developing a scenario-agnostic framework. To address these gaps, we propose PromptCD, a simple yet effective framework that leverages soft prompt transfer for cognitive diagnosis. PromptCD is designed to adapt seamlessly across diverse CDCD scenarios, introducing PromptCD-S for student-aspect CDCD and PromptCD-E for exercise-aspect CDCD. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate the robustness and effectiveness of PromptCD, consistently achieving superior performance across various CDCD scenarios. Our work offers a unified and generalizable approach to CDCD, advancing both theoretical and practical understanding in this critical domain. The implementation of our framework is publicly available at https://github.com/Publisher-PromptCD/PromptCD.
FastMem: Fast Memorization of Prompt Improves Context Awareness of Large Language Models
Jun 23, 2024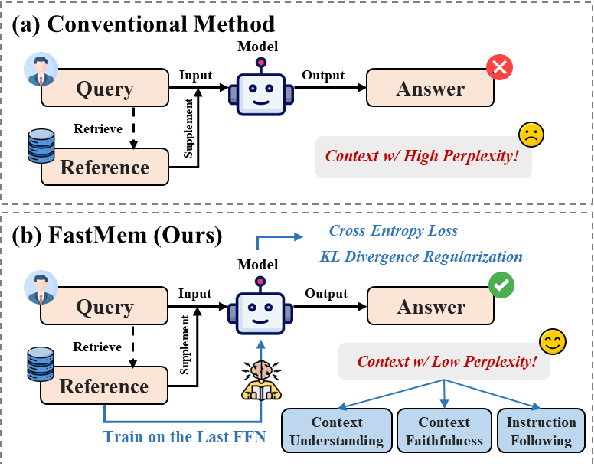
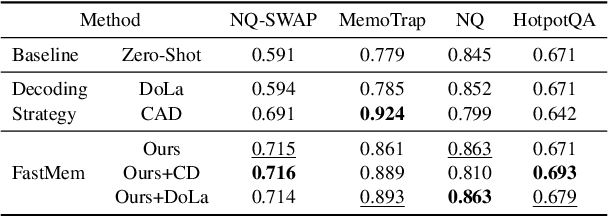
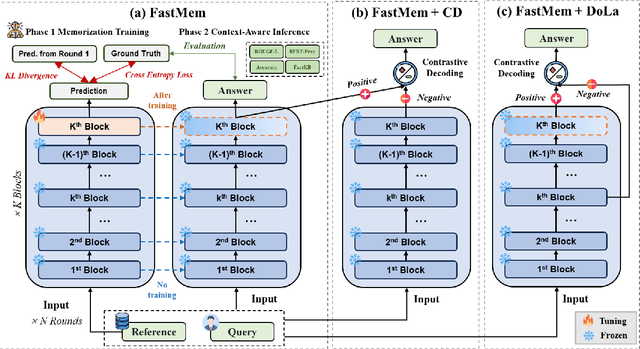
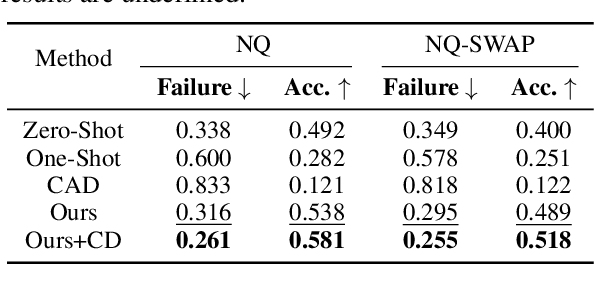
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) excel in generating coherent text, but they often struggle with context awareness, leading to inaccuracies in tasks requiring faithful adherence to provided information. We introduce FastMem, a novel method designed to enhance instruction fine-tuned LLMs' context awareness through fast memorization of the prompt. FastMem maximizes the likelihood of the prompt before inference by fine-tuning only the last Feed-Forward Network (FFN) module. This targeted approach ensures efficient optimization without overfitting, significantly improving the model's ability to comprehend and accurately follow the context. Our experiments demonstrate substantial gains in reading comprehension, text summarization and adherence to output structures. For instance, FastMem improves the accuracy of Llama 3-8B-Inst on the NQ-SWAP dataset from 59.1% to 71.6%, and reduces the output structure failure rate of Qwen 1.5-4B-Chat from 34.9% to 25.5%. Extensive experimental results highlight FastMem's potential to offer a robust solution to enhance the reliability and accuracy of LLMs in various applications. Our code is available at: https://github.com/IAAR-Shanghai/FastMem
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge