Shengwei Ji
Prompt Transfer for Dual-Aspect Cross Domain Cognitive Diagnosis
Dec 06, 2024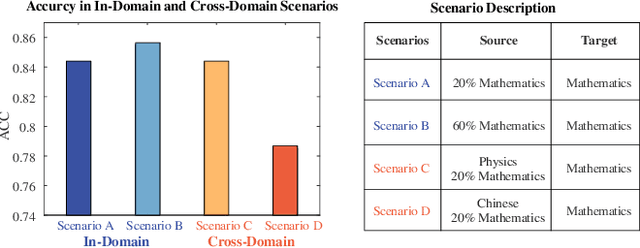
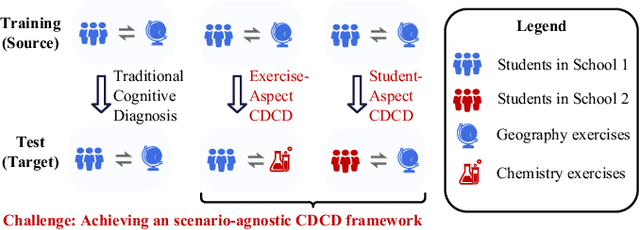
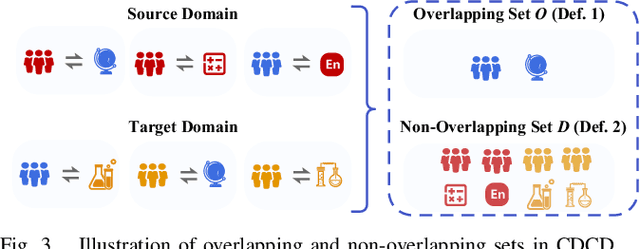
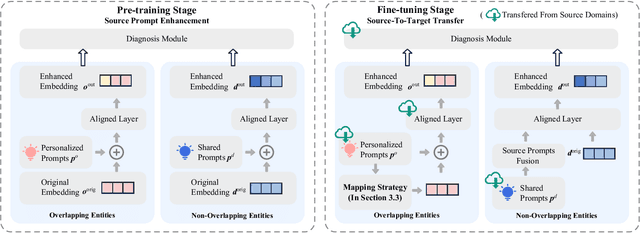
Abstract:Cognitive Diagnosis (CD) aims to evaluate students' cognitive states based on their interaction data, enabling downstream applications such as exercise recommendation and personalized learning guidance. However, existing methods often struggle with accuracy drops in cross-domain cognitive diagnosis (CDCD), a practical yet challenging task. While some efforts have explored exercise-aspect CDCD, such as crosssubject scenarios, they fail to address the broader dual-aspect nature of CDCD, encompassing both student- and exerciseaspect variations. This diversity creates significant challenges in developing a scenario-agnostic framework. To address these gaps, we propose PromptCD, a simple yet effective framework that leverages soft prompt transfer for cognitive diagnosis. PromptCD is designed to adapt seamlessly across diverse CDCD scenarios, introducing PromptCD-S for student-aspect CDCD and PromptCD-E for exercise-aspect CDCD. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate the robustness and effectiveness of PromptCD, consistently achieving superior performance across various CDCD scenarios. Our work offers a unified and generalizable approach to CDCD, advancing both theoretical and practical understanding in this critical domain. The implementation of our framework is publicly available at https://github.com/Publisher-PromptCD/PromptCD.
PromptGCN: Bridging Subgraph Gaps in Lightweight GCNs
Oct 14, 2024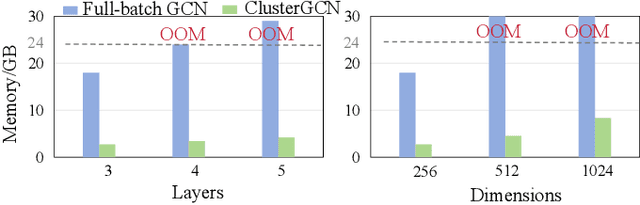
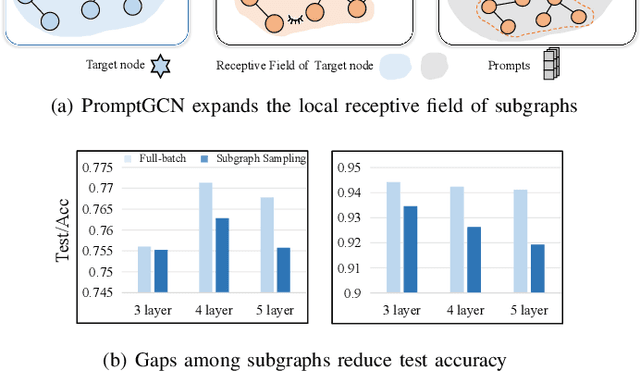
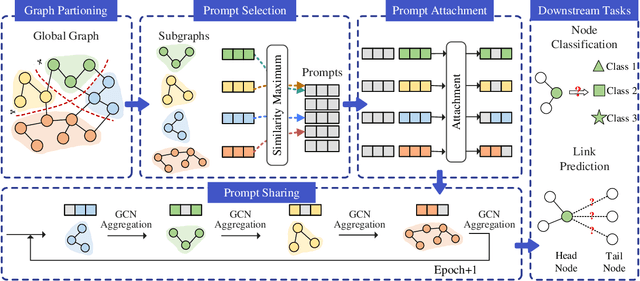
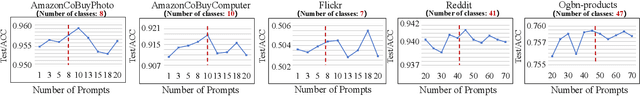
Abstract:Graph Convolutional Networks (GCNs) are widely used in graph-based applications, such as social networks and recommendation systems. Nevertheless, large-scale graphs or deep aggregation layers in full-batch GCNs consume significant GPU memory, causing out of memory (OOM) errors on mainstream GPUs (e.g., 29GB memory consumption on the Ogbnproducts graph with 5 layers). The subgraph sampling methods reduce memory consumption to achieve lightweight GCNs by partitioning the graph into multiple subgraphs and sequentially training GCNs on each subgraph. However, these methods yield gaps among subgraphs, i.e., GCNs can only be trained based on subgraphs instead of global graph information, which reduces the accuracy of GCNs. In this paper, we propose PromptGCN, a novel prompt-based lightweight GCN model to bridge the gaps among subgraphs. First, the learnable prompt embeddings are designed to obtain global information. Then, the prompts are attached into each subgraph to transfer the global information among subgraphs. Extensive experimental results on seven largescale graphs demonstrate that PromptGCN exhibits superior performance compared to baselines. Notably, PromptGCN improves the accuracy of subgraph sampling methods by up to 5.48% on the Flickr dataset. Overall, PromptGCN can be easily combined with any subgraph sampling method to obtain a lightweight GCN model with higher accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge