Shotaro Sano
Preferred Elements, Inc.
PLaMo 2 Technical Report
Sep 05, 2025Abstract:In this report, we introduce PLaMo 2, a series of Japanese-focused large language models featuring a hybrid Samba-based architecture that transitions to full attention via continual pre-training to support 32K token contexts. Training leverages extensive synthetic corpora to overcome data scarcity, while computational efficiency is achieved through weight reuse and structured pruning. This efficient pruning methodology produces an 8B model that achieves performance comparable to our previous 100B model. Post-training further refines the models using a pipeline of supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and direct preference optimization (DPO), enhanced by synthetic Japanese instruction data and model merging techniques. Optimized for inference using vLLM and quantization with minimal accuracy loss, the PLaMo 2 models achieve state-of-the-art results on Japanese benchmarks, outperforming similarly-sized open models in instruction-following, language fluency, and Japanese-specific knowledge.
PLaMo-100B: A Ground-Up Language Model Designed for Japanese Proficiency
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:We introduce PLaMo-100B, a large-scale language model designed for Japanese proficiency. The model was trained from scratch using 2 trillion tokens, with architecture such as QK Normalization and Z-Loss to ensure training stability during the training process. Post-training techniques, including Supervised Fine-Tuning and Direct Preference Optimization, were applied to refine the model's performance. Benchmark evaluations suggest that PLaMo-100B performs well, particularly in Japanese-specific tasks, achieving results that are competitive with frontier models like GPT-4.
Team PFDet's Methods for Open Images Challenge 2019
Oct 25, 2019

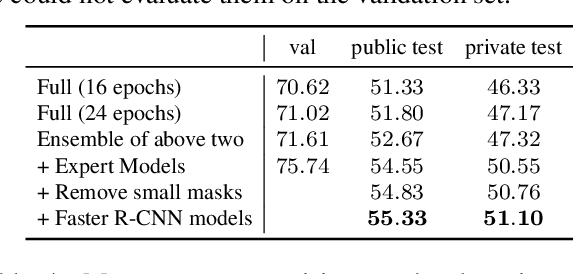

Abstract:We present the instance segmentation and the object detection method used by team PFDet for Open Images Challenge 2019. We tackle a massive dataset size, huge class imbalance and federated annotations. Using this method, the team PFDet achieved 3rd and 4th place in the instance segmentation and the object detection track, respectively.
Optuna: A Next-generation Hyperparameter Optimization Framework
Jul 25, 2019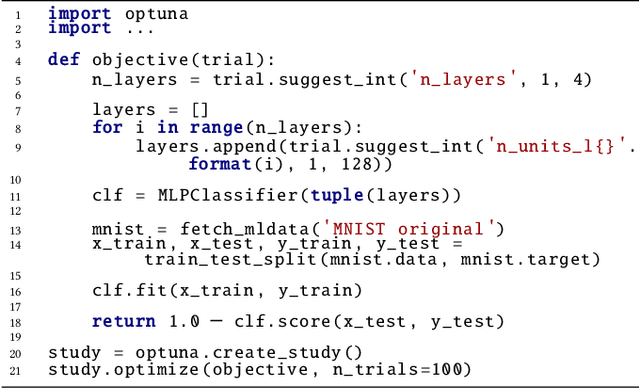
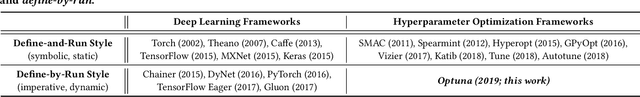

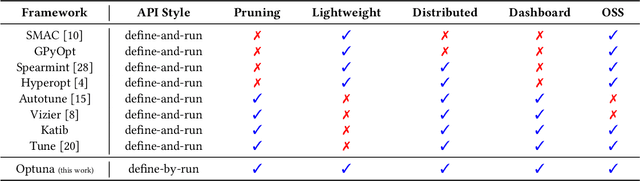
Abstract:The purpose of this study is to introduce new design-criteria for next-generation hyperparameter optimization software. The criteria we propose include (1) define-by-run API that allows users to construct the parameter search space dynamically, (2) efficient implementation of both searching and pruning strategies, and (3) easy-to-setup, versatile architecture that can be deployed for various purposes, ranging from scalable distributed computing to light-weight experiment conducted via interactive interface. In order to prove our point, we will introduce Optuna, an optimization software which is a culmination of our effort in the development of a next generation optimization software. As an optimization software designed with define-by-run principle, Optuna is particularly the first of its kind. We will present the design-techniques that became necessary in the development of the software that meets the above criteria, and demonstrate the power of our new design through experimental results and real world applications. Our software is available under the MIT license (https://github.com/pfnet/optuna/).
Sampling Techniques for Large-Scale Object Detection from Sparsely Annotated Objects
Nov 27, 2018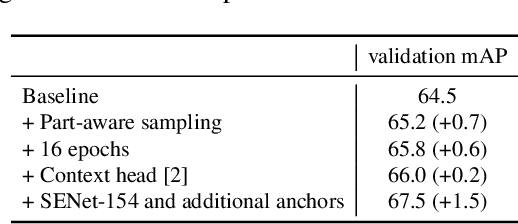

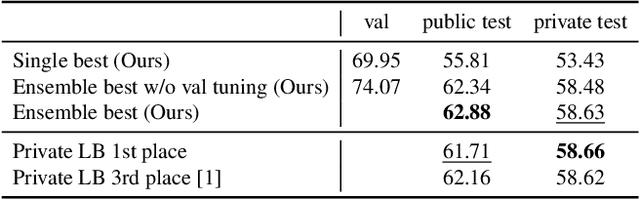
Abstract:Efficient and reliable methods for training of object detectors are in higher demand than ever, and more and more data relevant to the field is becoming available. However, large datasets like Open Images Dataset v4 (OID) are sparsely annotated, and some measure must be taken in order to ensure the training of a reliable detector. In order to take the incompleteness of these datasets into account, one possibility is to use pretrained models to detect the presence of the unverified objects. However, the performance of such a strategy depends largely on the power of the pretrained model. In this study, we propose part-aware sampling, a method that uses human intuition for the hierarchical relation between objects. In terse terms, our method works by making assumptions like "a bounding box for a car should contain a bounding box for a tire". We demonstrate the power of our method on OID and compare the performance against a method based on a pretrained model. Our method also won the first and second place on the public and private test sets of the Google AI Open Images Competition 2018.
PFDet: 2nd Place Solution to Open Images Challenge 2018 Object Detection Track
Sep 04, 2018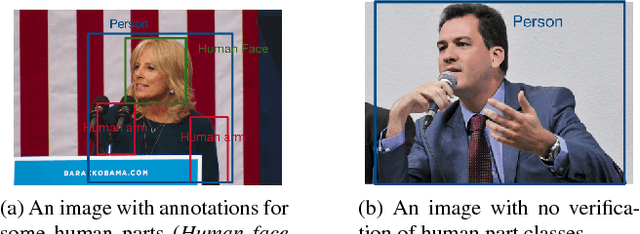
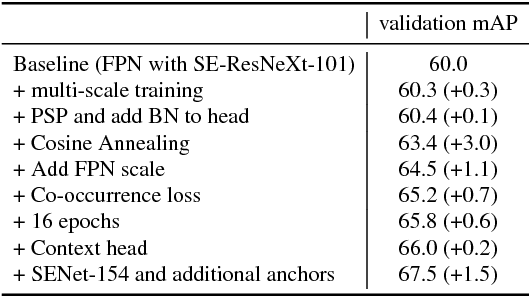
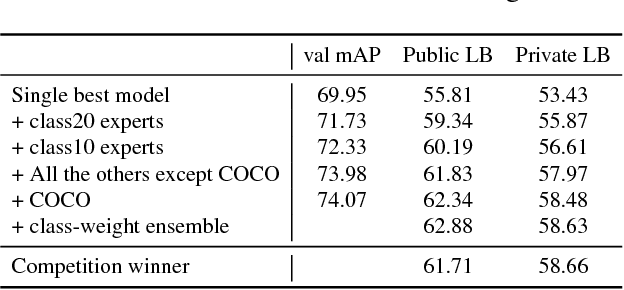
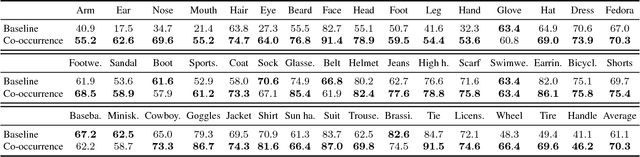
Abstract:We present a large-scale object detection system by team PFDet. Our system enables training with huge datasets using 512 GPUs, handles sparsely verified classes, and massive class imbalance. Using our method, we achieved 2nd place in the Google AI Open Images Object Detection Track 2018 on Kaggle.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge