Toshihiko Yanase
Preferred Elements, Inc.
A Prefixed Patch Time Series Transformer for Two-Point Boundary Value Problems in Three-Body Problems
Apr 02, 2025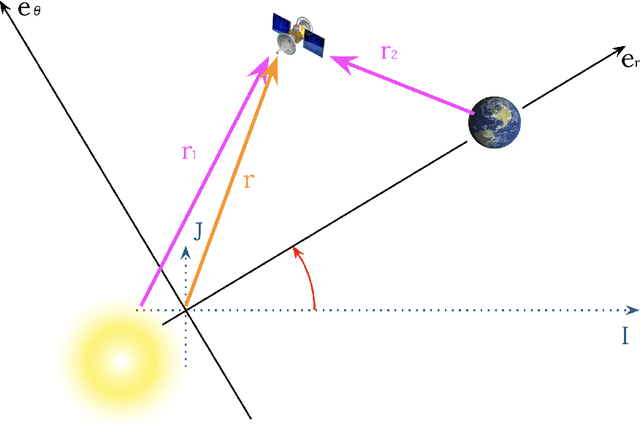
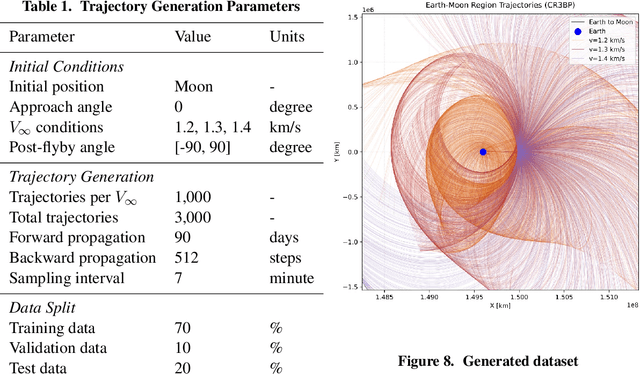
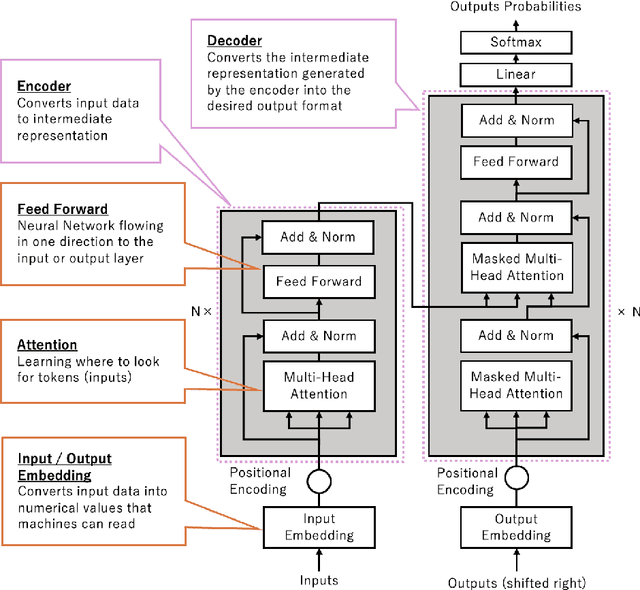
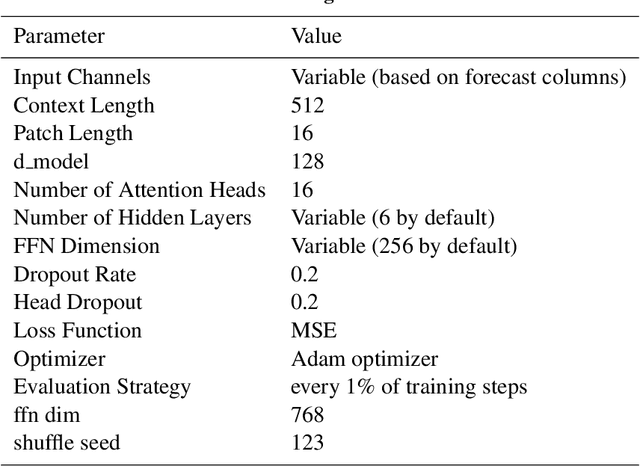
Abstract:Two-point boundary value problems for cislunar trajectories present significant challenges in circler restricted three body problem, making traditional analytical methods like Lambert's problem inapplicable. This study proposes a novel approach using a prefixed patch time series Transformer model that automates the solution of two-point boundary value problems from lunar flyby to arbitrary terminal conditions. Using prefix tokens of terminal conditions in our deep generative model enables solving boundary value problems in three-body dynamics. The training dataset consists of trajectories obtained through forward propagation rather than solving boundary value problems directly. The model demonstrates potential practical utility for preliminary trajectory design in cislunar mission scenarios.
PLaMo-100B: A Ground-Up Language Model Designed for Japanese Proficiency
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:We introduce PLaMo-100B, a large-scale language model designed for Japanese proficiency. The model was trained from scratch using 2 trillion tokens, with architecture such as QK Normalization and Z-Loss to ensure training stability during the training process. Post-training techniques, including Supervised Fine-Tuning and Direct Preference Optimization, were applied to refine the model's performance. Benchmark evaluations suggest that PLaMo-100B performs well, particularly in Japanese-specific tasks, achieving results that are competitive with frontier models like GPT-4.
Optuna: A Next-generation Hyperparameter Optimization Framework
Jul 25, 2019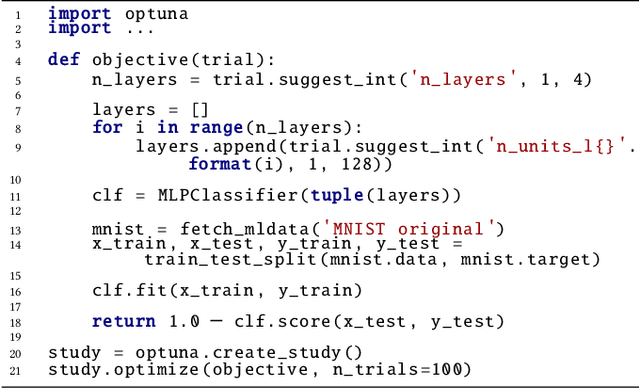
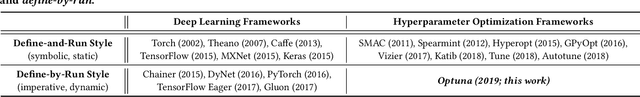

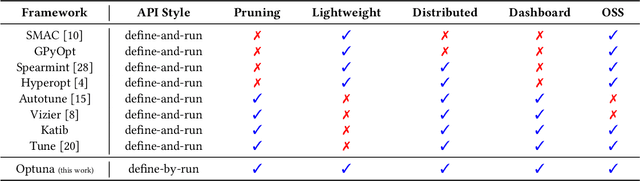
Abstract:The purpose of this study is to introduce new design-criteria for next-generation hyperparameter optimization software. The criteria we propose include (1) define-by-run API that allows users to construct the parameter search space dynamically, (2) efficient implementation of both searching and pruning strategies, and (3) easy-to-setup, versatile architecture that can be deployed for various purposes, ranging from scalable distributed computing to light-weight experiment conducted via interactive interface. In order to prove our point, we will introduce Optuna, an optimization software which is a culmination of our effort in the development of a next generation optimization software. As an optimization software designed with define-by-run principle, Optuna is particularly the first of its kind. We will present the design-techniques that became necessary in the development of the software that meets the above criteria, and demonstrate the power of our new design through experimental results and real world applications. Our software is available under the MIT license (https://github.com/pfnet/optuna/).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge