Shixian Luo
PEVLM: Parallel Encoding for Vision-Language Models
Jun 24, 2025



Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated strong performance in video-language tasks, yet their application to long video understanding remains constrained by the quadratic complexity of standard attention mechanisms. In this paper, we propose \textbf{PEVLM}, a parallel encoding strategy specifically designed to improve the prefill efficiency of VLMs without requiring model finetuning. PEVLM partitions the input into block-wise segments with a shared sink, preserves full-attention positional embeddings, and aligns attention weights to mimic full-attention distributions. This design reduces attention computation from $O((T \times N)^2)$ to $O(T \times N)$ while maintaining high accuracy. Extensive experiments on the LongVideoBench benchmark show that PEVLM achieves up to 8.37\% accuracy improvement over existing inference-efficient methods and delivers up to 7.47x speedup in attention computation and 40\% reduction in end-to-end latency. Under strict latency constraints, PEVLM significantly outperforms baselines, raising accuracy from 23.26\% to 61.03\%. These results highlight PEVLM's effectiveness for low-latency, long-context video understanding, making it well-suited for real-world applications such as autonomous driving.
GeoGramBench: Benchmarking the Geometric Program Reasoning in Modern LLMs
May 23, 2025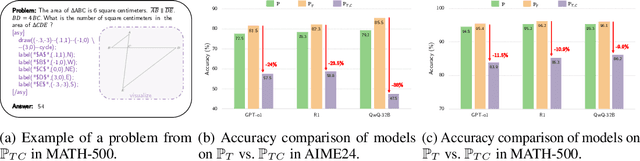
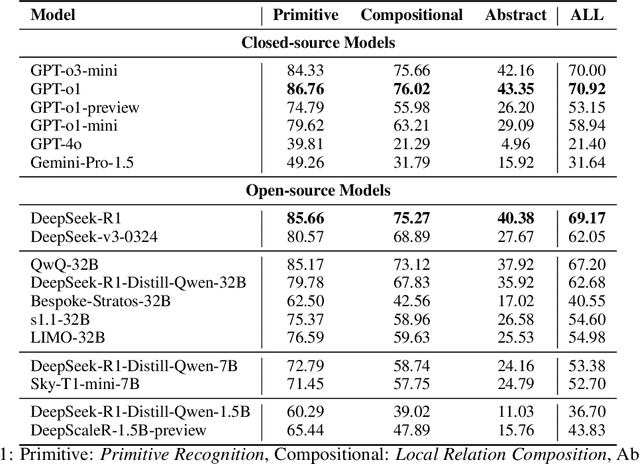
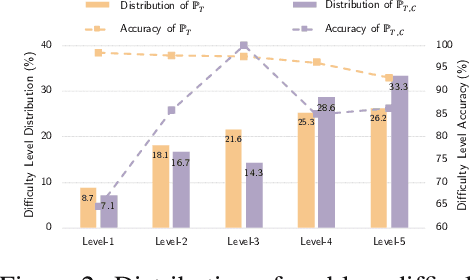
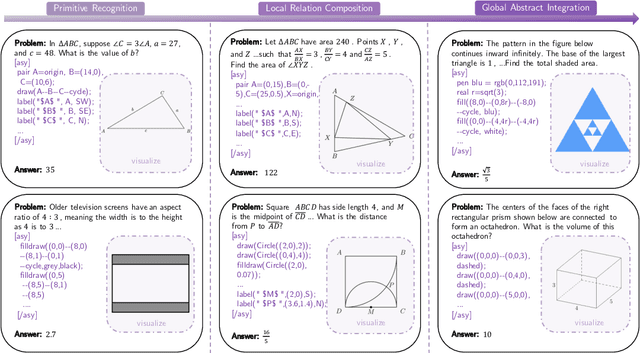
Abstract:Geometric spatial reasoning forms the foundation of many applications in artificial intelligence, yet the ability of large language models (LLMs) to operate over geometric spatial information expressed in procedural code remains underexplored. In this paper, we address this gap by formalizing the Program-to-Geometry task, which challenges models to translate programmatic drawing code into accurate and abstract geometric reasoning. To evaluate this capability, we present GeoGramBench, a benchmark of 500 carefully refined problems organized by a tailored three-level taxonomy that considers geometric complexity rather than traditional mathematical reasoning complexity. Our comprehensive evaluation of 17 frontier LLMs reveals consistent and pronounced deficiencies: even the most advanced models achieve less than 50% accuracy at the highest abstraction level. These results highlight the unique challenges posed by program-driven spatial reasoning and establish GeoGramBench as a valuable resource for advancing research in symbolic-to-spatial geometric reasoning. Project page: https://github.com/LiAuto-DSR/GeoGramBench.
Cognitive Memory in Large Language Models
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:This paper examines memory mechanisms in Large Language Models (LLMs), emphasizing their importance for context-rich responses, reduced hallucinations, and improved efficiency. It categorizes memory into sensory, short-term, and long-term, with sensory memory corresponding to input prompts, short-term memory processing immediate context, and long-term memory implemented via external databases or structures. The text-based memory section covers acquisition (selection and summarization), management (updating, accessing, storing, and resolving conflicts), and utilization (full-text search, SQL queries, semantic search). The KV cache-based memory section discusses selection methods (regularity-based summarization, score-based approaches, special token embeddings) and compression techniques (low-rank compression, KV merging, multimodal compression), along with management strategies like offloading and shared attention mechanisms. Parameter-based memory methods (LoRA, TTT, MoE) transform memories into model parameters to enhance efficiency, while hidden-state-based memory approaches (chunk mechanisms, recurrent transformers, Mamba model) improve long-text processing by combining RNN hidden states with current methods. Overall, the paper offers a comprehensive analysis of LLM memory mechanisms, highlighting their significance and future research directions.
Understanding Chinese Video and Language via Contrastive Multimodal Pre-Training
Apr 19, 2021



Abstract:The pre-trained neural models have recently achieved impressive performances in understanding multimodal content. However, it is still very challenging to pre-train neural models for video and language understanding, especially for Chinese video-language data, due to the following reasons. Firstly, existing video-language pre-training algorithms mainly focus on the co-occurrence of words and video frames, but ignore other valuable semantic and structure information of video-language content, e.g., sequential order and spatiotemporal relationships. Secondly, there exist conflicts between video sentence alignment and other proxy tasks. Thirdly, there is a lack of large-scale and high-quality Chinese video-language datasets (e.g., including 10 million unique videos), which are the fundamental success conditions for pre-training techniques. In this work, we propose a novel video-language understanding framework named VICTOR, which stands for VIdeo-language understanding via Contrastive mulTimOdal pRe-training. Besides general proxy tasks such as masked language modeling, VICTOR constructs several novel proxy tasks under the contrastive learning paradigm, making the model be more robust and able to capture more complex multimodal semantic and structural relationships from different perspectives. VICTOR is trained on a large-scale Chinese video-language dataset, including over 10 million complete videos with corresponding high-quality textual descriptions. We apply the pre-trained VICTOR model to a series of downstream applications and demonstrate its superior performances, comparing against the state-of-the-art pre-training methods such as VideoBERT and UniVL. The codes and trained checkpoints will be publicly available to nourish further developments of the research community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge