Shengjie Chen
NTIRE 2022 Challenge on Super-Resolution and Quality Enhancement of Compressed Video: Dataset, Methods and Results
Apr 25, 2022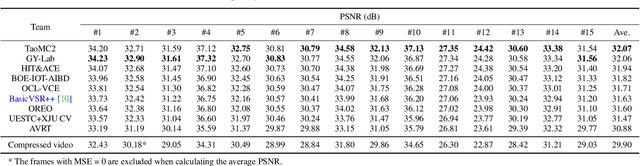
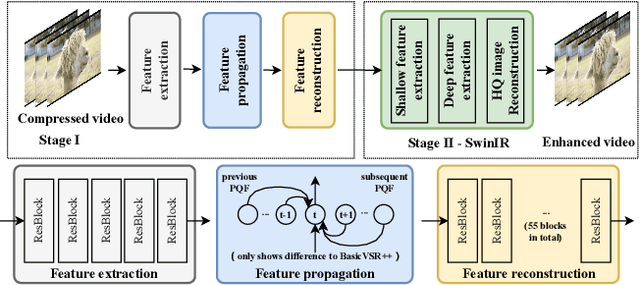
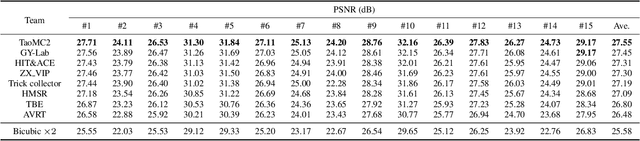
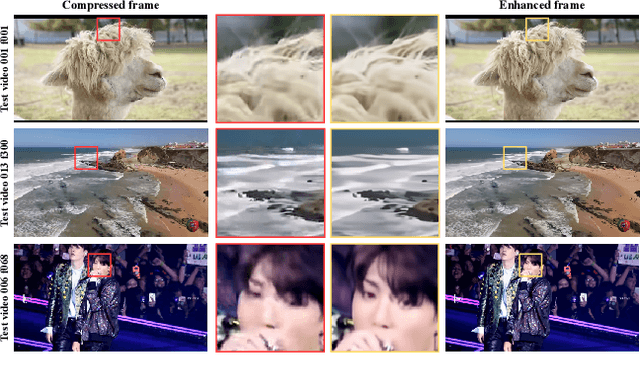
Abstract:This paper reviews the NTIRE 2022 Challenge on Super-Resolution and Quality Enhancement of Compressed Video. In this challenge, we proposed the LDV 2.0 dataset, which includes the LDV dataset (240 videos) and 95 additional videos. This challenge includes three tracks. Track 1 aims at enhancing the videos compressed by HEVC at a fixed QP. Track 2 and Track 3 target both the super-resolution and quality enhancement of HEVC compressed video. They require x2 and x4 super-resolution, respectively. The three tracks totally attract more than 600 registrations. In the test phase, 8 teams, 8 teams and 12 teams submitted the final results to Tracks 1, 2 and 3, respectively. The proposed methods and solutions gauge the state-of-the-art of super-resolution and quality enhancement of compressed video. The proposed LDV 2.0 dataset is available at https://github.com/RenYang-home/LDV_dataset. The homepage of this challenge (including open-sourced codes) is at https://github.com/RenYang-home/NTIRE22_VEnh_SR.
Augmenting Anchors by the Detector Itself
May 28, 2021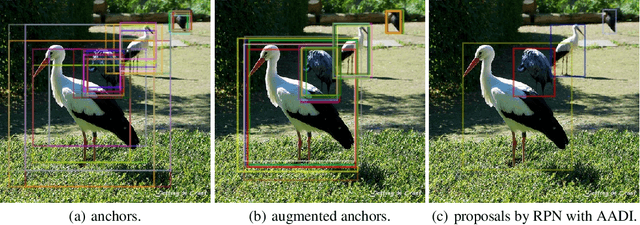
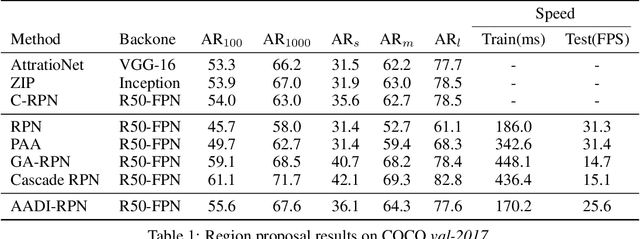
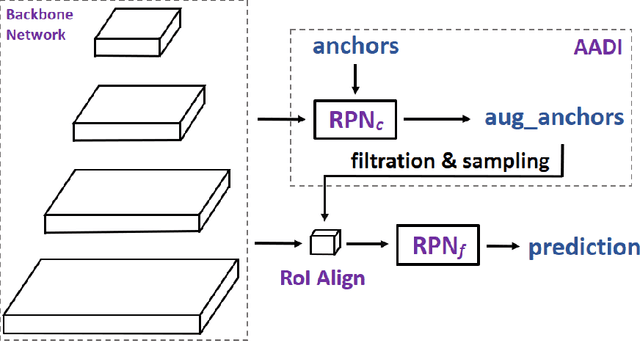

Abstract:It is difficult to determine the scale and aspect ratio of anchors for anchor-based object detection methods. Current state-of-the-art object detectors either determine anchor parameters according to objects' shape and scale in a dataset, or avoid this problem by utilizing anchor-free method. In this paper, we propose a gradient-free anchor augmentation method named AADI, which means Augmenting Anchors by the Detector Itself. AADI is not an anchor-free method, but it converts the scale and aspect ratio of anchors from a continuous space to a discrete space, which greatly alleviates the problem of anchors' designation. Furthermore, AADI does not add any parameters or hyper-parameters, which is beneficial for future research and downstream tasks. Extensive experiments on COCO dataset show that AADI has obvious advantages for both two-stage and single-stage methods, specifically, AADI achieves at least 2.1 AP improvements on Faster R-CNN and 1.6 AP improvements on RetinaNet, using ResNet-50 model. We hope that this simple and cost-efficient method can be widely used in object detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge