Shanlei Mu
Hybrid Contrastive Constraints for Multi-Scenario Ad Ranking
Feb 06, 2023Abstract:Multi-scenario ad ranking aims at leveraging the data from multiple domains or channels for training a unified ranking model to improve the performance at each individual scenario. Although the research on this task has made important progress, it still lacks the consideration of cross-scenario relations, thus leading to limitation in learning capability and difficulty in interrelation modeling. In this paper, we propose a Hybrid Contrastive Constrained approach (HC^2) for multi-scenario ad ranking. To enhance the modeling of data interrelation, we elaborately design a hybrid contrastive learning approach to capture commonalities and differences among multiple scenarios. The core of our approach consists of two elaborated contrastive losses, namely generalized and individual contrastive loss, which aim at capturing common knowledge and scenario-specific knowledge, respectively. To adapt contrastive learning to the complex multi-scenario setting, we propose a series of important improvements. For generalized contrastive loss, we enhance contrastive learning by extending the contrastive samples (label-aware and diffusion noise enhanced contrastive samples) and reweighting the contrastive samples (reciprocal similarity weighting). For individual contrastive loss, we use the strategies of dropout-based augmentation and {cross-scenario encoding} for generating meaningful positive and negative contrastive samples, respectively. Extensive experiments on both offline evaluation and online test have demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed HC$^2$ by comparing it with a number of competitive baselines.
RecBole 2.0: Towards a More Up-to-Date Recommendation Library
Jun 16, 2022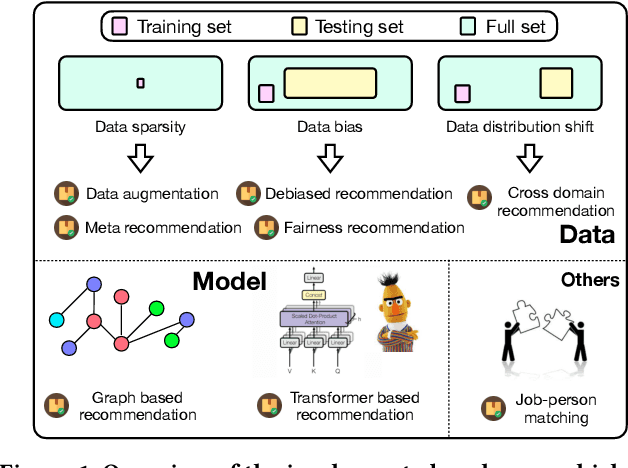
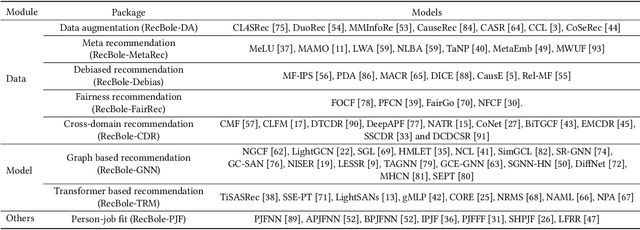
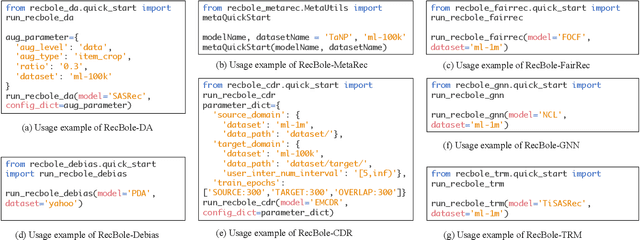
Abstract:In order to support the study of recent advances in recommender systems, this paper presents an extended recommendation library consisting of eight packages for up-to-date topics and architectures. First of all, from a data perspective, we consider three important topics related to data issues (i.e., sparsity, bias and distribution shift), and develop five packages accordingly: meta-learning, data augmentation, debiasing, fairness and cross-domain recommendation. Furthermore, from a model perspective, we develop two benchmarking packages for Transformer-based and graph neural network (GNN)-based models, respectively. All the packages (consisting of 65 new models) are developed based on a popular recommendation framework RecBole, ensuring that both the implementation and interface are unified. For each package, we provide complete implementations from data loading, experimental setup, evaluation and algorithm implementation. This library provides a valuable resource to facilitate the up-to-date research in recommender systems. The project is released at the link: https://github.com/RUCAIBox/RecBole2.0.
Towards Universal Sequence Representation Learning for Recommender Systems
Jun 13, 2022



Abstract:In order to develop effective sequential recommenders, a series of sequence representation learning (SRL) methods are proposed to model historical user behaviors. Most existing SRL methods rely on explicit item IDs for developing the sequence models to better capture user preference. Though effective to some extent, these methods are difficult to be transferred to new recommendation scenarios, due to the limitation by explicitly modeling item IDs. To tackle this issue, we present a novel universal sequence representation learning approach, named UniSRec. The proposed approach utilizes the associated description text of items to learn transferable representations across different recommendation scenarios. For learning universal item representations, we design a lightweight item encoding architecture based on parametric whitening and mixture-of-experts enhanced adaptor. For learning universal sequence representations, we introduce two contrastive pre-training tasks by sampling multi-domain negatives. With the pre-trained universal sequence representation model, our approach can be effectively transferred to new recommendation domains or platforms in a parameter-efficient way, under either inductive or transductive settings. Extensive experiments conducted on real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach. Especially, our approach also leads to a performance improvement in a cross-platform setting, showing the strong transferability of the proposed universal SRL method. The code and pre-trained model are available at: https://github.com/RUCAIBox/UniSRec.
ID-Agnostic User Behavior Pre-training for Sequential Recommendation
Jun 06, 2022



Abstract:Recently, sequential recommendation has emerged as a widely studied topic. Existing researches mainly design effective neural architectures to model user behavior sequences based on item IDs. However, this kind of approach highly relies on user-item interaction data and neglects the attribute- or characteristic-level correlations among similar items preferred by a user. In light of these issues, we propose IDA-SR, which stands for ID-Agnostic User Behavior Pre-training approach for Sequential Recommendation. Instead of explicitly learning representations for item IDs, IDA-SR directly learns item representations from rich text information. To bridge the gap between text semantics and sequential user behaviors, we utilize the pre-trained language model as text encoder, and conduct a pre-training architecture on the sequential user behaviors. In this way, item text can be directly utilized for sequential recommendation without relying on item IDs. Extensive experiments show that the proposed approach can achieve comparable results when only using ID-agnostic item representations, and performs better than baselines by a large margin when fine-tuned with ID information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge