Shangjie Li
MoE-CT: A Novel Approach For Large Language Models Training With Resistance To Catastrophic Forgetting
Jun 25, 2024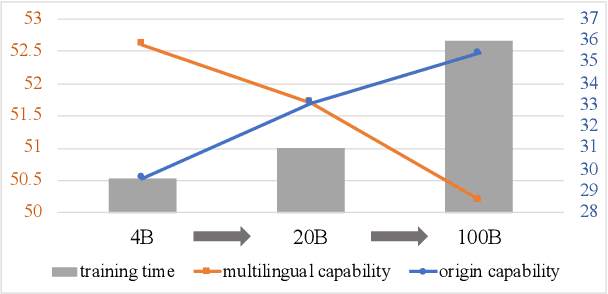

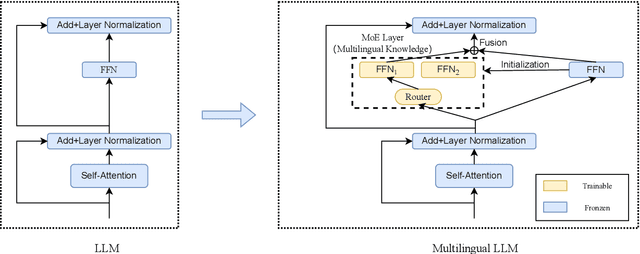
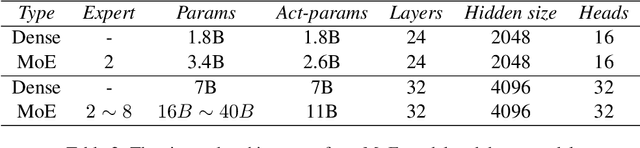
Abstract:The advent of large language models (LLMs) has predominantly catered to high-resource languages, leaving a disparity in performance for low-resource languages. Conventional Continual Training (CT) approaches to bridge this gap often undermine a model's original linguistic proficiency when expanding to multilingual contexts. Addressing this issue, we introduce a novel MoE-CT architecture, a paradigm that innovatively separates the base model's learning from the multilingual expansion process. Our design freezes the original LLM parameters, thus safeguarding its performance in high-resource languages, while an appended MoE module, trained on diverse language datasets, augments low-resource language proficiency. Our approach significantly outperforms conventional CT methods, as evidenced by our experiments, which show marked improvements in multilingual benchmarks without sacrificing the model's original language performance. Moreover, our MoE-CT framework demonstrates enhanced resistance to forgetting and superior transfer learning capabilities. By preserving the base model's integrity and focusing on strategic parameter expansion, our methodology advances multilingual language modeling and represents a significant step forward for low-resource language inclusion in LLMs, indicating a fruitful direction for future research in language technologies.
PolyLM: An Open Source Polyglot Large Language Model
Jul 12, 2023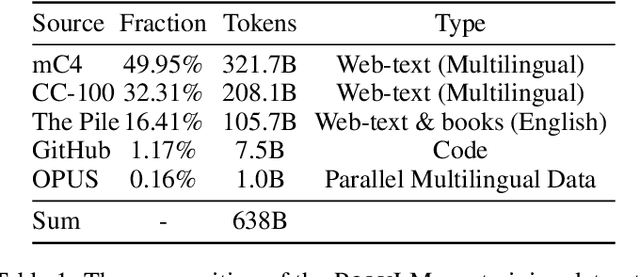
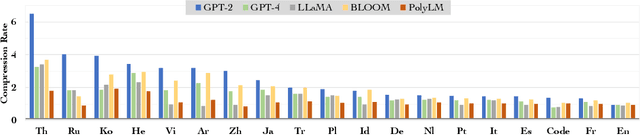
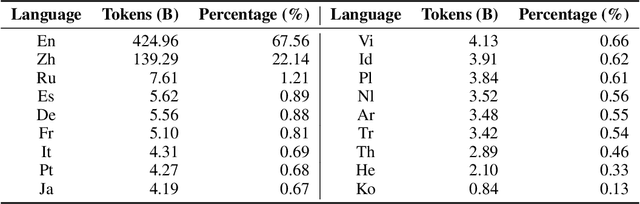
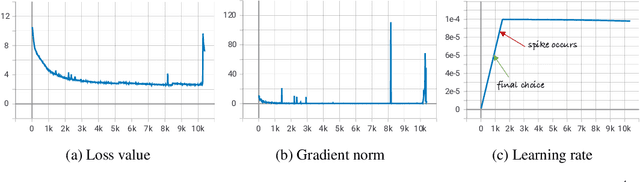
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable ability to comprehend, reason, and generate following nature language instructions. However, the development of LLMs has been primarily focused on high-resource languages, such as English, thereby limiting their applicability and research in other languages. Consequently, we present PolyLM, a multilingual LLM trained on 640 billion (B) tokens, avaliable in two model sizes: 1.7B and 13B. To enhance its multilingual capabilities, we 1) integrate bilingual data into training data; and 2) adopt a curriculum learning strategy that increases the proportion of non-English data from 30% in the first stage to 60% in the final stage during pre-training. Further, we propose a multilingual self-instruct method which automatically generates 132.7K diverse multilingual instructions for model fine-tuning. To assess the model's performance, we collect several existing multilingual tasks, including multilingual understanding, question answering, generation, and translation. Extensive experiments show that PolyLM surpasses other open-source models such as LLaMA and BLOOM on multilingual tasks while maintaining comparable performance in English. Our models, alone with the instruction data and multilingual benchmark, are available at: \url{https://modelscope.cn/models/damo/nlp_polylm_13b_text_generation}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge