Sewon Park
Possibility for Proactive Anomaly Detection
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Time-series anomaly detection, which detects errors and failures in a workflow, is one of the most important topics in real-world applications. The purpose of time-series anomaly detection is to reduce potential damages or losses. However, existing anomaly detection models detect anomalies through the error between the model output and the ground truth (observed) value, which makes them impractical. In this work, we present a \textit{proactive} approach for time-series anomaly detection based on a time-series forecasting model specialized for anomaly detection and a data-driven anomaly detection model. Our proactive approach establishes an anomaly threshold from training data with a data-driven anomaly detection model, and anomalies are subsequently detected by identifying predicted values that exceed the anomaly threshold. In addition, we extensively evaluated the model using four anomaly detection benchmarks and analyzed both predictable and unpredictable anomalies. We attached the source code as supplementary material.
MadSGM: Multivariate Anomaly Detection with Score-based Generative Models
Aug 29, 2023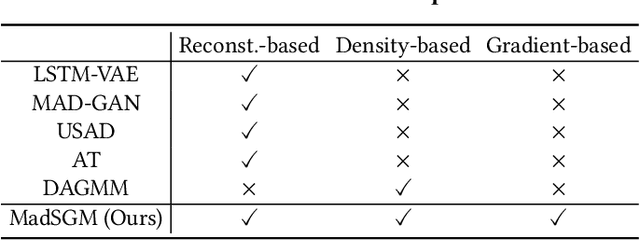
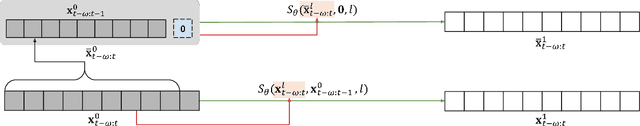
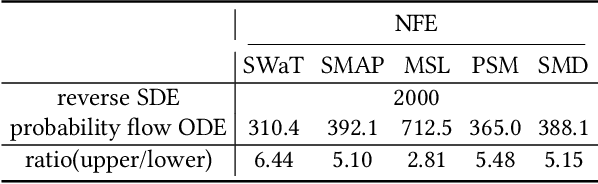
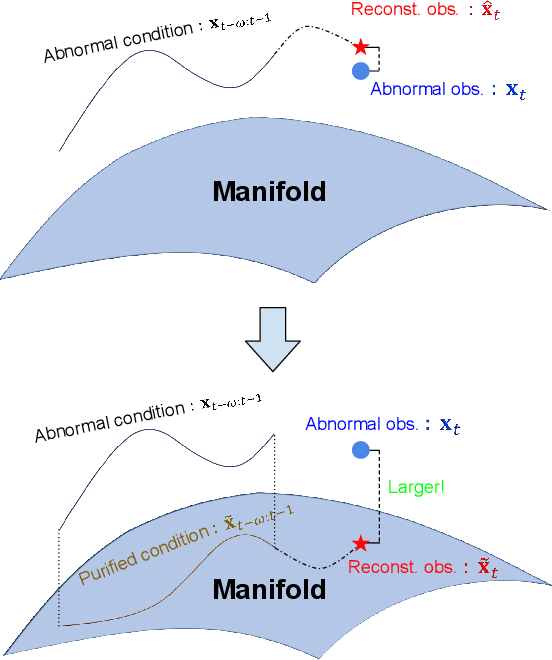
Abstract:The time-series anomaly detection is one of the most fundamental tasks for time-series. Unlike the time-series forecasting and classification, the time-series anomaly detection typically requires unsupervised (or self-supervised) training since collecting and labeling anomalous observations are difficult. In addition, most existing methods resort to limited forms of anomaly measurements and therefore, it is not clear whether they are optimal in all circumstances. To this end, we present a multivariate time-series anomaly detector based on score-based generative models, called MadSGM, which considers the broadest ever set of anomaly measurement factors: i) reconstruction-based, ii) density-based, and iii) gradient-based anomaly measurements. We also design a conditional score network and its denoising score matching loss for the time-series anomaly detection. Experiments on five real-world benchmark datasets illustrate that MadSGM achieves the most robust and accurate predictions.
Regular Time-series Generation using SGM
Jan 20, 2023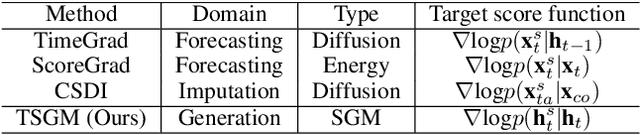
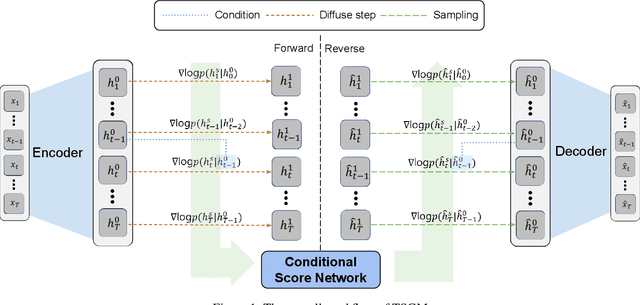
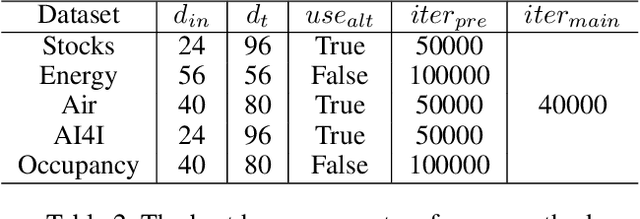
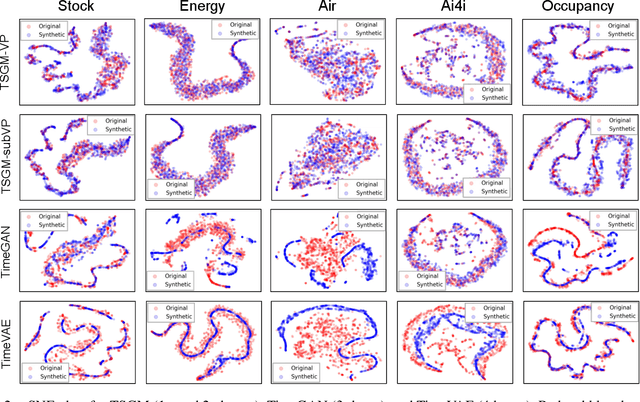
Abstract:Score-based generative models (SGMs) are generative models that are in the spotlight these days. Time-series frequently occurs in our daily life, e.g., stock data, climate data, and so on. Especially, time-series forecasting and classification are popular research topics in the field of machine learning. SGMs are also known for outperforming other generative models. As a result, we apply SGMs to synthesize time-series data by learning conditional score functions. We propose a conditional score network for the time-series generation domain. Furthermore, we also derive the loss function between the score matching and the denoising score matching in the time-series generation domain. Finally, we achieve state-of-the-art results on real-world datasets in terms of sampling diversity and quality.
SOS: Score-based Oversampling for Tabular Data
Jun 17, 2022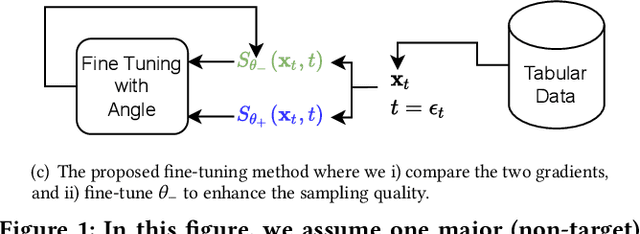
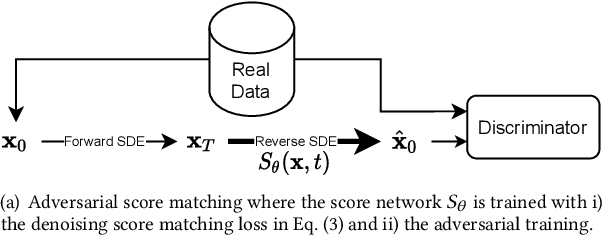
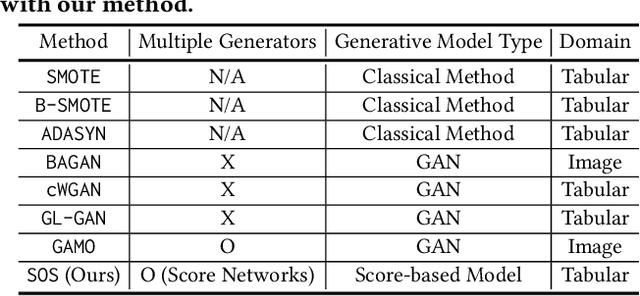
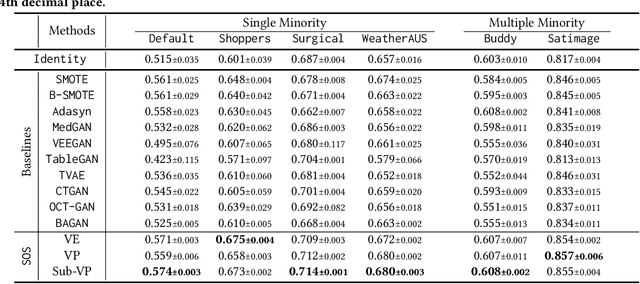
Abstract:Score-based generative models (SGMs) are a recent breakthrough in generating fake images. SGMs are known to surpass other generative models, e.g., generative adversarial networks (GANs) and variational autoencoders (VAEs). Being inspired by their big success, in this work, we fully customize them for generating fake tabular data. In particular, we are interested in oversampling minor classes since imbalanced classes frequently lead to sub-optimal training outcomes. To our knowledge, we are the first presenting a score-based tabular data oversampling method. Firstly, we re-design our own score network since we have to process tabular data. Secondly, we propose two options for our generation method: the former is equivalent to a style transfer for tabular data and the latter uses the standard generative policy of SGMs. Lastly, we define a fine-tuning method, which further enhances the oversampling quality. In our experiments with 6 datasets and 10 baselines, our method outperforms other oversampling methods in all cases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge