Seongheon Park
Towards Reducible Uncertainty Modeling for Reliable Large Language Model Agents
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Uncertainty quantification (UQ) for large language models (LLMs) is a key building block for safety guardrails of daily LLM applications. Yet, even as LLM agents are increasingly deployed in highly complex tasks, most UQ research still centers on single-turn question-answering. We argue that UQ research must shift to realistic settings with interactive agents, and that a new principled framework for agent UQ is needed. This paper presents the first general formulation of agent UQ that subsumes broad classes of existing UQ setups. Under this formulation, we show that prior works implicitly treat LLM UQ as an uncertainty accumulation process, a viewpoint that breaks down for interactive agents in an open world. In contrast, we propose a novel perspective, a conditional uncertainty reduction process, that explicitly models reducible uncertainty over an agent's trajectory by highlighting "interactivity" of actions. From this perspective, we outline a conceptual framework to provide actionable guidance for designing UQ in LLM agent setups. Finally, we conclude with practical implications of the agent UQ in frontier LLM development and domain-specific applications, as well as open remaining problems.
GLSim: Detecting Object Hallucinations in LVLMs via Global-Local Similarity
Aug 27, 2025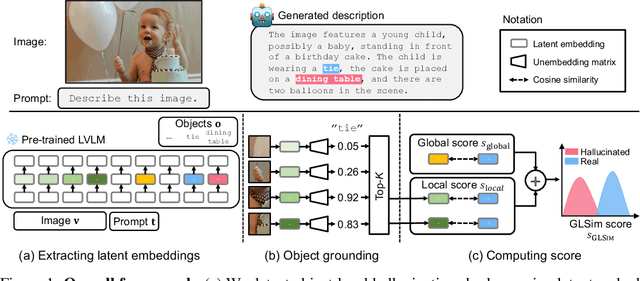
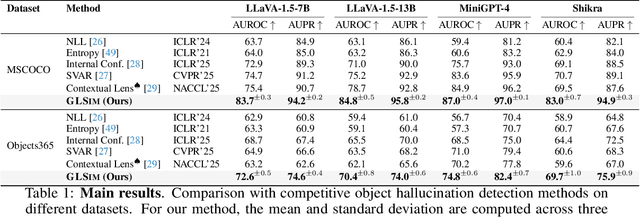
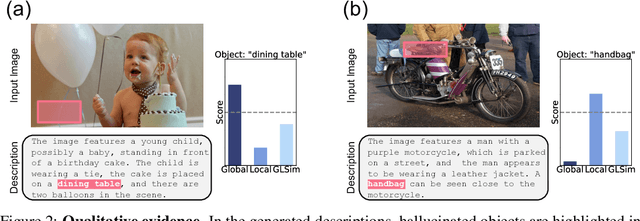
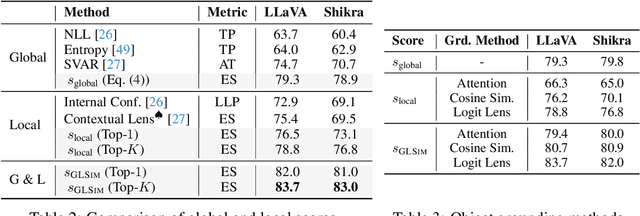
Abstract:Object hallucination in large vision-language models presents a significant challenge to their safe deployment in real-world applications. Recent works have proposed object-level hallucination scores to estimate the likelihood of object hallucination; however, these methods typically adopt either a global or local perspective in isolation, which may limit detection reliability. In this paper, we introduce GLSim, a novel training-free object hallucination detection framework that leverages complementary global and local embedding similarity signals between image and text modalities, enabling more accurate and reliable hallucination detection in diverse scenarios. We comprehensively benchmark existing object hallucination detection methods and demonstrate that GLSim achieves superior detection performance, outperforming competitive baselines by a significant margin.
GeoRanker: Distance-Aware Ranking for Worldwide Image Geolocalization
May 19, 2025Abstract:Worldwide image geolocalization-the task of predicting GPS coordinates from images taken anywhere on Earth-poses a fundamental challenge due to the vast diversity in visual content across regions. While recent approaches adopt a two-stage pipeline of retrieving candidates and selecting the best match, they typically rely on simplistic similarity heuristics and point-wise supervision, failing to model spatial relationships among candidates. In this paper, we propose GeoRanker, a distance-aware ranking framework that leverages large vision-language models to jointly encode query-candidate interactions and predict geographic proximity. In addition, we introduce a multi-order distance loss that ranks both absolute and relative distances, enabling the model to reason over structured spatial relationships. To support this, we curate GeoRanking, the first dataset explicitly designed for geographic ranking tasks with multimodal candidate information. GeoRanker achieves state-of-the-art results on two well-established benchmarks (IM2GPS3K and YFCC4K), significantly outperforming current best methods.
Can Your Uncertainty Scores Detect Hallucinated Entity?
Feb 17, 2025



Abstract:To mitigate the impact of hallucination nature of LLMs, many studies propose detecting hallucinated generation through uncertainty estimation. However, these approaches predominantly operate at the sentence or paragraph level, failing to pinpoint specific spans or entities responsible for hallucinated content. This lack of granularity is especially problematic for long-form outputs that mix accurate and fabricated information. To address this limitation, we explore entity-level hallucination detection. We propose a new data set, HalluEntity, which annotates hallucination at the entity level. Based on the dataset, we comprehensively evaluate uncertainty-based hallucination detection approaches across 17 modern LLMs. Our experimental results show that uncertainty estimation approaches focusing on individual token probabilities tend to over-predict hallucinations, while context-aware methods show better but still suboptimal performance. Through an in-depth qualitative study, we identify relationships between hallucination tendencies and linguistic properties and highlight important directions for future research.
Rethinking Open-World Semi-Supervised Learning: Distribution Mismatch and Inductive Inference
May 31, 2024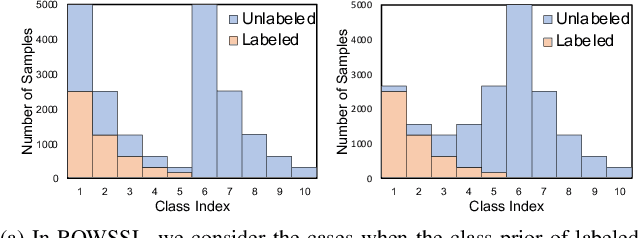
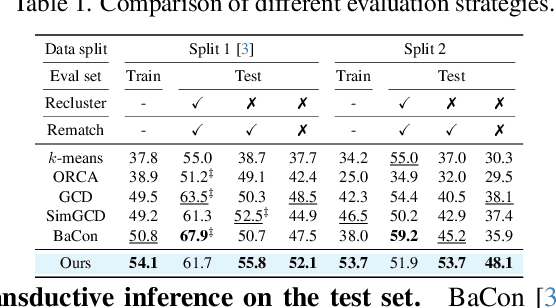
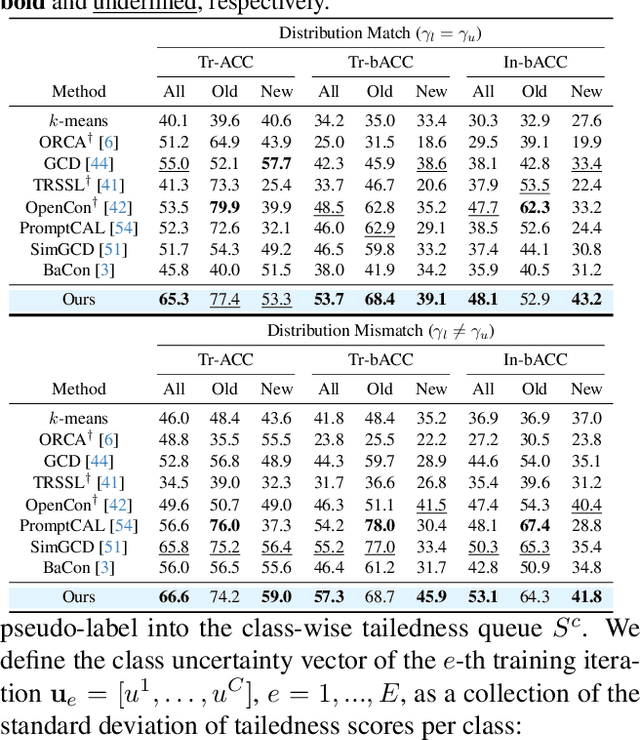
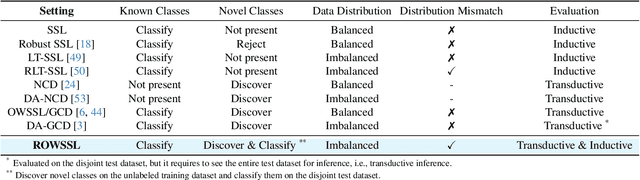
Abstract:Open-world semi-supervised learning (OWSSL) extends conventional semi-supervised learning to open-world scenarios by taking account of novel categories in unlabeled datasets. Despite the recent advancements in OWSSL, the success often relies on the assumptions that 1) labeled and unlabeled datasets share the same balanced class prior distribution, which does not generally hold in real-world applications, and 2) unlabeled training datasets are utilized for evaluation, where such transductive inference might not adequately address challenges in the wild. In this paper, we aim to generalize OWSSL by addressing them. Our work suggests that practical OWSSL may require different training settings, evaluation methods, and learning strategies compared to those prevalent in the existing literature.
Hierarchical Visual Primitive Experts for Compositional Zero-Shot Learning
Aug 08, 2023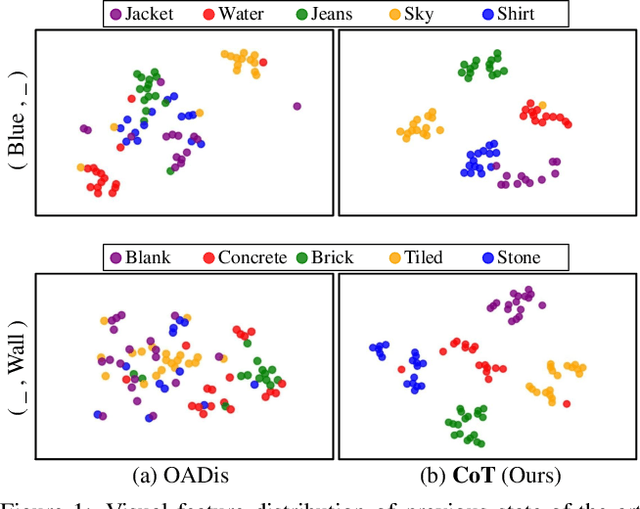
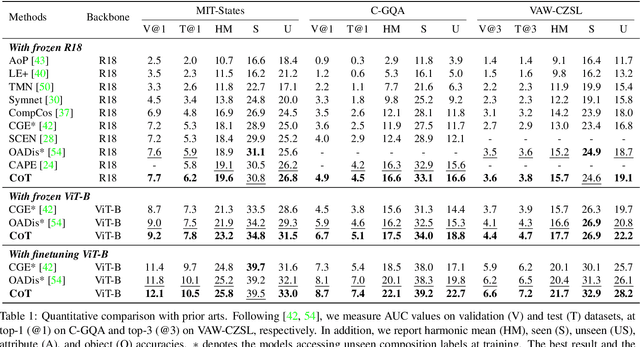
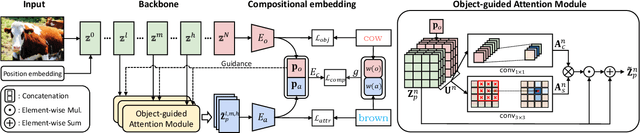
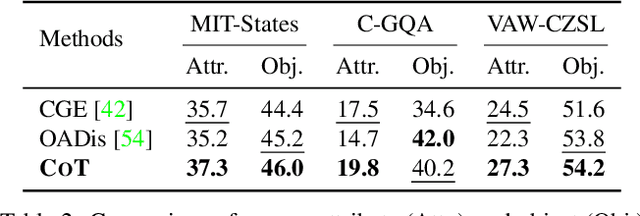
Abstract:Compositional zero-shot learning (CZSL) aims to recognize unseen compositions with prior knowledge of known primitives (attribute and object). Previous works for CZSL often suffer from grasping the contextuality between attribute and object, as well as the discriminability of visual features, and the long-tailed distribution of real-world compositional data. We propose a simple and scalable framework called Composition Transformer (CoT) to address these issues. CoT employs object and attribute experts in distinctive manners to generate representative embeddings, using the visual network hierarchically. The object expert extracts representative object embeddings from the final layer in a bottom-up manner, while the attribute expert makes attribute embeddings in a top-down manner with a proposed object-guided attention module that models contextuality explicitly. To remedy biased prediction caused by imbalanced data distribution, we develop a simple minority attribute augmentation (MAA) that synthesizes virtual samples by mixing two images and oversampling minority attribute classes. Our method achieves SoTA performance on several benchmarks, including MIT-States, C-GQA, and VAW-CZSL. We also demonstrate the effectiveness of CoT in improving visual discrimination and addressing the model bias from the imbalanced data distribution. The code is available at https://github.com/HanjaeKim98/CoT.
PartMix: Regularization Strategy to Learn Part Discovery for Visible-Infrared Person Re-identification
Apr 04, 2023Abstract:Modern data augmentation using a mixture-based technique can regularize the models from overfitting to the training data in various computer vision applications, but a proper data augmentation technique tailored for the part-based Visible-Infrared person Re-IDentification (VI-ReID) models remains unexplored. In this paper, we present a novel data augmentation technique, dubbed PartMix, that synthesizes the augmented samples by mixing the part descriptors across the modalities to improve the performance of part-based VI-ReID models. Especially, we synthesize the positive and negative samples within the same and across different identities and regularize the backbone model through contrastive learning. In addition, we also present an entropy-based mining strategy to weaken the adverse impact of unreliable positive and negative samples. When incorporated into existing part-based VI-ReID model, PartMix consistently boosts the performance. We conduct experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness of our PartMix over the existing VI-ReID methods and provide ablation studies.
Language-free Training for Zero-shot Video Grounding
Oct 24, 2022



Abstract:Given an untrimmed video and a language query depicting a specific temporal moment in the video, video grounding aims to localize the time interval by understanding the text and video simultaneously. One of the most challenging issues is an extremely time- and cost-consuming annotation collection, including video captions in a natural language form and their corresponding temporal regions. In this paper, we present a simple yet novel training framework for video grounding in the zero-shot setting, which learns a network with only video data without any annotation. Inspired by the recent language-free paradigm, i.e. training without language data, we train the network without compelling the generation of fake (pseudo) text queries into a natural language form. Specifically, we propose a method for learning a video grounding model by selecting a temporal interval as a hypothetical correct answer and considering the visual feature selected by our method in the interval as a language feature, with the help of the well-aligned visual-language space of CLIP. Extensive experiments demonstrate the prominence of our language-free training framework, outperforming the existing zero-shot video grounding method and even several weakly-supervised approaches with large margins on two standard datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge