Hanjae Kim
Hierarchical Visual Primitive Experts for Compositional Zero-Shot Learning
Aug 08, 2023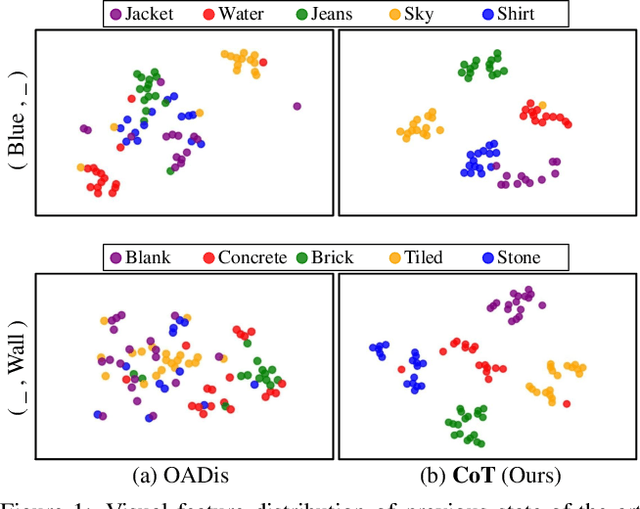
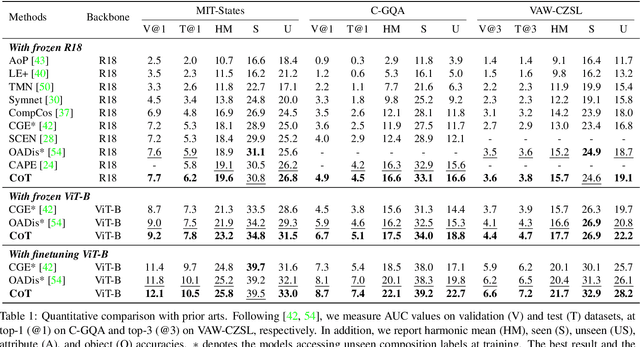
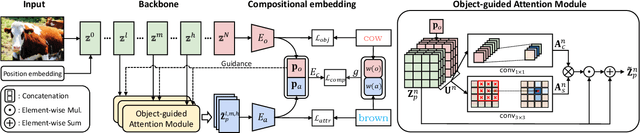
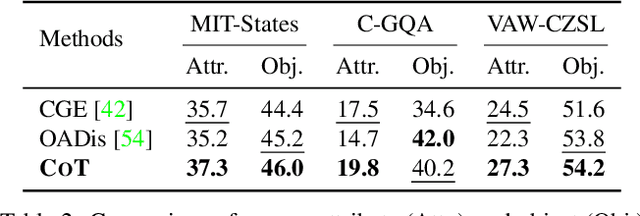
Abstract:Compositional zero-shot learning (CZSL) aims to recognize unseen compositions with prior knowledge of known primitives (attribute and object). Previous works for CZSL often suffer from grasping the contextuality between attribute and object, as well as the discriminability of visual features, and the long-tailed distribution of real-world compositional data. We propose a simple and scalable framework called Composition Transformer (CoT) to address these issues. CoT employs object and attribute experts in distinctive manners to generate representative embeddings, using the visual network hierarchically. The object expert extracts representative object embeddings from the final layer in a bottom-up manner, while the attribute expert makes attribute embeddings in a top-down manner with a proposed object-guided attention module that models contextuality explicitly. To remedy biased prediction caused by imbalanced data distribution, we develop a simple minority attribute augmentation (MAA) that synthesizes virtual samples by mixing two images and oversampling minority attribute classes. Our method achieves SoTA performance on several benchmarks, including MIT-States, C-GQA, and VAW-CZSL. We also demonstrate the effectiveness of CoT in improving visual discrimination and addressing the model bias from the imbalanced data distribution. The code is available at https://github.com/HanjaeKim98/CoT.
Cylindrical Convolutional Networks for Joint Object Detection and Viewpoint Estimation
Mar 25, 2020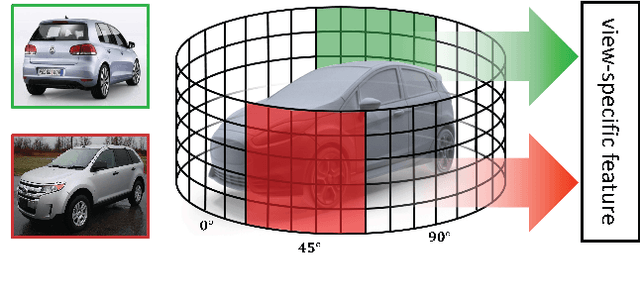
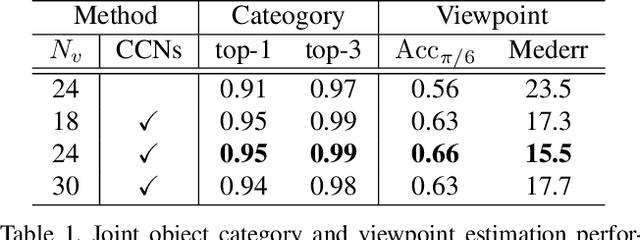
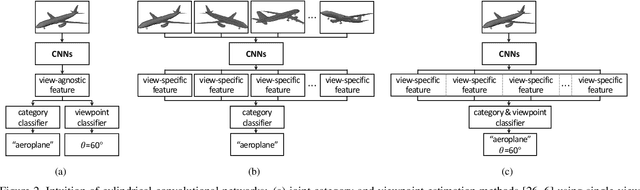
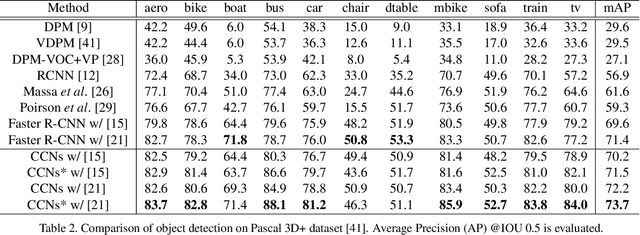
Abstract:Existing techniques to encode spatial invariance within deep convolutional neural networks only model 2D transformation fields. This does not account for the fact that objects in a 2D space are a projection of 3D ones, and thus they have limited ability to severe object viewpoint changes. To overcome this limitation, we introduce a learnable module, cylindrical convolutional networks (CCNs), that exploit cylindrical representation of a convolutional kernel defined in the 3D space. CCNs extract a view-specific feature through a view-specific convolutional kernel to predict object category scores at each viewpoint. With the view-specific feature, we simultaneously determine objective category and viewpoints using the proposed sinusoidal soft-argmax module. Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the cylindrical convolutional networks on joint object detection and viewpoint estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge