Sunghun Joung
Learning Canonical 3D Object Representation for Fine-Grained Recognition
Aug 10, 2021
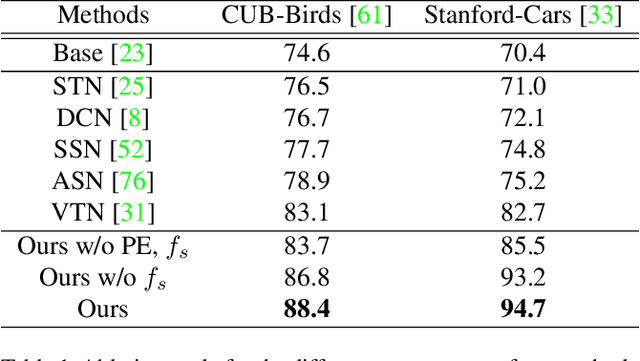
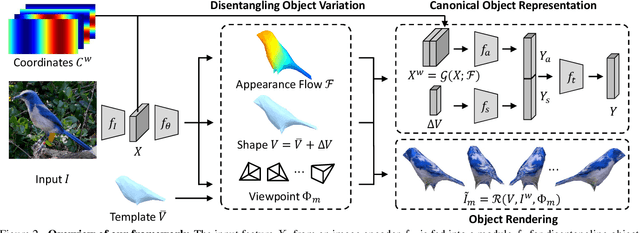
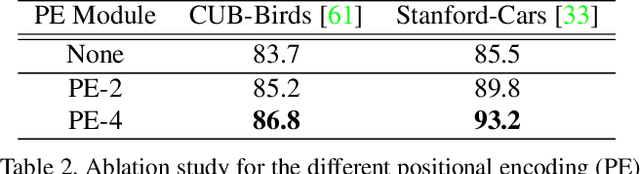
Abstract:We propose a novel framework for fine-grained object recognition that learns to recover object variation in 3D space from a single image, trained on an image collection without using any ground-truth 3D annotation. We accomplish this by representing an object as a composition of 3D shape and its appearance, while eliminating the effect of camera viewpoint, in a canonical configuration. Unlike conventional methods modeling spatial variation in 2D images only, our method is capable of reconfiguring the appearance feature in a canonical 3D space, thus enabling the subsequent object classifier to be invariant under 3D geometric variation. Our representation also allows us to go beyond existing methods, by incorporating 3D shape variation as an additional cue for object recognition. To learn the model without ground-truth 3D annotation, we deploy a differentiable renderer in an analysis-by-synthesis framework. By incorporating 3D shape and appearance jointly in a deep representation, our method learns the discriminative representation of the object and achieves competitive performance on fine-grained image recognition and vehicle re-identification. We also demonstrate that the performance of 3D shape reconstruction is improved by learning fine-grained shape deformation in a boosting manner.
Cross-Domain Grouping and Alignment for Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation
Dec 17, 2020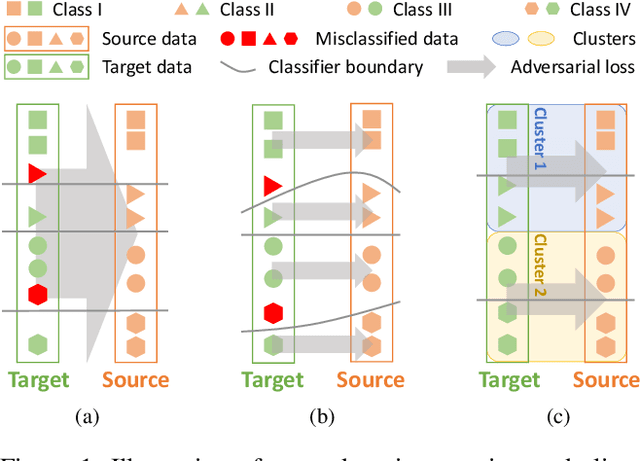
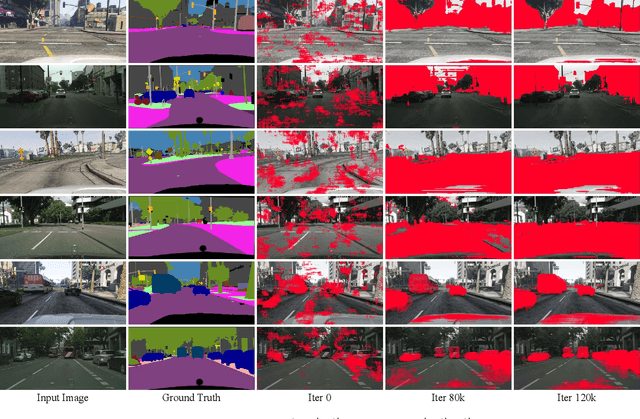
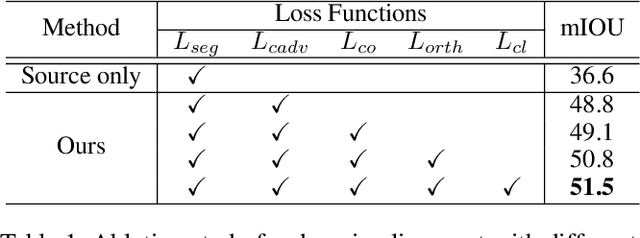

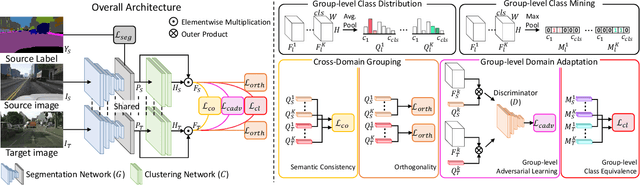
Abstract:Existing techniques to adapt semantic segmentation networks across the source and target domains within deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) deal with all the samples from the two domains in a global or category-aware manner. They do not consider an inter-class variation within the target domain itself or estimated category, providing the limitation to encode the domains having a multi-modal data distribution. To overcome this limitation, we introduce a learnable clustering module, and a novel domain adaptation framework called cross-domain grouping and alignment. To cluster the samples across domains with an aim to maximize the domain alignment without forgetting precise segmentation ability on the source domain, we present two loss functions, in particular, for encouraging semantic consistency and orthogonality among the clusters. We also present a loss so as to solve a class imbalance problem, which is the other limitation of the previous methods. Our experiments show that our method consistently boosts the adaptation performance in semantic segmentation, outperforming the state-of-the-arts on various domain adaptation settings.
Cylindrical Convolutional Networks for Joint Object Detection and Viewpoint Estimation
Mar 25, 2020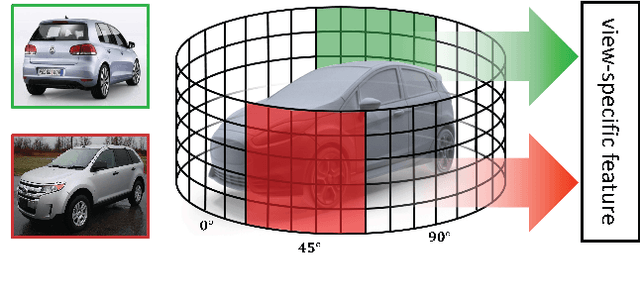
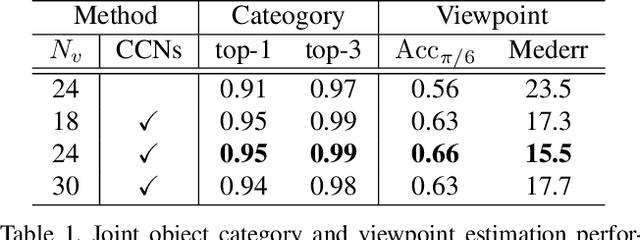
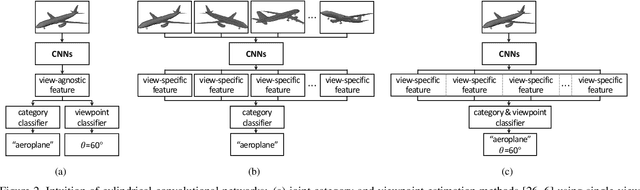
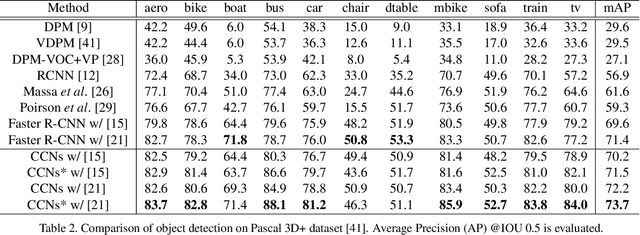
Abstract:Existing techniques to encode spatial invariance within deep convolutional neural networks only model 2D transformation fields. This does not account for the fact that objects in a 2D space are a projection of 3D ones, and thus they have limited ability to severe object viewpoint changes. To overcome this limitation, we introduce a learnable module, cylindrical convolutional networks (CCNs), that exploit cylindrical representation of a convolutional kernel defined in the 3D space. CCNs extract a view-specific feature through a view-specific convolutional kernel to predict object category scores at each viewpoint. With the view-specific feature, we simultaneously determine objective category and viewpoints using the proposed sinusoidal soft-argmax module. Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the cylindrical convolutional networks on joint object detection and viewpoint estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge