Sayyed M. Zahiri
De-Biased Modelling of Search Click Behavior with Reinforcement Learning
May 21, 2021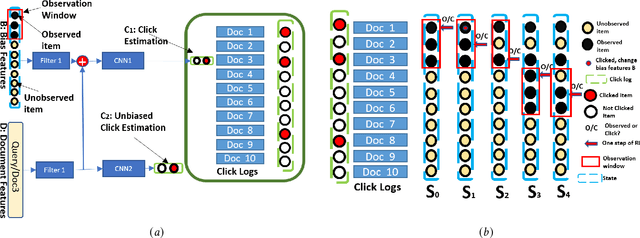

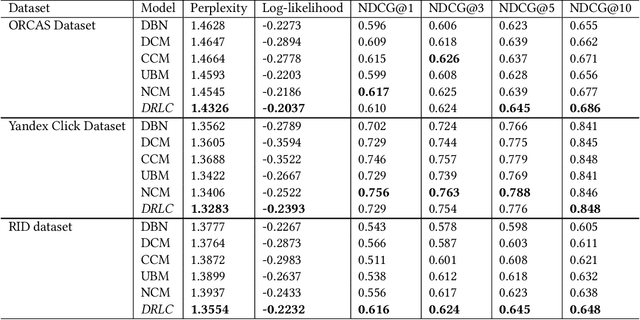
Abstract:Users' clicks on Web search results are one of the key signals for evaluating and improving web search quality and have been widely used as part of current state-of-the-art Learning-To-Rank(LTR) models. With a large volume of search logs available for major search engines, effective models of searcher click behavior have emerged to evaluate and train LTR models. However, when modeling the users' click behavior, considering the bias of the behavior is imperative. In particular, when a search result is not clicked, it is not necessarily chosen as not relevant by the user, but instead could have been simply missed, especially for lower-ranked results. These kinds of biases in the click log data can be incorporated into the click models, propagating the errors to the resulting LTR ranking models or evaluation metrics. In this paper, we propose the De-biased Reinforcement Learning Click model (DRLC). The DRLC model relaxes previously made assumptions about the users' examination behavior and resulting latent states. To implement the DRLC model, convolutional neural networks are used as the value networks for reinforcement learning, trained to learn a policy to reduce bias in the click logs. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the DRLC model, we first compare performance with the previous state-of-art approaches using established click prediction metrics, including log-likelihood and perplexity. We further show that DRLC also leads to improvements in ranking performance. Our experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the DRLC model in learning to reduce bias in click logs, leading to improved modeling performance and showing the potential for using DRLC for improving Web search quality.
APRF-Net: Attentive Pseudo-Relevance Feedback Network for Query Categorization
May 10, 2021
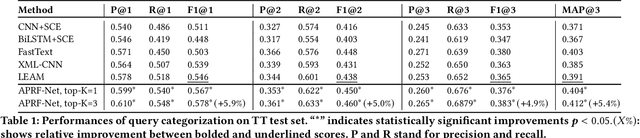
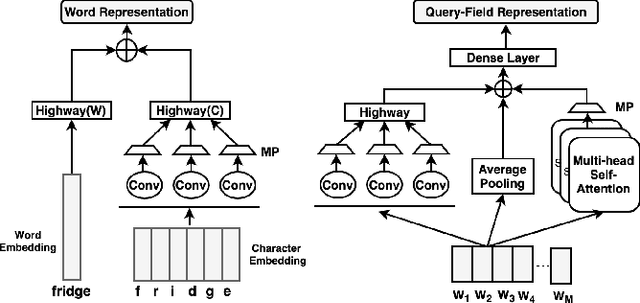
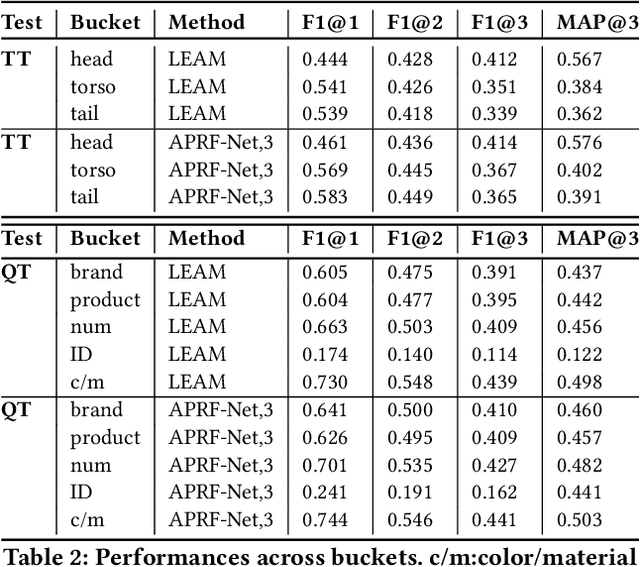
Abstract:Query categorization is an essential part of query intent understanding in e-commerce search. A common query categorization task is to select the relevant fine-grained product categories in a product taxonomy. For frequent queries, rich customer behavior (e.g., click-through data) can be used to infer the relevant product categories. However, for more rare queries, which cover a large volume of search traffic, relying solely on customer behavior may not suffice due to the lack of this signal. To improve categorization of rare queries, we adapt the Pseudo-Relevance Feedback (PRF) approach to utilize the latent knowledge embedded in semantically or lexically similar product documents to enrich the representation of the more rare queries. To this end, we propose a novel deep neural model named Attentive Pseudo Relevance Feedback Network (APRF-Net) to enhance the representation of rare queries for query categorization. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, we collect search queries from a large commercial search engine, and compare APRF-Net to state-of-the-art deep learning models for text classification. Our results show that the APRF-Net significantly improves query categorization by 5.9% on F1@1 score over the baselines, which increases to 8.2% improvement for the rare (tail) queries. The findings of this paper can be leveraged for further improvements in search query representation and understanding.
CRAB: Class Representation Attentive BERT for Hate Speech Identification in Social Media
Oct 25, 2020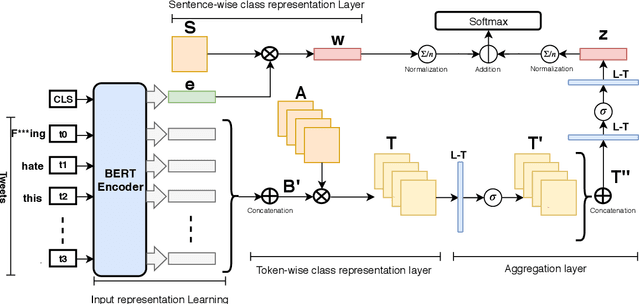
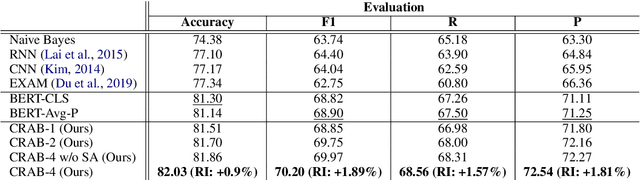
Abstract:In recent years, social media platforms have hosted an explosion of hate speech and objectionable content. The urgent need for effective automatic hate speech detection models have drawn remarkable investment from companies and researchers. Social media posts are generally short and their semantics could drastically be altered by even a single token. Thus, it is crucial for this task to learn context-aware input representations, and consider relevancy scores between input embeddings and class representations as an additional signal. To accommodate these needs, this paper introduces CRAB (Class Representation Attentive BERT), a neural model for detecting hate speech in social media. The model benefits from two semantic representations: (i) trainable token-wise and sentence-wise class representations, and (ii) contextualized input embeddings from state-of-the-art BERT encoder. To investigate effectiveness of CRAB, we train our model on Twitter data and compare it against strong baselines. Our results show that CRAB achieves 1.89% relative improved Macro-averaged F1 over state-of-the-art baseline. The results of this research open an opportunity for the future research on automated abusive behavior detection in social media
Active Learning for Product Type Ontology Enhancement in E-commerce
Sep 19, 2020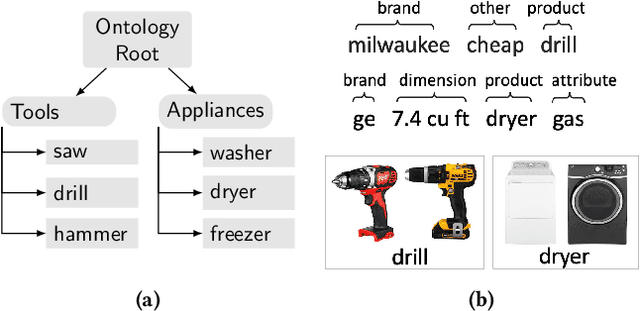
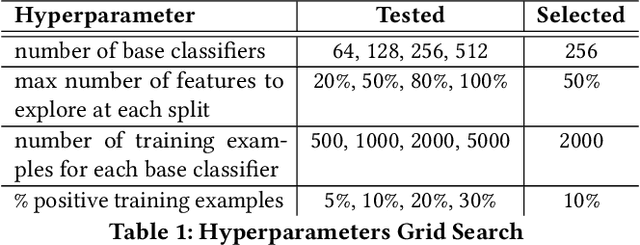
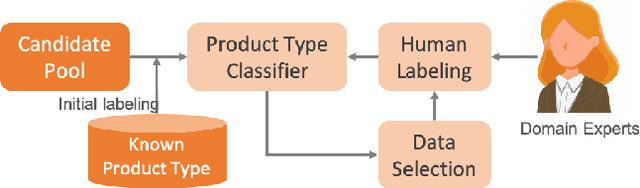
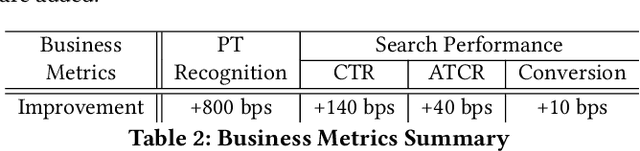
Abstract:Entity-based semantic search has been widely adopted in modern search engines to improve search accuracy by understanding users' intent. In e-commerce, an accurate and complete product type (PT) ontology is essential for recognizing product entities in queries and retrieving relevant products from catalog. However, finding product types (PTs) to construct such an ontology is usually expensive due to the considerable amount of human efforts it may involve. In this work, we propose an active learning framework that efficiently utilizes domain experts' knowledge for PT discovery. We also show the quality and coverage of the resulting PTs in the experiment results.
Emotion Detection on TV Show Transcripts with Sequence-based Convolutional Neural Networks
Aug 14, 2017



Abstract:While there have been significant advances in detecting emotions from speech and image recognition, emotion detection on text is still under-explored and remained as an active research field. This paper introduces a corpus for text-based emotion detection on multiparty dialogue as well as deep neural models that outperform the existing approaches for document classification. We first present a new corpus that provides annotation of seven emotions on consecutive utterances in dialogues extracted from the show, Friends. We then suggest four types of sequence-based convolutional neural network models with attention that leverage the sequence information encapsulated in dialogue. Our best model shows the accuracies of 37.9% and 54% for fine- and coarse-grained emotions, respectively. Given the difficulty of this task, this is promising.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge