Saurabh Saini
Prototype Guided Backdoor Defense
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Deep learning models are susceptible to {\em backdoor attacks} involving malicious attackers perturbing a small subset of training data with a {\em trigger} to causes misclassifications. Various triggers have been used, including semantic triggers that are easily realizable without requiring the attacker to manipulate the image. The emergence of generative AI has eased the generation of varied poisoned samples. Robustness across types of triggers is crucial to effective defense. We propose Prototype Guided Backdoor Defense (PGBD), a robust post-hoc defense that scales across different trigger types, including previously unsolved semantic triggers. PGBD exploits displacements in the geometric spaces of activations to penalize movements toward the trigger. This is done using a novel sanitization loss of a post-hoc fine-tuning step. The geometric approach scales easily to all types of attacks. PGBD achieves better performance across all settings. We also present the first defense against a new semantic attack on celebrity face images. Project page: \hyperlink{https://venkatadithya9.github.io/pgbd.github.io/}{this https URL}.
Deep Learning Descriptor Hybridization with Feature Reduction for Accurate Cervical Cancer Colposcopy Image Classification
May 01, 2024Abstract:Cervical cancer stands as a predominant cause of female mortality, underscoring the need for regular screenings to enable early diagnosis and preemptive treatment of pre-cancerous conditions. The transformation zone in the cervix, where cellular differentiation occurs, plays a critical role in the detection of abnormalities. Colposcopy has emerged as a pivotal tool in cervical cancer prevention since it provides a meticulous examination of cervical abnormalities. However, challenges in visual evaluation necessitate the development of Computer Aided Diagnosis (CAD) systems. We propose a novel CAD system that combines the strengths of various deep-learning descriptors (ResNet50, ResNet101, and ResNet152) with appropriate feature normalization (min-max) as well as feature reduction technique (LDA). The combination of different descriptors ensures that all the features (low-level like edges and colour, high-level like shape and texture) are captured, feature normalization prevents biased learning, and feature reduction avoids overfitting. We do experiments on the IARC dataset provided by WHO. The dataset is initially segmented and balanced. Our approach achieves exceptional performance in the range of 97%-100% for both the normal-abnormal and the type classification. A competitive approach for type classification on the same dataset achieved 81%-91% performance.
Specularity Factorization for Low-Light Enhancement
Apr 02, 2024Abstract:We present a new additive image factorization technique that treats images to be composed of multiple latent specular components which can be simply estimated recursively by modulating the sparsity during decomposition. Our model-driven {\em RSFNet} estimates these factors by unrolling the optimization into network layers requiring only a few scalars to be learned. The resultant factors are interpretable by design and can be fused for different image enhancement tasks via a network or combined directly by the user in a controllable fashion. Based on RSFNet, we detail a zero-reference Low Light Enhancement (LLE) application trained without paired or unpaired supervision. Our system improves the state-of-the-art performance on standard benchmarks and achieves better generalization on multiple other datasets. We also integrate our factors with other task specific fusion networks for applications like deraining, deblurring and dehazing with negligible overhead thereby highlighting the multi-domain and multi-task generalizability of our proposed RSFNet. The code and data is released for reproducibility on the project homepage.
Concept Distillation: Leveraging Human-Centered Explanations for Model Improvement
Nov 26, 2023



Abstract:Humans use abstract concepts for understanding instead of hard features. Recent interpretability research has focused on human-centered concept explanations of neural networks. Concept Activation Vectors (CAVs) estimate a model's sensitivity and possible biases to a given concept. In this paper, we extend CAVs from post-hoc analysis to ante-hoc training in order to reduce model bias through fine-tuning using an additional Concept Loss. Concepts were defined on the final layer of the network in the past. We generalize it to intermediate layers using class prototypes. This facilitates class learning in the last convolution layer, which is known to be most informative. We also introduce Concept Distillation to create richer concepts using a pre-trained knowledgeable model as the teacher. Our method can sensitize or desensitize a model towards concepts. We show applications of concept-sensitive training to debias several classification problems. We also use concepts to induce prior knowledge into IID, a reconstruction problem. Concept-sensitive training can improve model interpretability, reduce biases, and induce prior knowledge. Please visit https://avani17101.github.io/Concept-Distilllation/ for code and more details.
Interactive Segmentation of Radiance Fields
Dec 27, 2022
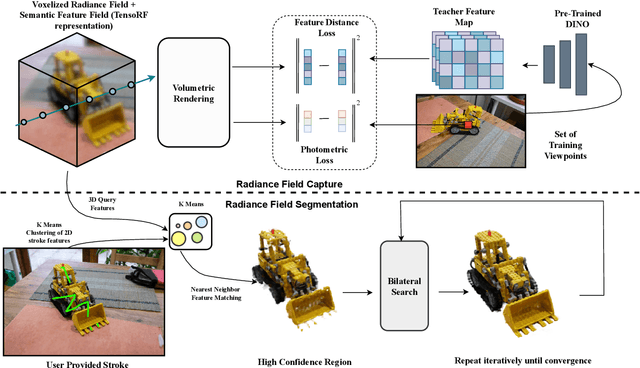
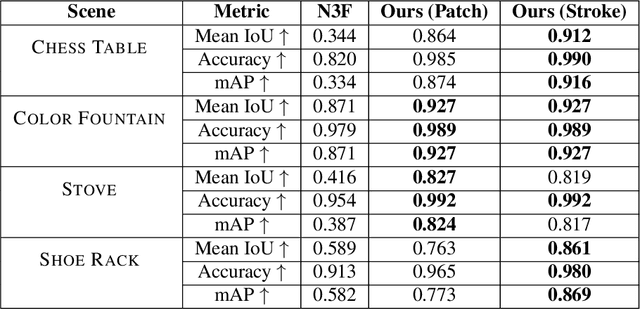
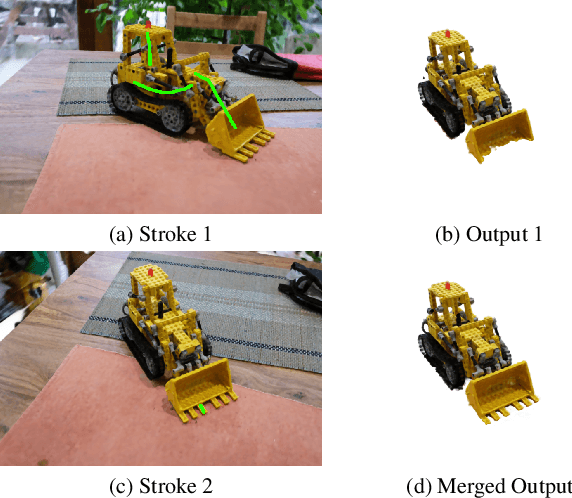
Abstract:Radiance Fields (RF) are popular to represent casually-captured scenes for new view generation and have been used for applications beyond it. Understanding and manipulating scenes represented as RFs have to naturally follow to facilitate mixed reality on personal spaces. Semantic segmentation of objects in the 3D scene is an important step for that. Prior segmentation efforts using feature distillation show promise but don't scale to complex objects with diverse appearance. We present a framework to interactively segment objects with fine structure. Nearest neighbor feature matching identifies high-confidence regions of the objects using distilled features. Bilateral filtering in a joint spatio-semantic space grows the region to recover accurate segmentation. We show state-of-the-art results of segmenting objects from RFs and compositing them to another scene, changing appearance, etc., moving closer to rich scene manipulation and understanding. Project Page: https://rahul-goel.github.io/isrf/
StyleTRF: Stylizing Tensorial Radiance Fields
Dec 19, 2022Abstract:Stylized view generation of scenes captured casually using a camera has received much attention recently. The geometry and appearance of the scene are typically captured as neural point sets or neural radiance fields in the previous work. An image stylization method is used to stylize the captured appearance by training its network jointly or iteratively with the structure capture network. The state-of-the-art SNeRF method trains the NeRF and stylization network in an alternating manner. These methods have high training time and require joint optimization. In this work, we present StyleTRF, a compact, quick-to-optimize strategy for stylized view generation using TensoRF. The appearance part is fine-tuned using sparse stylized priors of a few views rendered using the TensoRF representation for a few iterations. Our method thus effectively decouples style-adaption from view capture and is much faster than the previous methods. We show state-of-the-art results on several scenes used for this purpose.
Learning to Stylize Novel Views
May 27, 2021



Abstract:We tackle a 3D scene stylization problem - generating stylized images of a scene from arbitrary novel views given a set of images of the same scene and a reference image of the desired style as inputs. Direct solution of combining novel view synthesis and stylization approaches lead to results that are blurry or not consistent across different views. We propose a point cloud-based method for consistent 3D scene stylization. First, we construct the point cloud by back-projecting the image features to the 3D space. Second, we develop point cloud aggregation modules to gather the style information of the 3D scene, and then modulate the features in the point cloud with a linear transformation matrix. Finally, we project the transformed features to 2D space to obtain the novel views. Experimental results on two diverse datasets of real-world scenes validate that our method generates consistent stylized novel view synthesis results against other alternative approaches.
Semantic Hierarchical Priors for Intrinsic Image Decomposition
Feb 11, 2019



Abstract:Intrinsic Image Decomposition (IID) is a challenging and interesting computer vision problem with various applications in several fields. We present novel semantic priors and an integrated approach for single image IID that involves analyzing image at three hierarchical context levels. Local context priors capture scene properties at each pixel within a small neighbourhood. Mid-level context priors encode object level semantics. Global context priors establish correspondences at the scene level. Our semantic priors are designed on both fixed and flexible regions, using selective search method and Convolutional Neural Network features. Our IID method is an iterative multistage optimization scheme and consists of two complementary formulations: $L_2$ smoothing for shading and $L_1$ sparsity for reflectance. Experiments and analysis of our method indicate the utility of our semantic priors and structured hierarchical analysis in an IID framework. We compare our method with other contemporary IID solutions and show results with lesser artifacts. Finally, we highlight that proper choice and encoding of prior knowledge can produce competitive results even when compared to end-to-end deep learning IID methods, signifying the importance of such priors. We believe that the insights and techniques presented in this paper would be useful in the future IID research.
Learning to Hash-tag Videos with Tag2Vec
Dec 13, 2016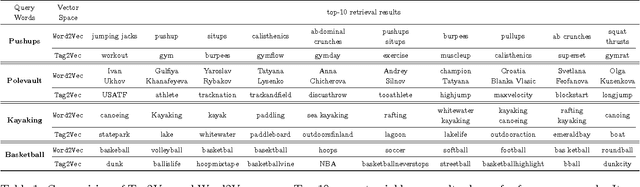
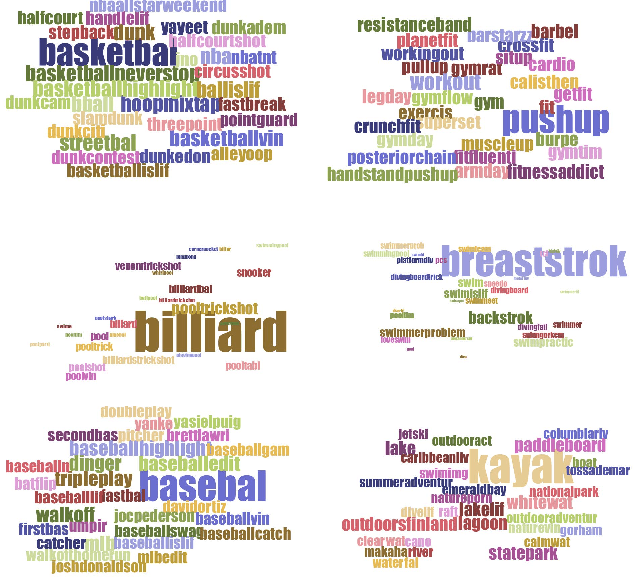

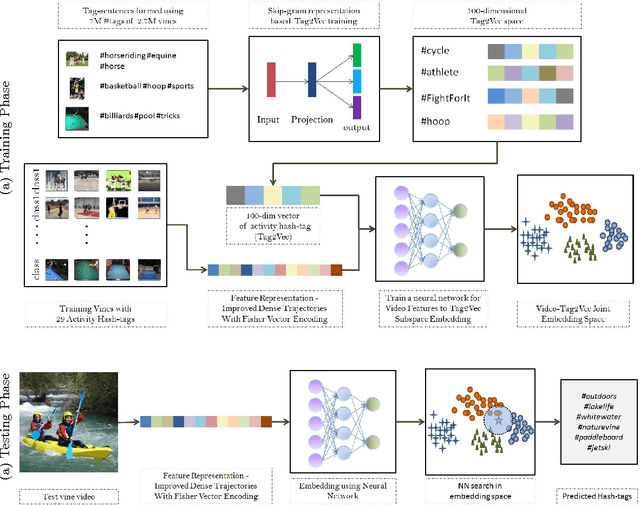
Abstract:User-given tags or labels are valuable resources for semantic understanding of visual media such as images and videos. Recently, a new type of labeling mechanism known as hash-tags have become increasingly popular on social media sites. In this paper, we study the problem of generating relevant and useful hash-tags for short video clips. Traditional data-driven approaches for tag enrichment and recommendation use direct visual similarity for label transfer and propagation. We attempt to learn a direct low-cost mapping from video to hash-tags using a two step training process. We first employ a natural language processing (NLP) technique, skip-gram models with neural network training to learn a low-dimensional vector representation of hash-tags (Tag2Vec) using a corpus of 10 million hash-tags. We then train an embedding function to map video features to the low-dimensional Tag2vec space. We learn this embedding for 29 categories of short video clips with hash-tags. A query video without any tag-information can then be directly mapped to the vector space of tags using the learned embedding and relevant tags can be found by performing a simple nearest-neighbor retrieval in the Tag2Vec space. We validate the relevance of the tags suggested by our system qualitatively and quantitatively with a user study.
From Traditional to Modern : Domain Adaptation for Action Classification in Short Social Video Clips
Oct 18, 2016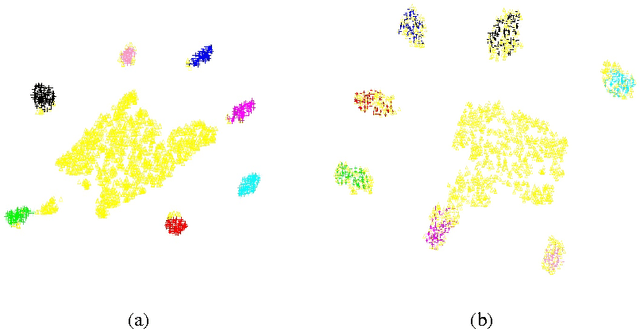
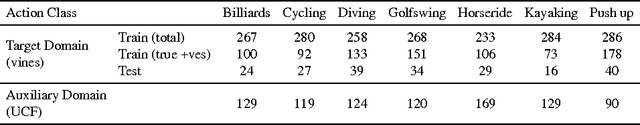

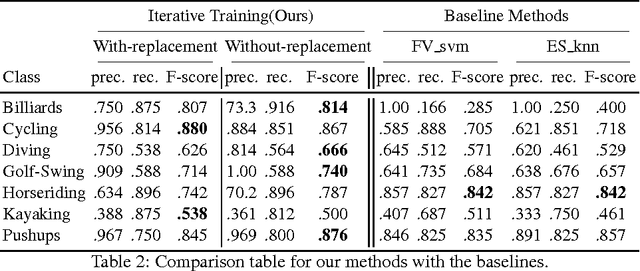
Abstract:Short internet video clips like vines present a significantly wild distribution compared to traditional video datasets. In this paper, we focus on the problem of unsupervised action classification in wild vines using traditional labeled datasets. To this end, we use a data augmentation based simple domain adaptation strategy. We utilise semantic word2vec space as a common subspace to embed video features from both, labeled source domain and unlablled target domain. Our method incrementally augments the labeled source with target samples and iteratively modifies the embedding function to bring the source and target distributions together. Additionally, we utilise a multi-modal representation that incorporates noisy semantic information available in form of hash-tags. We show the effectiveness of this simple adaptation technique on a test set of vines and achieve notable improvements in performance.
* 9 pages, GCPR, 2016
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge