Sana Sabah Al-Azzawi
TaskComplexity: A Dataset for Task Complexity Classification with In-Context Learning, FLAN-T5 and GPT-4o Benchmarks
Sep 30, 2024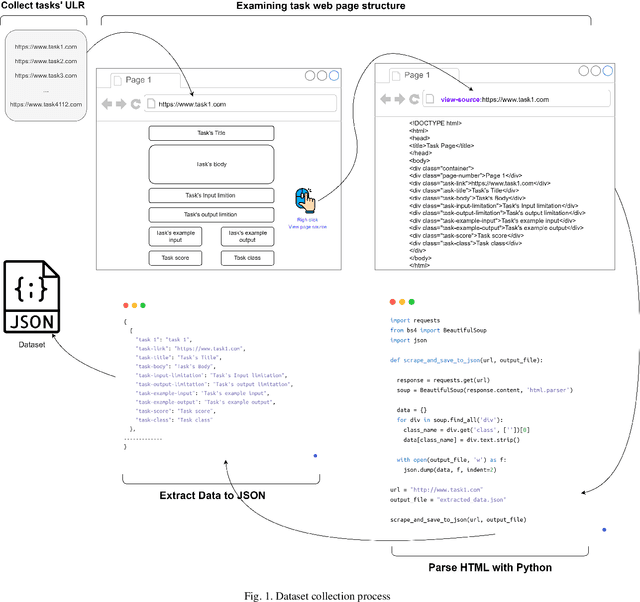
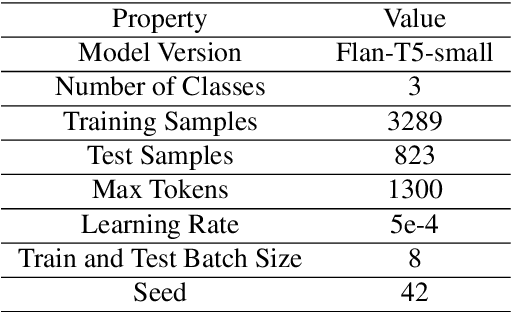
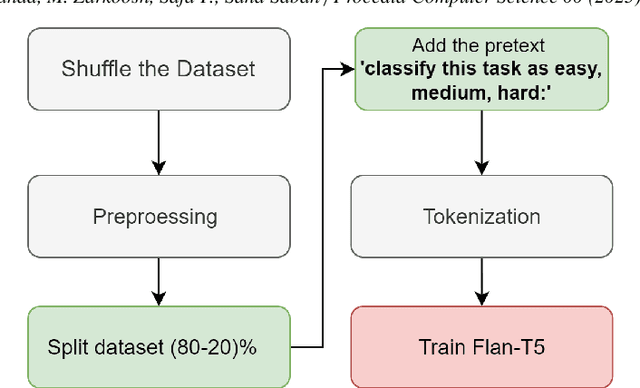
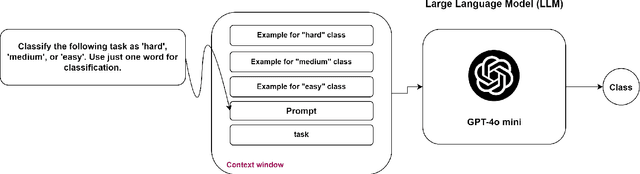
Abstract:This paper addresses the challenge of classifying and assigning programming tasks to experts, a process that typically requires significant effort, time, and cost. To tackle this issue, a novel dataset containing a total of 4,112 programming tasks was created by extracting tasks from various websites. Web scraping techniques were employed to collect this dataset of programming problems systematically. Specific HTML tags were tracked to extract key elements of each issue, including the title, problem description, input-output, examples, problem class, and complexity score. Examples from the dataset are provided in the appendix to illustrate the variety and complexity of tasks included. The dataset's effectiveness has been evaluated and benchmarked using two approaches; the first approach involved fine-tuning the FLAN-T5 small model on the dataset, while the second approach used in-context learning (ICL) with the GPT-4o mini. The performance was assessed using standard metrics: accuracy, recall, precision, and F1-score. The results indicated that in-context learning with GPT-4o-mini outperformed the FLAN-T5 model.
NLP-LTU at SemEval-2023 Task 10: The Impact of Data Augmentation and Semi-Supervised Learning Techniques on Text Classification Performance on an Imbalanced Dataset
Apr 25, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a methodology for task 10 of SemEval23, focusing on detecting and classifying online sexism in social media posts. The task is tackling a serious issue, as detecting harmful content on social media platforms is crucial for mitigating the harm of these posts on users. Our solution for this task is based on an ensemble of fine-tuned transformer-based models (BERTweet, RoBERTa, and DeBERTa). To alleviate problems related to class imbalance, and to improve the generalization capability of our model, we also experiment with data augmentation and semi-supervised learning. In particular, for data augmentation, we use back-translation, either on all classes, or on the underrepresented classes only. We analyze the impact of these strategies on the overall performance of the pipeline through extensive experiments. while for semi-supervised learning, we found that with a substantial amount of unlabelled, in-domain data available, semi-supervised learning can enhance the performance of certain models. Our proposed method (for which the source code is available on Github attains an F1-score of 0.8613 for sub-taskA, which ranked us 10th in the competition
Masakhane-Afrisenti at SemEval-2023 Task 12: Sentiment Analysis using Afro-centric Language Models and Adapters for Low-resource African Languages
Apr 13, 2023



Abstract:AfriSenti-SemEval Shared Task 12 of SemEval-2023. The task aims to perform monolingual sentiment classification (sub-task A) for 12 African languages, multilingual sentiment classification (sub-task B), and zero-shot sentiment classification (task C). For sub-task A, we conducted experiments using classical machine learning classifiers, Afro-centric language models, and language-specific models. For task B, we fine-tuned multilingual pre-trained language models that support many of the languages in the task. For task C, we used we make use of a parameter-efficient Adapter approach that leverages monolingual texts in the target language for effective zero-shot transfer. Our findings suggest that using pre-trained Afro-centric language models improves performance for low-resource African languages. We also ran experiments using adapters for zero-shot tasks, and the results suggest that we can obtain promising results by using adapters with a limited amount of resources.
Lon-eå at SemEval-2023 Task 11: A Comparison of\\Activation Functions for Soft and Hard Label Prediction
Mar 04, 2023Abstract:We study the influence of different activation functions in the output layer of deep neural network models for soft and hard label prediction in the learning with disagreement task. In this task, the goal is to quantify the amount of disagreement via predicting soft labels. To predict the soft labels, we use BERT-based preprocessors and encoders and vary the activation function used in the output layer, while keeping other parameters constant. The soft labels are then used for the hard label prediction. The activation functions considered are sigmoid as well as a step-function that is added to the model post-training and a sinusoidal activation function, which is introduced for the first time in this paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge