Peyman Hosseini
CG-TTRL: Context-Guided Test-Time Reinforcement Learning for On-Device Large Language Models
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:Test-time Reinforcement Learning (TTRL) has shown promise in adapting foundation models for complex tasks at test-time, resulting in large performance improvements. TTRL leverages an elegant two-phase sampling strategy: first, multi-sampling derives a pseudo-label via majority voting, while subsequent downsampling and reward-based fine-tuning encourages the model to explore and learn diverse valid solutions, with the pseudo-label modulating the reward signal. Meanwhile, in-context learning has been widely explored at inference time and demonstrated the ability to enhance model performance without weight updates. However, TTRL's two-phase sampling strategy under-utilizes contextual guidance, which can potentially improve pseudo-label accuracy in the initial exploitation phase while regulating exploration in the second. To address this, we propose context-guided TTRL (CG-TTRL), integrating context dynamically into both sampling phases and propose a method for efficient context selection for on-device applications. Our evaluations on mathematical and scientific QA benchmarks show CG-TTRL outperforms TTRL (e.g. additional 7% relative accuracy improvement over TTRL), while boosting efficiency by obtaining strong performance after only a few steps of test-time training (e.g. 8% relative improvement rather than 1% over TTRL after 3 steps).
Efficient Solutions For An Intriguing Failure of LLMs: Long Context Window Does Not Mean LLMs Can Analyze Long Sequences Flawlessly
Aug 03, 2024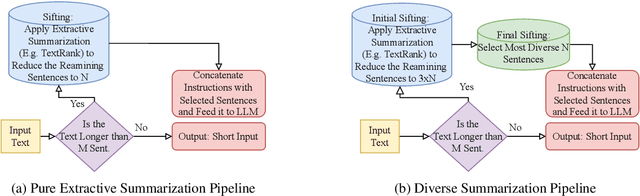
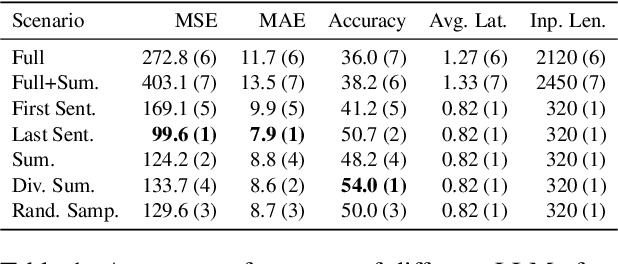
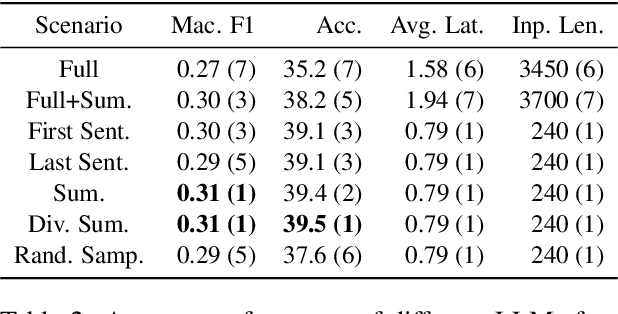
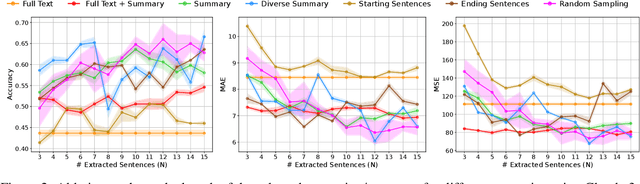
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in comprehending and analyzing lengthy sequential inputs, owing to their extensive context windows that allow processing millions of tokens in a single forward pass. However, this paper uncovers a surprising limitation: LLMs fall short when handling long input sequences. We investigate this issue using three datasets and two tasks (sentiment analysis and news categorization) across various LLMs, including Claude 3, Gemini Pro, GPT 3.5 Turbo, Llama 3 Instruct, and Mistral Instruct models. To address this limitation, we propose and evaluate ad-hoc solutions that substantially enhance LLMs' performance on long input sequences by up to 50%, while reducing API cost and latency by up to 93% and 50%, respectively.
You Need to Pay Better Attention
Mar 03, 2024


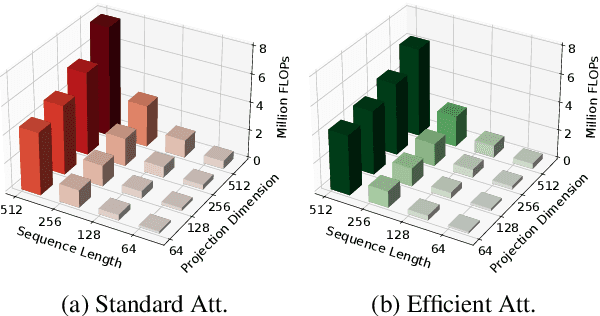
Abstract:We introduce three new attention mechanisms that outperform standard multi-head attention in terms of efficiency and learning capabilities, thereby improving the performance and broader deployability of Transformer models. Our first contribution is Optimised Attention, which performs similarly to standard attention, but has 3/4 as many parameters and one matrix multiplication fewer per head. Next, we introduce Efficient Attention, which performs on par with standard attention with only 1/2 as many parameters as many parameters and two matrix multiplications fewer per head and is up to twice as fast as standard attention. Lastly, we introduce Super Attention, which surpasses standard attention by a significant margin in both vision and natural language processing tasks while having fewer parameters and matrix multiplications. In addition to providing rigorous mathematical comparisons, we evaluate the presented attention mechanisms on MNIST, CIFAR100, IMDB Movie Reviews, and Amazon Reviews datasets.
Can We Generate Realistic Hands Only Using Convolution?
Jan 03, 2024
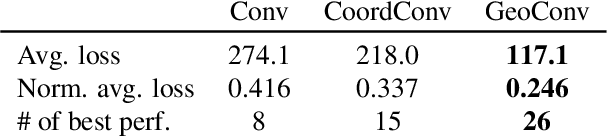
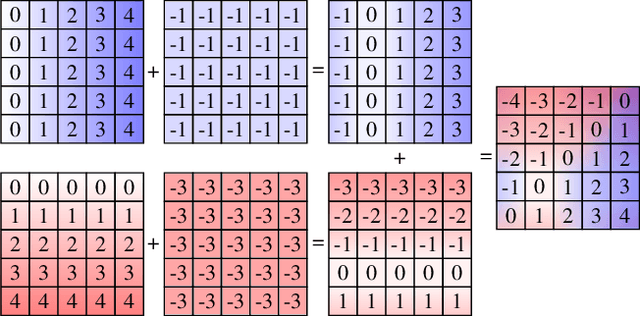
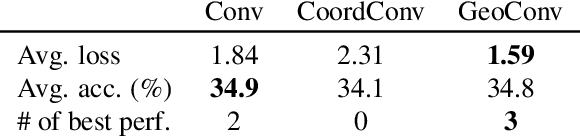
Abstract:The enduring inability of image generative models to recreate intricate geometric features, such as those present in human hands and fingers has been an ongoing problem in image generation for nearly a decade. While strides have been made by increasing model sizes and diversifying training datasets, this issue remains prevalent across all models, from denoising diffusion models to Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN), pointing to a fundamental shortcoming in the underlying architectures. In this paper, we demonstrate how this problem can be mitigated by augmenting convolution layers geometric capabilities through providing them with a single input channel incorporating the relative $n$-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system. We show that this drastically improves quality of hand and face images generated by GANs and Variational AutoEncoders (VAE).
Lon-eå at SemEval-2023 Task 11: A Comparison of\\Activation Functions for Soft and Hard Label Prediction
Mar 04, 2023Abstract:We study the influence of different activation functions in the output layer of deep neural network models for soft and hard label prediction in the learning with disagreement task. In this task, the goal is to quantify the amount of disagreement via predicting soft labels. To predict the soft labels, we use BERT-based preprocessors and encoders and vary the activation function used in the output layer, while keeping other parameters constant. The soft labels are then used for the hard label prediction. The activation functions considered are sigmoid as well as a step-function that is added to the model post-training and a sinusoidal activation function, which is introduced for the first time in this paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge