Iacopo Ghinassi
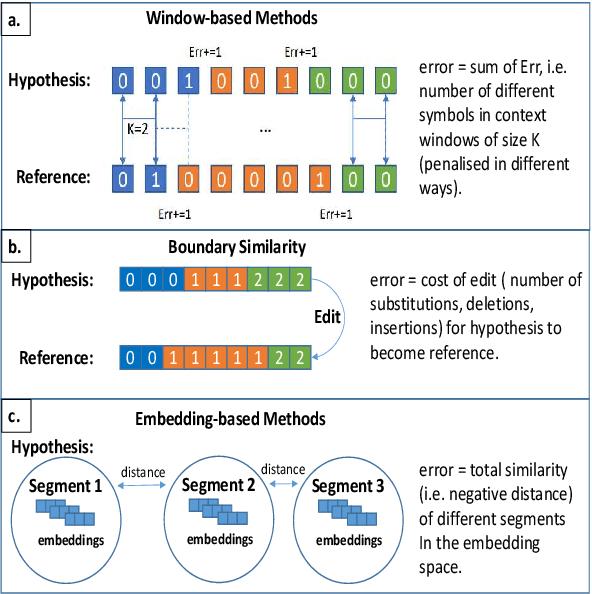
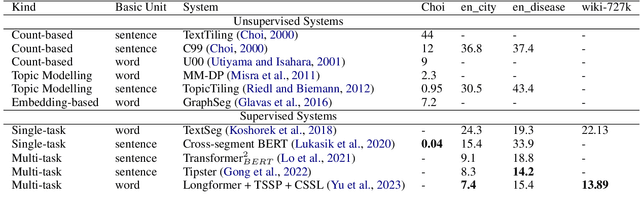
Recent Trends in Linear Text Segmentation: a Survey
Nov 25, 2024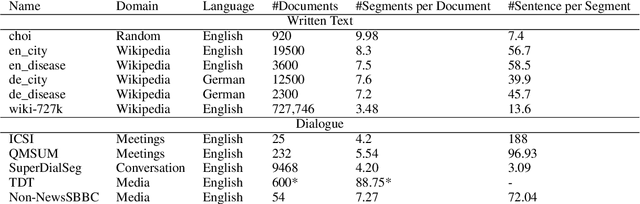
Abstract:Linear Text Segmentation is the task of automatically tagging text documents with topic shifts, i.e. the places in the text where the topics change. A well-established area of research in Natural Language Processing, drawing from well-understood concepts in linguistic and computational linguistic research, the field has recently seen a lot of interest as a result of the surge of text, video, and audio available on the web, which in turn require ways of summarising and categorizing the mole of content for which linear text segmentation is a fundamental step. In this survey, we provide an extensive overview of current advances in linear text segmentation, describing the state of the art in terms of resources and approaches for the task. Finally, we highlight the limitations of available resources and of the task itself, while indicating ways forward based on the most recent literature and under-explored research directions.
Efficient Aspect-Based Summarization of Climate Change Reports with Small Language Models
Nov 21, 2024
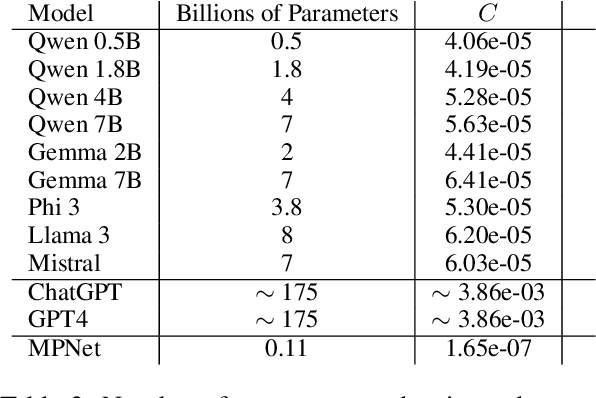
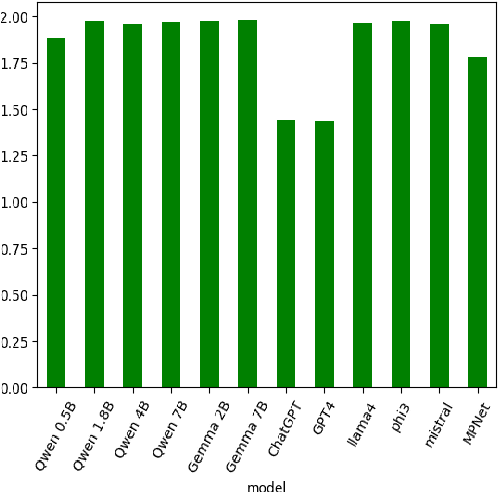
Abstract:The use of Natural Language Processing (NLP) for helping decision-makers with Climate Change action has recently been highlighted as a use case aligning with a broader drive towards NLP technologies for social good. In this context, Aspect-Based Summarization (ABS) systems that extract and summarize relevant information are particularly useful as they provide stakeholders with a convenient way of finding relevant information in expert-curated reports. In this work, we release a new dataset for ABS of Climate Change reports and we employ different Large Language Models (LLMs) and so-called Small Language Models (SLMs) to tackle this problem in an unsupervised way. Considering the problem at hand, we also show how SLMs are not significantly worse for the problem while leading to reduced carbon footprint; we do so by applying for the first time an existing framework considering both energy efficiency and task performance to the evaluation of zero-shot generative models for ABS. Overall, our results show that modern language models, both big and small, can effectively tackle ABS for Climate Change reports but more research is needed when we frame the problem as a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) problem and our work and dataset will help foster efforts in this direction.
Efficient Solutions For An Intriguing Failure of LLMs: Long Context Window Does Not Mean LLMs Can Analyze Long Sequences Flawlessly
Aug 03, 2024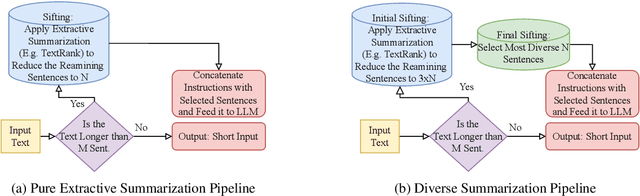
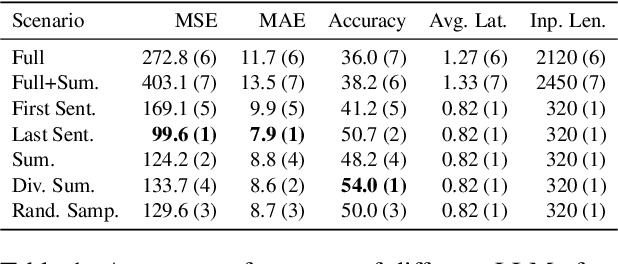
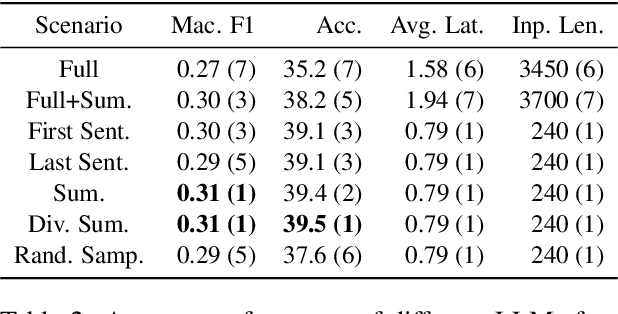
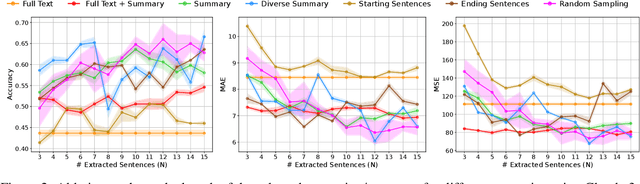
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in comprehending and analyzing lengthy sequential inputs, owing to their extensive context windows that allow processing millions of tokens in a single forward pass. However, this paper uncovers a surprising limitation: LLMs fall short when handling long input sequences. We investigate this issue using three datasets and two tasks (sentiment analysis and news categorization) across various LLMs, including Claude 3, Gemini Pro, GPT 3.5 Turbo, Llama 3 Instruct, and Mistral Instruct models. To address this limitation, we propose and evaluate ad-hoc solutions that substantially enhance LLMs' performance on long input sequences by up to 50%, while reducing API cost and latency by up to 93% and 50%, respectively.
MoralBERT: Detecting Moral Values in Social Discourse
Mar 12, 2024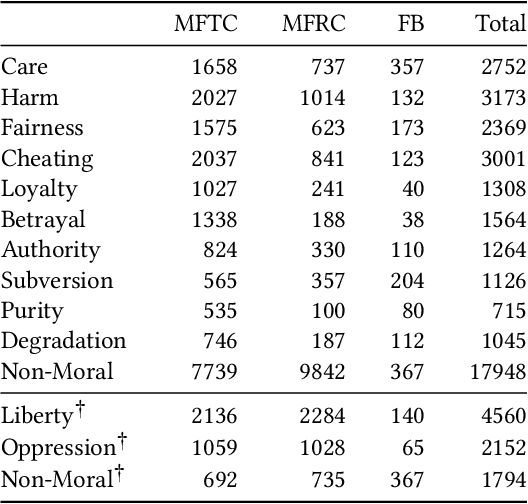
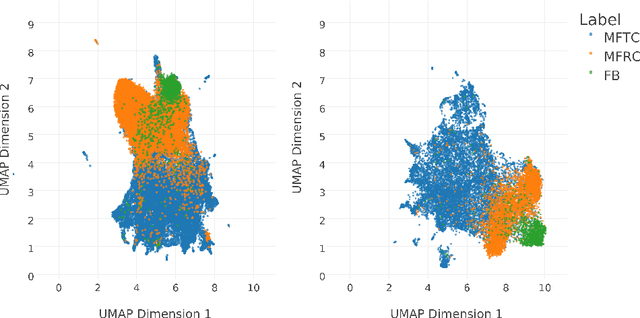
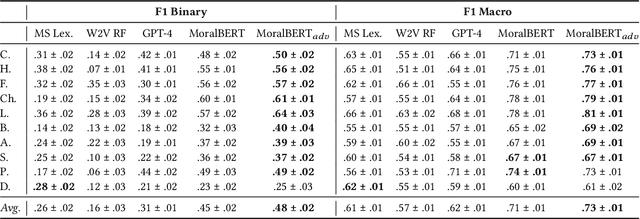
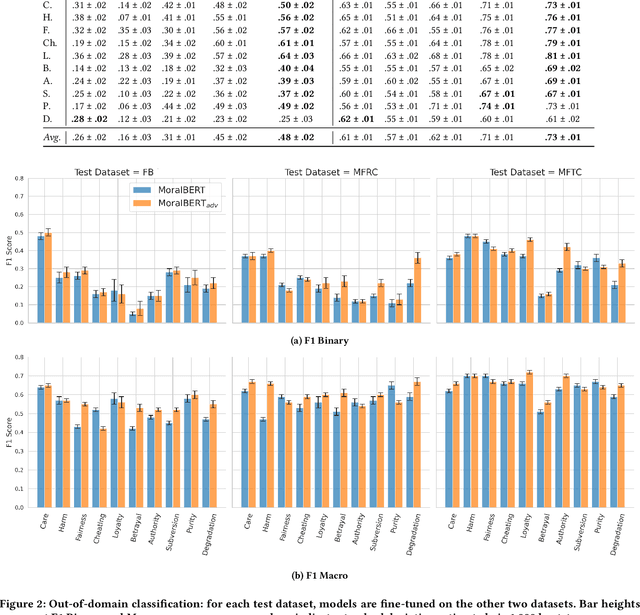
Abstract:Morality plays a fundamental role in how we perceive information while greatly influencing our decisions and judgements. Controversial topics, including vaccination, abortion, racism, and sexuality, often elicit opinions and attitudes that are not solely based on evidence but rather reflect moral worldviews. Recent advances in natural language processing have demonstrated that moral values can be gauged in human-generated textual content. Here, we design a range of language representation models fine-tuned to capture exactly the moral nuances in text, called MoralBERT. We leverage annotated moral data from three distinct sources: Twitter, Reddit, and Facebook user-generated content covering various socially relevant topics. This approach broadens linguistic diversity and potentially enhances the models' ability to comprehend morality in various contexts. We also explore a domain adaptation technique and compare it to the standard fine-tuned BERT model, using two different frameworks for moral prediction: single-label and multi-label. We compare in-domain approaches with conventional models relying on lexicon-based techniques, as well as a Machine Learning classifier with Word2Vec representation. Our results showed that in-domain prediction models significantly outperformed traditional models. While the single-label setting reaches a higher accuracy than previously achieved for the task when using BERT pretrained models. Experiments in an out-of-domain setting, instead, suggest that further work is needed for existing domain adaptation techniques to generalise between different social media platforms, especially for the multi-label task. The investigations and outcomes from this study pave the way for further exploration, enabling a more profound comprehension of moral narratives about controversial social issues.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge