Efficient Aspect-Based Summarization of Climate Change Reports with Small Language Models
Paper and Code
Nov 21, 2024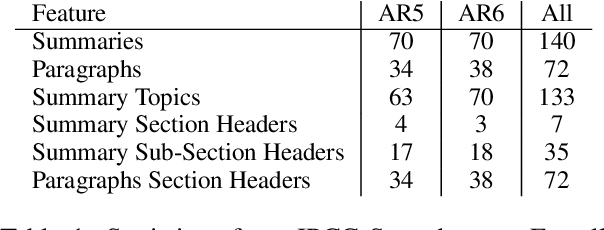
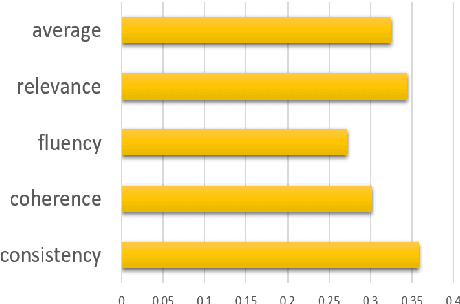
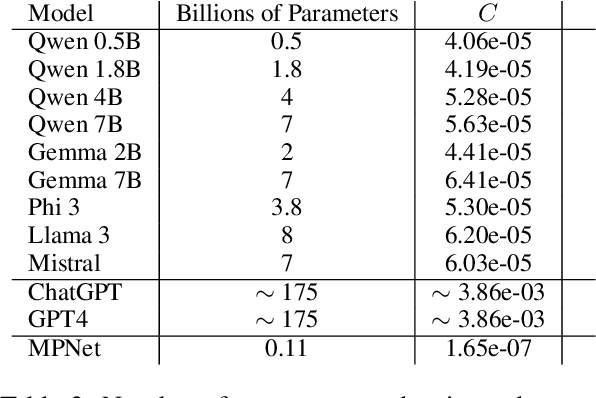
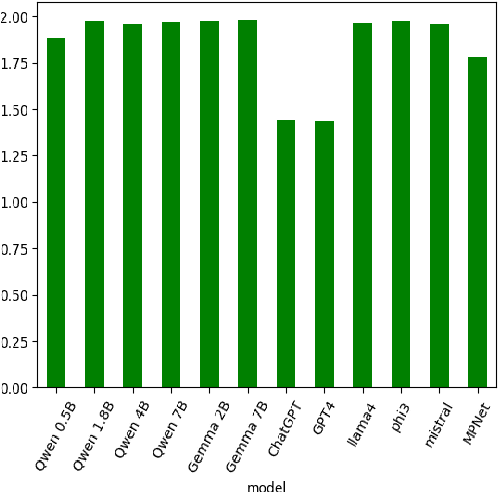
The use of Natural Language Processing (NLP) for helping decision-makers with Climate Change action has recently been highlighted as a use case aligning with a broader drive towards NLP technologies for social good. In this context, Aspect-Based Summarization (ABS) systems that extract and summarize relevant information are particularly useful as they provide stakeholders with a convenient way of finding relevant information in expert-curated reports. In this work, we release a new dataset for ABS of Climate Change reports and we employ different Large Language Models (LLMs) and so-called Small Language Models (SLMs) to tackle this problem in an unsupervised way. Considering the problem at hand, we also show how SLMs are not significantly worse for the problem while leading to reduced carbon footprint; we do so by applying for the first time an existing framework considering both energy efficiency and task performance to the evaluation of zero-shot generative models for ABS. Overall, our results show that modern language models, both big and small, can effectively tackle ABS for Climate Change reports but more research is needed when we frame the problem as a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) problem and our work and dataset will help foster efforts in this direction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge