Ryan Li
OpenCUA: Open Foundations for Computer-Use Agents
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Vision-language models have demonstrated impressive capabilities as computer-use agents (CUAs) capable of automating diverse computer tasks. As their commercial potential grows, critical details of the most capable CUA systems remain closed. As these agents will increasingly mediate digital interactions and execute consequential decisions on our behalf, the research community needs access to open CUA frameworks to study their capabilities, limitations, and risks. To bridge this gap, we propose OpenCUA, a comprehensive open-source framework for scaling CUA data and foundation models. Our framework consists of: (1) an annotation infrastructure that seamlessly captures human computer-use demonstrations; (2) AgentNet, the first large-scale computer-use task dataset spanning 3 operating systems and 200+ applications and websites; (3) a scalable pipeline that transforms demonstrations into state-action pairs with reflective long Chain-of-Thought reasoning that sustain robust performance gains as data scales. Our end-to-end agent models demonstrate strong performance across CUA benchmarks. In particular, OpenCUA-32B achieves an average success rate of 34.8% on OSWorld-Verified, establishing a new state-of-the-art (SOTA) among open-source models and surpassing OpenAI CUA (GPT-4o). Further analysis confirms that our approach generalizes well across domains and benefits significantly from increased test-time computation. We release our annotation tool, datasets, code, and models to build open foundations for further CUA research.
BountyBench: Dollar Impact of AI Agent Attackers and Defenders on Real-World Cybersecurity Systems
May 21, 2025Abstract:AI agents have the potential to significantly alter the cybersecurity landscape. To help us understand this change, we introduce the first framework to capture offensive and defensive cyber-capabilities in evolving real-world systems. Instantiating this framework with BountyBench, we set up 25 systems with complex, real-world codebases. To capture the vulnerability lifecycle, we define three task types: Detect (detecting a new vulnerability), Exploit (exploiting a specific vulnerability), and Patch (patching a specific vulnerability). For Detect, we construct a new success indicator, which is general across vulnerability types and provides localized evaluation. We manually set up the environment for each system, including installing packages, setting up server(s), and hydrating database(s). We add 40 bug bounties, which are vulnerabilities with monetary awards from \$10 to \$30,485, and cover 9 of the OWASP Top 10 Risks. To modulate task difficulty, we devise a new strategy based on information to guide detection, interpolating from identifying a zero day to exploiting a specific vulnerability. We evaluate 5 agents: Claude Code, OpenAI Codex CLI, and custom agents with GPT-4.1, Gemini 2.5 Pro Preview, and Claude 3.7 Sonnet Thinking. Given up to three attempts, the top-performing agents are Claude Code (5% on Detect, mapping to \$1,350), Custom Agent with Claude 3.7 Sonnet Thinking (5% on Detect, mapping to \$1,025; 67.5% on Exploit), and OpenAI Codex CLI (5% on Detect, mapping to \$2,400; 90% on Patch, mapping to \$14,422). OpenAI Codex CLI and Claude Code are more capable at defense, achieving higher Patch scores of 90% and 87.5%, compared to Exploit scores of 32.5% and 57.5% respectively; in contrast, the custom agents are relatively balanced between offense and defense, achieving Exploit scores of 40-67.5% and Patch scores of 45-60%.
FedGAT: A Privacy-Preserving Federated Approximation Algorithm for Graph Attention Networks
Dec 20, 2024



Abstract:Federated training methods have gained popularity for graph learning with applications including friendship graphs of social media sites and customer-merchant interaction graphs of huge online marketplaces. However, privacy regulations often require locally generated data to be stored on local clients. The graph is then naturally partitioned across clients, with no client permitted access to information stored on another. Cross-client edges arise naturally in such cases and present an interesting challenge to federated training methods, as training a graph model at one client requires feature information of nodes on the other end of cross-client edges. Attempting to retain such edges often incurs significant communication overhead, and dropping them altogether reduces model performance. In simpler models such as Graph Convolutional Networks, this can be fixed by communicating a limited amount of feature information across clients before training, but GATs (Graph Attention Networks) require additional information that cannot be pre-communicated, as it changes from training round to round. We introduce the Federated Graph Attention Network (FedGAT) algorithm for semi-supervised node classification, which approximates the behavior of GATs with provable bounds on the approximation error. FedGAT requires only one pre-training communication round, significantly reducing the communication overhead for federated GAT training. We then analyze the error in the approximation and examine the communication overhead and computational complexity of the algorithm. Experiments show that FedGAT achieves nearly the same accuracy as a GAT model in a centralised setting, and its performance is robust to the number of clients as well as data distribution.
Sketch2Code: Evaluating Vision-Language Models for Interactive Web Design Prototyping
Oct 21, 2024Abstract:Sketches are a natural and accessible medium for UI designers to conceptualize early-stage ideas. However, existing research on UI/UX automation often requires high-fidelity inputs like Figma designs or detailed screenshots, limiting accessibility and impeding efficient design iteration. To bridge this gap, we introduce Sketch2Code, a benchmark that evaluates state-of-the-art Vision Language Models (VLMs) on automating the conversion of rudimentary sketches into webpage prototypes. Beyond end-to-end benchmarking, Sketch2Code supports interactive agent evaluation that mimics real-world design workflows, where a VLM-based agent iteratively refines its generations by communicating with a simulated user, either passively receiving feedback instructions or proactively asking clarification questions. We comprehensively analyze ten commercial and open-source models, showing that Sketch2Code is challenging for existing VLMs; even the most capable models struggle to accurately interpret sketches and formulate effective questions that lead to steady improvement. Nevertheless, a user study with UI/UX experts reveals a significant preference for proactive question-asking over passive feedback reception, highlighting the need to develop more effective paradigms for multi-turn conversational agents.
Enhancing Language Model Reasoning via Weighted Reasoning in Self-Consistency
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:While large language models (LLMs) have rapidly improved their performance on a broad number of tasks, they still often fall short on reasoning tasks. As LLMs become more integrated in diverse real-world tasks, advancing their reasoning capabilities is crucial to their effectiveness in nuanced, complex problems. Wang et al's self-consistency framework reveals that sampling multiple rationales before taking a majority vote reliably improves model performance across various closed-answer reasoning tasks. Standard methods based on this framework aggregate the final decisions of these rationales but fail to utilize the detailed step-by-step reasoning paths applied by these paths. Our work enhances this approach by incorporating and analyzing both the reasoning paths of these rationales in addition to their final decisions before taking a majority vote. These methods not only improve the reliability of reasoning paths but also cause more robust performance on complex reasoning tasks.
CultureBank: An Online Community-Driven Knowledge Base Towards Culturally Aware Language Technologies
Apr 23, 2024Abstract:To enhance language models' cultural awareness, we design a generalizable pipeline to construct cultural knowledge bases from different online communities on a massive scale. With the pipeline, we construct CultureBank, a knowledge base built upon users' self-narratives with 12K cultural descriptors sourced from TikTok and 11K from Reddit. Unlike previous cultural knowledge resources, CultureBank contains diverse views on cultural descriptors to allow flexible interpretation of cultural knowledge, and contextualized cultural scenarios to help grounded evaluation. With CultureBank, we evaluate different LLMs' cultural awareness, and identify areas for improvement. We also fine-tune a language model on CultureBank: experiments show that it achieves better performances on two downstream cultural tasks in a zero-shot setting. Finally, we offer recommendations based on our findings for future culturally aware language technologies. The project page is https://culturebank.github.io . The code and model is at https://github.com/SALT-NLP/CultureBank . The released CultureBank dataset is at https://huggingface.co/datasets/SALT-NLP/CultureBank .
NL2INTERFACE: Interactive Visualization Interface Generation from Natural Language Queries
Sep 24, 2022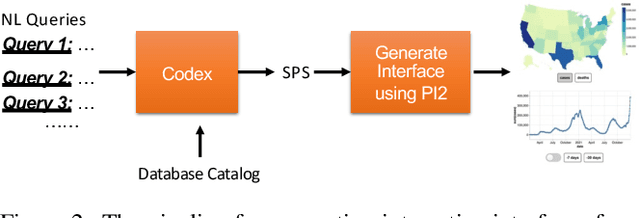
Abstract:We develop NL2INTERFACE to explore the potential of generating usable interactive multi-visualization interfaces from natural language queries. With NL2INTERFACE, users can directly write natural language queries to automatically generate a fully interactive multi-visualization interface without any extra effort of learning a tool or programming language. Further, users can interact with the interfaces to easily transform the data and quickly see the results in the visualizations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge