Ruyi Zhang
Attonsecond Streaking Phase Retrieval Via Deep Learning Methods
May 06, 2025Abstract:Attosecond streaking phase retrieval is essential for resolving electron dynamics on sub-femtosecond time scales yet traditional algorithms rely on iterative minimization and central momentum approximations that degrade accuracy for broadband pulses. In this work phase retrieval is reformulated as a supervised computer-vision problem and four neural architectures are systematically compared. A convolutional network demonstrates strong sensitivity to local streak edges but lacks global context; a vision transformer captures long-range delay-energy correlations at the expense of local inductive bias; a hybrid CNN-ViT model unites local feature extraction and full-graph attention; and a capsule network further enforces spatial pose agreement through dynamic routing. A theoretical analysis introduces local, global and positional sensitivity measures and derives surrogate error bounds that predict the strict ordering $CNN<ViT<Hybrid<Capsule$. Controlled experiments on synthetic streaking spectrograms confirm this hierarchy, with the capsule network achieving the highest retrieval fidelity. Looking forward, embedding the strong-field integral into physics-informed neural networks and exploring photonic hardware implementations promise pathways toward real-time attosecond pulse characterization under demanding experimental conditions.
Reciprocal Point Learning Network with Large Electromagnetic Kernel for SAR Open-Set Recognition
Nov 07, 2024



Abstract:The limitations of existing Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Automatic Target Recognition (ATR) methods lie in their confinement by the closed-environment assumption, hindering their effective and robust handling of unknown target categories in open environments. Open Set Recognition (OSR), a pivotal facet for algorithmic practicality, intends to categorize known classes while denoting unknown ones as "unknown." The chief challenge in OSR involves concurrently mitigating risks associated with generalizing features from a restricted set of known classes to numerous unknown samples and the open space exposure to potential unknown data. To enhance open-set SAR classification, a method called scattering kernel with reciprocal learning network is proposed. Initially, a feature learning framework is constructed based on reciprocal point learning (RPL), establishing a bounded space for potential unknown classes. This approach indirectly introduces unknown information into a learner confined to known classes, thereby acquiring more concise and discriminative representations. Subsequently, considering the variability in the imaging of targets at different angles and the discreteness of components in SAR images, a proposal is made to design convolutional kernels based on large-sized attribute scattering center models. This enhances the ability to extract intrinsic non-linear features and specific scattering characteristics in SAR images, thereby improving the discriminative features of the model and mitigating the impact of imaging variations on classification performance. Experiments on the MSTAR datasets substantiate the superior performance of the proposed approach called ASC-RPL over mainstream methods.
Angel or Devil: Discriminating Hard Samples and Anomaly Contaminations for Unsupervised Time Series Anomaly Detection
Oct 26, 2024



Abstract:Training in unsupervised time series anomaly detection is constantly plagued by the discrimination between harmful `anomaly contaminations' and beneficial `hard normal samples'. These two samples exhibit analogous loss behavior that conventional loss-based methodologies struggle to differentiate. To tackle this problem, we propose a novel approach that supplements traditional loss behavior with `parameter behavior', enabling a more granular characterization of anomalous patterns. Parameter behavior is formalized by measuring the parametric response to minute perturbations in input samples. Leveraging the complementary nature of parameter and loss behaviors, we further propose a dual Parameter-Loss Data Augmentation method (termed PLDA), implemented within the reinforcement learning paradigm. During the training phase of anomaly detection, PLDA dynamically augments the training data through an iterative process that simultaneously mitigates anomaly contaminations while amplifying informative hard normal samples. PLDA demonstrates remarkable versatility, which can serve as an additional component that seamlessly integrated with existing anomaly detectors to enhance their detection performance. Extensive experiments on ten datasets show that PLDA significantly improves the performance of four distinct detectors by up to 8\%, outperforming three state-of-the-art data augmentation methods.
Improving Ranking Correlation of Supernet with Candidates Enhancement and Progressive Training
Aug 12, 2021
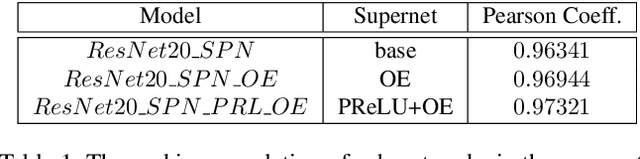

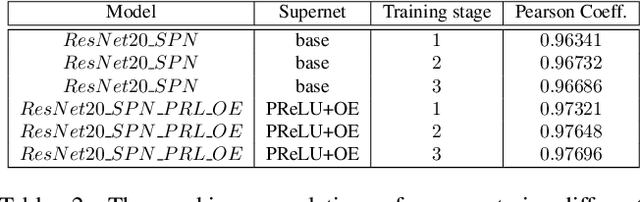
Abstract:One-shot neural architecture search (NAS) applies weight-sharing supernet to reduce the unaffordable computation overhead of automated architecture designing. However, the weight-sharing technique worsens the ranking consistency of performance due to the interferences between different candidate networks. To address this issue, we propose a candidates enhancement method and progressive training pipeline to improve the ranking correlation of supernet. Specifically, we carefully redesign the sub-networks in the supernet and map the original supernet to a new one of high capacity. In addition, we gradually add narrow branches of supernet to reduce the degree of weight sharing which effectively alleviates the mutual interference between sub-networks. Finally, our method ranks the 1st place in the Supernet Track of CVPR2021 1st Lightweight NAS Challenge.
Cascade Bagging for Accuracy Prediction with Few Training Samples
Aug 12, 2021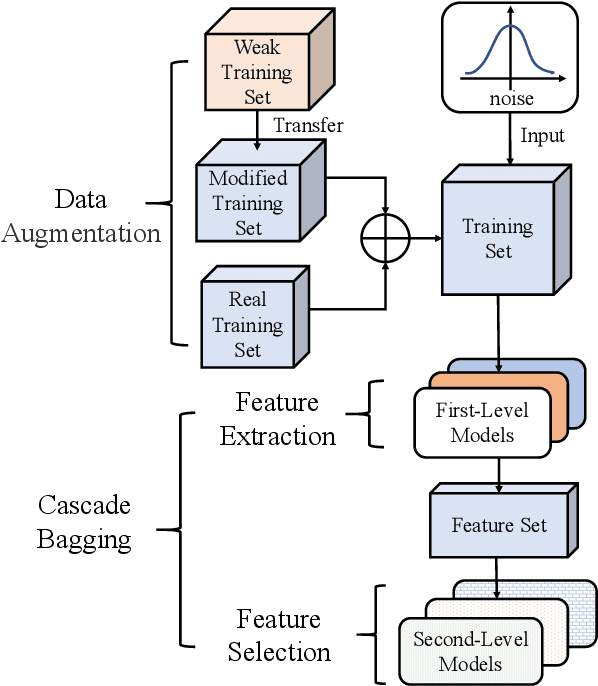


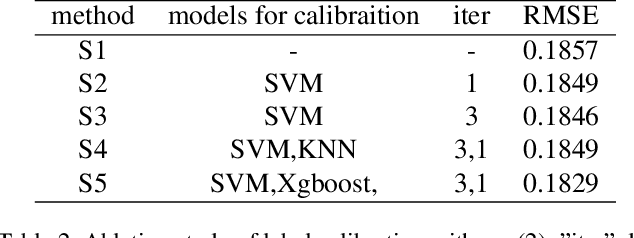
Abstract:Accuracy predictor is trained to predict the validation accuracy of an network from its architecture encoding. It can effectively assist in designing networks and improving Neural Architecture Search(NAS) efficiency. However, a high-performance predictor depends on adequate trainning samples, which requires unaffordable computation overhead. To alleviate this problem, we propose a novel framework to train an accuracy predictor under few training samples. The framework consists ofdata augmentation methods and an ensemble learning algorithm. The data augmentation methods calibrate weak labels and inject noise to feature space. The ensemble learning algorithm, termed cascade bagging, trains two-level models by sampling data and features. In the end, the advantages of above methods are proved in the Performance Prediciton Track of CVPR2021 1st Lightweight NAS Challenge. Our code is made public at: https://github.com/dlongry/Solutionto-CVPR2021-NAS-Track2.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge