Rui Qiu
Completing A Systematic Review in Hours instead of Months with Interactive AI Agents
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:Systematic reviews (SRs) are vital for evidence-based practice in high stakes disciplines, such as healthcare, but are often impeded by intensive labors and lengthy processes that can take months to complete. Due to the high demand for domain expertise, existing automatic summarization methods fail to accurately identify relevant studies and generate high-quality summaries. To that end, we introduce InsightAgent, a human-centered interactive AI agent powered by large language models that revolutionize this workflow. InsightAgent partitions a large literature corpus based on semantics and employs a multi-agent design for more focused processing of literature, leading to significant improvement in the quality of generated SRs. InsightAgent also provides intuitive visualizations of the corpus and agent trajectories, allowing users to effortlessly monitor the actions of the agent and provide real-time feedback based on their expertise. Our user studies with 9 medical professionals demonstrate that the visualization and interaction mechanisms can effectively improve the quality of synthesized SRs by 27.2%, reaching 79.7% of human-written quality. At the same time, user satisfaction is improved by 34.4%. With InsightAgent, it only takes a clinician about 1.5 hours, rather than months, to complete a high-quality systematic review.
PIG: Prompt Images Guidance for Night-Time Scene Parsing
Jun 15, 2024



Abstract:Night-time scene parsing aims to extract pixel-level semantic information in night images, aiding downstream tasks in understanding scene object distribution. Due to limited labeled night image datasets, unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) has become the predominant method for studying night scenes. UDA typically relies on paired day-night image pairs to guide adaptation, but this approach hampers dataset construction and restricts generalization across night scenes in different datasets. Moreover, UDA, focusing on network architecture and training strategies, faces difficulties in handling classes with few domain similarities. In this paper, we leverage Prompt Images Guidance (PIG) to enhance UDA with supplementary night knowledge. We propose a Night-Focused Network (NFNet) to learn night-specific features from both target domain images and prompt images. To generate high-quality pseudo-labels, we propose Pseudo-label Fusion via Domain Similarity Guidance (FDSG). Classes with fewer domain similarities are predicted by NFNet, which excels in parsing night features, while classes with more domain similarities are predicted by UDA, which has rich labeled semantics. Additionally, we propose two data augmentation strategies: the Prompt Mixture Strategy (PMS) and the Alternate Mask Strategy (AMS), aimed at mitigating the overfitting of the NFNet to a few prompt images. We conduct extensive experiments on four night-time datasets: NightCity, NightCity+, Dark Zurich, and ACDC. The results indicate that utilizing PIG can enhance the parsing accuracy of UDA.
Semi-supervised Fréchet Regression
Apr 16, 2024Abstract:This paper explores the field of semi-supervised Fr\'echet regression, driven by the significant costs associated with obtaining non-Euclidean labels. Methodologically, we propose two novel methods: semi-supervised NW Fr\'echet regression and semi-supervised kNN Fr\'echet regression, both based on graph distance acquired from all feature instances. These methods extend the scope of existing semi-supervised Euclidean regression methods. We establish their convergence rates with limited labeled data and large amounts of unlabeled data, taking into account the low-dimensional manifold structure of the feature space. Through comprehensive simulations across diverse settings and applications to real data, we demonstrate the superior performance of our methods over their supervised counterparts. This study addresses existing research gaps and paves the way for further exploration and advancements in the field of semi-supervised Fr\'echet regression.
SKG: A Versatile Information Retrieval and Analysis Framework for Academic Papers with Semantic Knowledge Graphs
Jun 07, 2023Abstract:The number of published research papers has experienced exponential growth in recent years, which makes it crucial to develop new methods for efficient and versatile information extraction and knowledge discovery. To address this need, we propose a Semantic Knowledge Graph (SKG) that integrates semantic concepts from abstracts and other meta-information to represent the corpus. The SKG can support various semantic queries in academic literature thanks to the high diversity and rich information content stored within. To extract knowledge from unstructured text, we develop a Knowledge Extraction Module that includes a semi-supervised pipeline for entity extraction and entity normalization. We also create an ontology to integrate the concepts with other meta information, enabling us to build the SKG. Furthermore, we design and develop a dataflow system that demonstrates how to conduct various semantic queries flexibly and interactively over the SKG. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, we conduct the research based on the visualization literature and provide real-world use cases to show the usefulness of the SKG. The dataset and codes for this work are available at https://osf.io/aqv8p/?view_only=2c26b36e3e3941ce999df47e4616207f.
3D Random Occlusion and Multi-Layer Projection for Deep Multi-Camera Pedestrian Localization
Jul 25, 2022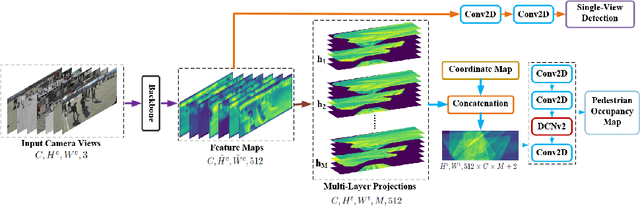
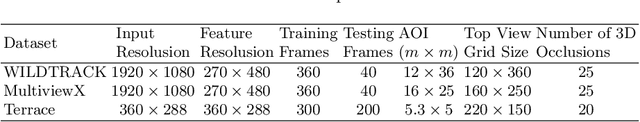
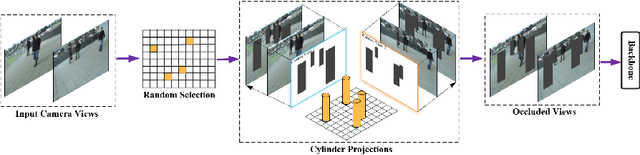
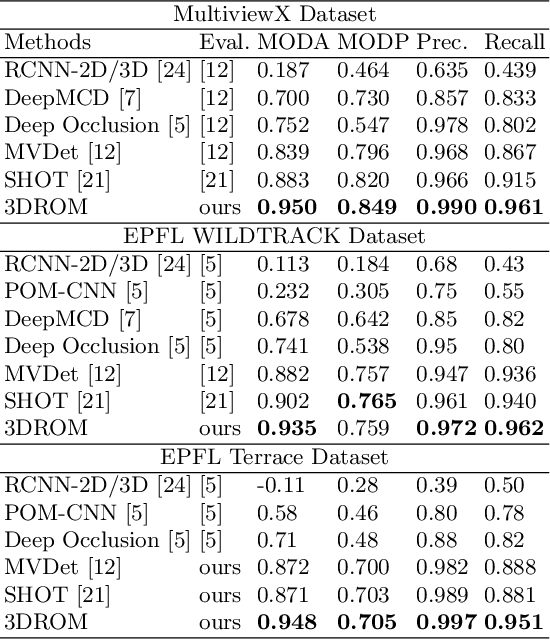
Abstract:Although deep-learning based methods for monocular pedestrian detection have made great progress, they are still vulnerable to heavy occlusions. Using multi-view information fusion is a potential solution but has limited applications, due to the lack of annotated training samples in existing multi-view datasets, which increases the risk of overfitting. To address this problem, a data augmentation method is proposed to randomly generate 3D cylinder occlusions, on the ground plane, which are of the average size of pedestrians and projected to multiple views, to relieve the impact of overfitting in the training. Moreover, the feature map of each view is projected to multiple parallel planes at different heights, by using homographies, which allows the CNNs to fully utilize the features across the height of each pedestrian to infer the locations of pedestrians on the ground plane. The proposed 3DROM method has a greatly improved performance in comparison with the state-of-the-art deep-learning based methods for multi-view pedestrian detection.
Random Forests Weighted Local Fréchet Regression with Theoretical Guarantee
Feb 10, 2022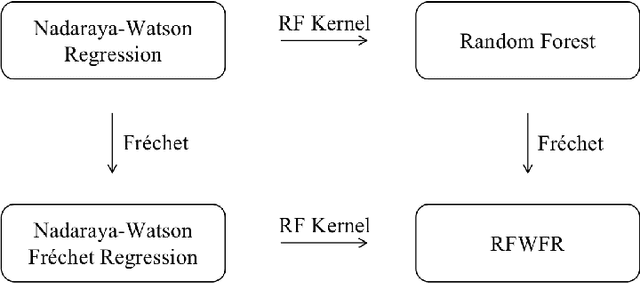
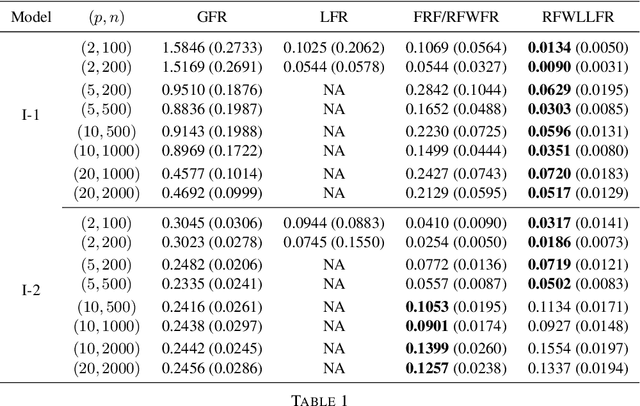
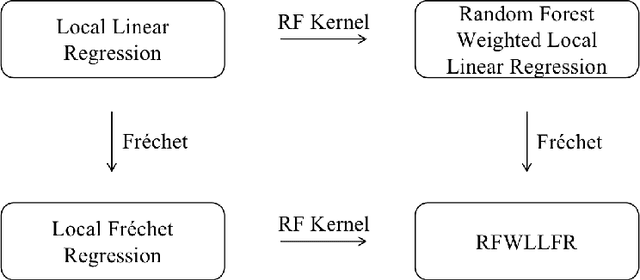

Abstract:Statistical analysis is increasingly confronted with complex data from general metric spaces, such as symmetric positive definite matrix-valued data and probability distribution functions. [47] and [17] establish a general paradigm of Fr\'echet regression with complex metric space valued responses and Euclidean predictors. However, their proposed local Fr\'echet regression approach involves nonparametric kernel smoothing and suffers from the curse of dimensionality. To address this issue, we in this paper propose a novel random forests weighted local Fr\'echet regression paradigm. The main mechanism of our approach relies on the adaptive kernels generated by random forests. Our first method utilizes these weights as the local average to solve the Fr\'echet mean, while the second method performs local linear Fr\'echet regression, making both methods locally adaptive. Our proposals significantly improve existing Fr\'echet regression methods. Based on the theory of infinite order U-processes and infinite order Mmn-estimator, we establish the consistency, rate of convergence, and asymptotic normality for our proposed random forests weighted Fr\'echet regression estimator, which covers the current large sample theory of random forests with Euclidean responses as a special case. Numerical studies show the superiority of our proposed two methods for Fr\'echet regression with several commonly encountered types of responses such as probability distribution functions, symmetric positive definite matrices, and sphere data. The practical merits of our proposals are also demonstrated through the application to the human mortality distribution data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge