Romain Paulus
CO-Search: COVID-19 Information Retrieval with Semantic Search, Question Answering, and Abstractive Summarization
Jun 17, 2020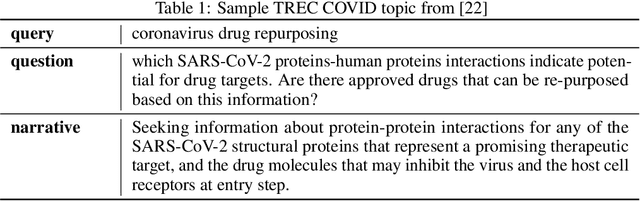
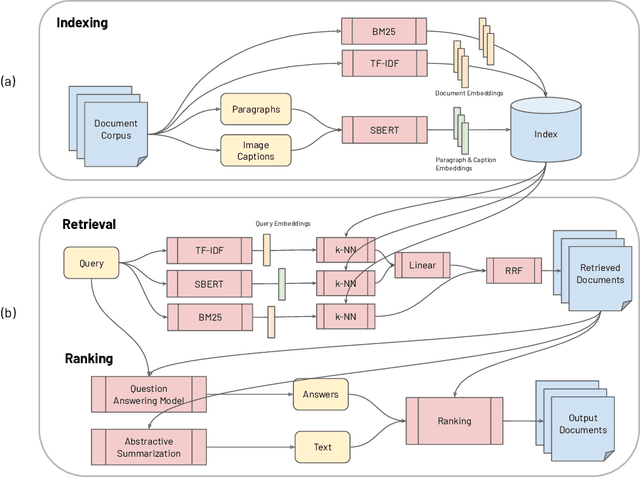
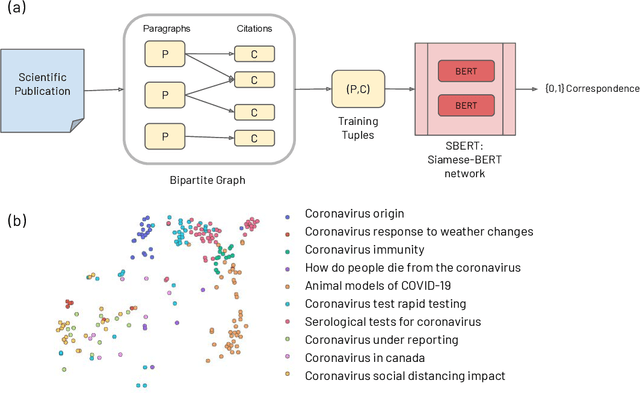

Abstract:The COVID-19 global pandemic has resulted in international efforts to understand, track, and mitigate the disease, yielding a significant corpus of COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2-related publications across scientific disciplines. As of May 2020, 128,000 coronavirus-related publications have been collected through the COVID-19 Open Research Dataset Challenge. Here we present CO-Search, a retriever-ranker semantic search engine designed to handle complex queries over the COVID-19 literature, potentially aiding overburdened health workers in finding scientific answers during a time of crisis. The retriever is built from a Siamese-BERT encoder that is linearly composed with a TF-IDF vectorizer, and reciprocal-rank fused with a BM25 vectorizer. The ranker is composed of a multi-hop question-answering module, that together with a multi-paragraph abstractive summarizer adjust retriever scores. To account for the domain-specific and relatively limited dataset, we generate a bipartite graph of document paragraphs and citations, creating 1.3 million (citation title, paragraph) tuples for training the encoder. We evaluate our system on the data of the TREC-COVID information retrieval challenge. CO-Search obtains top performance on the datasets of the first and second rounds, across several key metrics: normalized discounted cumulative gain, precision, mean average precision, and binary preference.
Improving Abstraction in Text Summarization
Aug 23, 2018



Abstract:Abstractive text summarization aims to shorten long text documents into a human readable form that contains the most important facts from the original document. However, the level of actual abstraction as measured by novel phrases that do not appear in the source document remains low in existing approaches. We propose two techniques to improve the level of abstraction of generated summaries. First, we decompose the decoder into a contextual network that retrieves relevant parts of the source document, and a pretrained language model that incorporates prior knowledge about language generation. Second, we propose a novelty metric that is optimized directly through policy learning to encourage the generation of novel phrases. Our model achieves results comparable to state-of-the-art models, as determined by ROUGE scores and human evaluations, while achieving a significantly higher level of abstraction as measured by n-gram overlap with the source document.
A Deep Reinforced Model for Abstractive Summarization
Nov 13, 2017



Abstract:Attentional, RNN-based encoder-decoder models for abstractive summarization have achieved good performance on short input and output sequences. For longer documents and summaries however these models often include repetitive and incoherent phrases. We introduce a neural network model with a novel intra-attention that attends over the input and continuously generated output separately, and a new training method that combines standard supervised word prediction and reinforcement learning (RL). Models trained only with supervised learning often exhibit "exposure bias" - they assume ground truth is provided at each step during training. However, when standard word prediction is combined with the global sequence prediction training of RL the resulting summaries become more readable. We evaluate this model on the CNN/Daily Mail and New York Times datasets. Our model obtains a 41.16 ROUGE-1 score on the CNN/Daily Mail dataset, an improvement over previous state-of-the-art models. Human evaluation also shows that our model produces higher quality summaries.
Ask Me Anything: Dynamic Memory Networks for Natural Language Processing
Mar 05, 2016

Abstract:Most tasks in natural language processing can be cast into question answering (QA) problems over language input. We introduce the dynamic memory network (DMN), a neural network architecture which processes input sequences and questions, forms episodic memories, and generates relevant answers. Questions trigger an iterative attention process which allows the model to condition its attention on the inputs and the result of previous iterations. These results are then reasoned over in a hierarchical recurrent sequence model to generate answers. The DMN can be trained end-to-end and obtains state-of-the-art results on several types of tasks and datasets: question answering (Facebook's bAbI dataset), text classification for sentiment analysis (Stanford Sentiment Treebank) and sequence modeling for part-of-speech tagging (WSJ-PTB). The training for these different tasks relies exclusively on trained word vector representations and input-question-answer triplets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge