Rodrigo Bonazzola
ChronoRoot 2.0: An Open AI-Powered Platform for 2D Temporal Plant Phenotyping
Apr 20, 2025



Abstract:The analysis of plant developmental plasticity, including root system architecture, is fundamental to understanding plant adaptability and development, particularly in the context of climate change and agricultural sustainability. While significant advances have been made in plant phenotyping technologies, comprehensive temporal analysis of root development remains challenging, with most existing solutions providing either limited throughput or restricted structural analysis capabilities. Here, we present ChronoRoot 2.0, an integrated open-source platform that combines affordable hardware with advanced artificial intelligence to enable sophisticated temporal plant phenotyping. The system introduces several major advances, offering an integral perspective of seedling development: (i) simultaneous multi-organ tracking of six distinct plant structures, (ii) quality control through real-time validation, (iii) comprehensive architectural measurements including novel gravitropic response parameters, and (iv) dual specialized user interfaces for both architectural analysis and high-throughput screening. We demonstrate the system's capabilities through three use cases for Arabidopsis thaliana: characterization of circadian growth patterns under different light conditions, detailed analysis of gravitropic responses in transgenic plants, and high-throughput screening of etiolation responses across multiple genotypes. ChronoRoot 2.0 maintains its predecessor's advantages of low cost and modularity while significantly expanding its capabilities, making sophisticated temporal phenotyping more accessible to the broader plant science community. The system's open-source nature, combined with extensive documentation and containerized deployment options, ensures reproducibility and enables community-driven development of new analytical capabilities.
Predicting risk of cardiovascular disease using retinal OCT imaging
Mar 26, 2024



Abstract:We investigated the potential of optical coherence tomography (OCT) as an additional imaging technique to predict future cardiovascular disease (CVD). We utilised a self-supervised deep learning approach based on Variational Autoencoders (VAE) to learn low-dimensional representations of high-dimensional 3D OCT images and to capture distinct characteristics of different retinal layers within the OCT image. A Random Forest (RF) classifier was subsequently trained using the learned latent features and participant demographic and clinical data, to differentiate between patients at risk of CVD events (MI or stroke) and non-CVD cases. Our predictive model, trained on multimodal data, was assessed based on its ability to correctly identify individuals likely to suffer from a CVD event(MI or stroke), within a 5-year interval after image acquisition. Our self-supervised VAE feature selection and multimodal Random Forest classifier differentiate between patients at risk of future CVD events and the control group with an AUC of 0.75, outperforming the clinically established QRISK3 score (AUC= 0.597). The choroidal layer visible in OCT images was identified as an important predictor of future CVD events using a novel approach to model explanability. Retinal OCT imaging provides a cost-effective and non-invasive alternative to predict the risk of cardiovascular disease and is readily accessible in optometry practices and hospitals.
Multi-view Hybrid Graph Convolutional Network for Volume-to-mesh Reconstruction in Cardiovascular MRI
Nov 22, 2023Abstract:Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging is emerging as a crucial tool to examine cardiac morphology and function. Essential to this endeavour are anatomical 3D surface and volumetric meshes derived from CMR images, which facilitate computational anatomy studies, biomarker discovery, and in-silico simulations. However, conventional surface mesh generation methods, such as active shape models and multi-atlas segmentation, are highly time-consuming and require complex processing pipelines to generate simulation-ready 3D meshes. In response, we introduce HybridVNet, a novel architecture for direct image-to-mesh extraction seamlessly integrating standard convolutional neural networks with graph convolutions, which we prove can efficiently handle surface and volumetric meshes by encoding them as graph structures. To further enhance accuracy, we propose a multiview HybridVNet architecture which processes both long axis and short axis CMR, showing that it can increase the performance of cardiac MR mesh generation. Our model combines traditional convolutional networks with variational graph generative models, deep supervision and mesh-specific regularisation. Experiments on a comprehensive dataset from the UK Biobank confirm the potential of HybridVNet to significantly advance cardiac imaging and computational cardiology by efficiently generating high-fidelity and simulation ready meshes from CMR images.
Learned Local Attention Maps for Synthesising Vessel Segmentations
Aug 24, 2023Abstract:Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is an imaging modality for visualising blood vessels. It is useful for several diagnostic applications and for assessing the risk of adverse events such as haemorrhagic stroke (resulting from the rupture of aneurysms in blood vessels). However, MRAs are not acquired routinely, hence, an approach to synthesise blood vessel segmentations from more routinely acquired MR contrasts such as T1 and T2, would be useful. We present an encoder-decoder model for synthesising segmentations of the main cerebral arteries in the circle of Willis (CoW) from only T2 MRI. We propose a two-phase multi-objective learning approach, which captures both global and local features. It uses learned local attention maps generated by dilating the segmentation labels, which forces the network to only extract information from the T2 MRI relevant to synthesising the CoW. Our synthetic vessel segmentations generated from only T2 MRI achieved a mean Dice score of $0.79 \pm 0.03$ in testing, compared to state-of-the-art segmentation networks such as transformer U-Net ($0.71 \pm 0.04$) and nnU-net($0.68 \pm 0.05$), while using only a fraction of the parameters. The main qualitative difference between our synthetic vessel segmentations and the comparative models was in the sharper resolution of the CoW vessel segments, especially in the posterior circulation.
Unsupervised ensemble-based phenotyping helps enhance the discoverability of genes related to heart morphology
Jan 07, 2023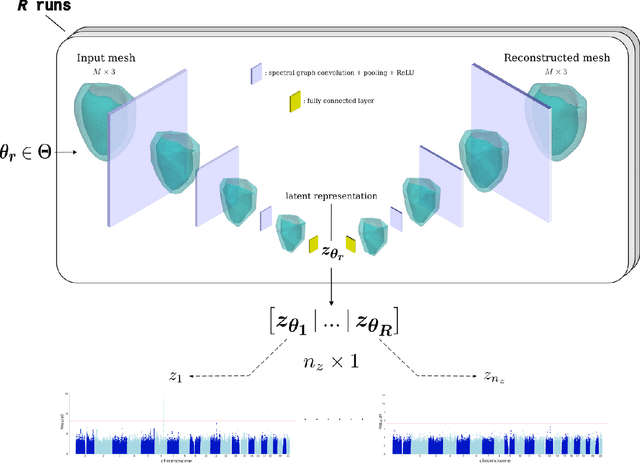
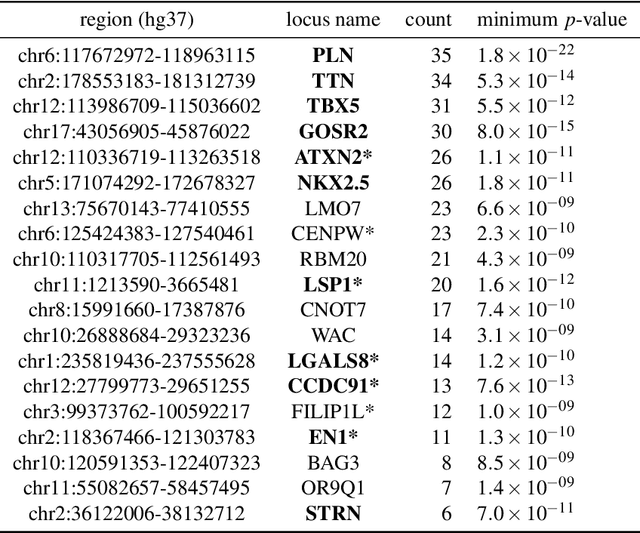
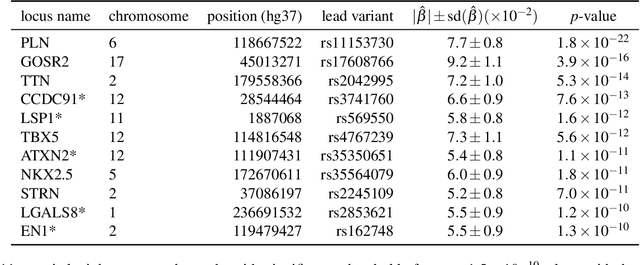
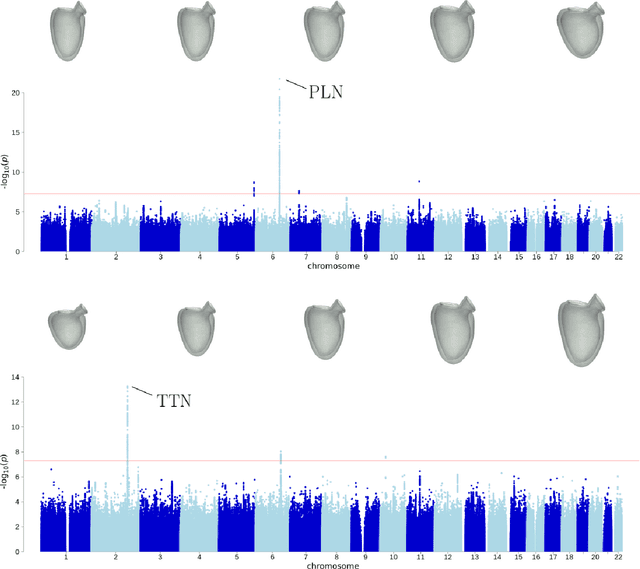
Abstract:Recent genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have been successful in identifying associations between genetic variants and simple cardiac parameters derived from cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) images. However, the emergence of big databases including genetic data linked to CMR, facilitates investigation of more nuanced patterns of shape variability. Here, we propose a new framework for gene discovery entitled Unsupervised Phenotype Ensembles (UPE). UPE builds a redundant yet highly expressive representation by pooling a set of phenotypes learned in an unsupervised manner, using deep learning models trained with different hyperparameters. These phenotypes are then analyzed via (GWAS), retaining only highly confident and stable associations across the ensemble. We apply our approach to the UK Biobank database to extract left-ventricular (LV) geometric features from image-derived three-dimensional meshes. We demonstrate that our approach greatly improves the discoverability of genes influencing LV shape, identifying 11 loci with study-wide significance and 8 with suggestive significance. We argue that our approach would enable more extensive discovery of gene associations with image-derived phenotypes for other organs or image modalities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge