Reza Zafarani
Is Less Really More? Fake News Detection with Limited Information
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:The threat that online fake news and misinformation pose to democracy, justice, public confidence, and especially to vulnerable populations, has led to a sharp increase in the need for fake news detection and intervention. Whether multi-modal or pure text-based, most fake news detection methods depend on textual analysis of entire articles. However, these fake news detection methods come with certain limitations. For instance, fake news detection methods that rely on full text can be computationally inefficient, demand large amounts of training data to achieve competitive accuracy, and may lack robustness across different datasets. This is because fake news datasets have strong variations in terms of the level and types of information they provide; where some can include large paragraphs of text with images and metadata, others can be a few short sentences. Perhaps if one could only use minimal information to detect fake news, fake news detection methods could become more robust and resilient to the lack of information. We aim to overcome these limitations by detecting fake news using systematically selected, limited information that is both effective and capable of delivering robust, promising performance. We propose a framework called SLIM Systematically-selected Limited Information) for fake news detection. In SLIM, we quantify the amount of information by introducing information-theoretic measures. SLIM leverages limited information to achieve performance in fake news detection comparable to that of state-of-the-art obtained using the full text. Furthermore, by combining various types of limited information, SLIM can perform even better while significantly reducing the quantity of information required for training compared to state-of-the-art language model-based fake news detection techniques.
Harnessing the Power of Noise: A Survey of Techniques and Applications
Oct 08, 2024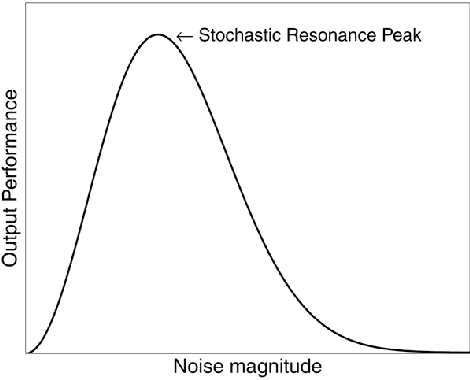

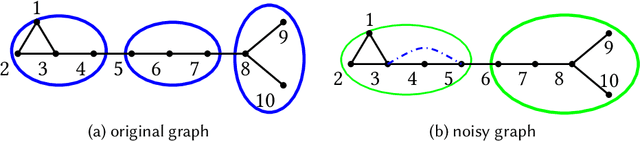
Abstract:Noise, traditionally considered a nuisance in computational systems, is reconsidered for its unexpected and counter-intuitive benefits across a wide spectrum of domains, including nonlinear information processing, signal processing, image processing, machine learning, network science, and natural language processing. Through a comprehensive review of both historical and contemporary research, this survey presents a dual perspective on noise, acknowledging its potential to both disrupt and enhance performance. Particularly, we highlight how noise-enhanced training strategies can lead to models that better generalize from noisy data, positioning noise not just as a challenge to overcome but as a strategic tool for improvement. This work calls for a shift in how we perceive noise, proposing that it can be a spark for innovation and advancement in the information era.
Linguistic-style-aware Neural Networks for Fake News Detection
Jan 07, 2023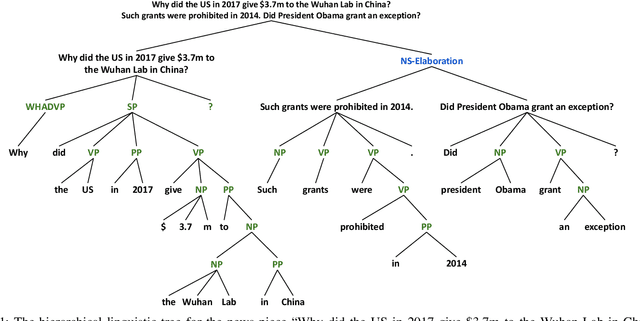
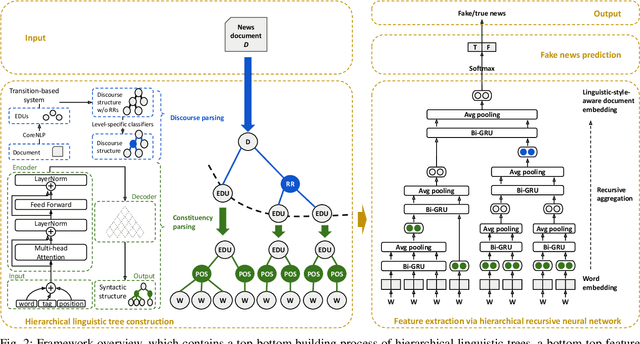
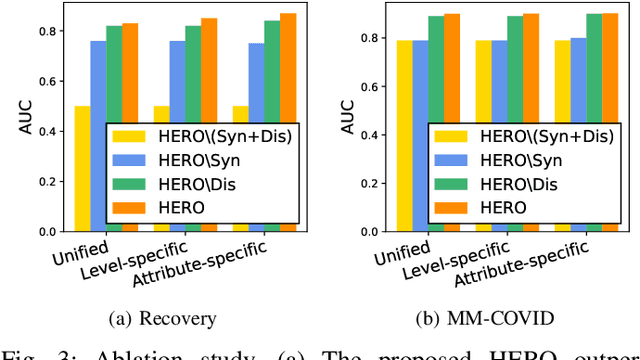
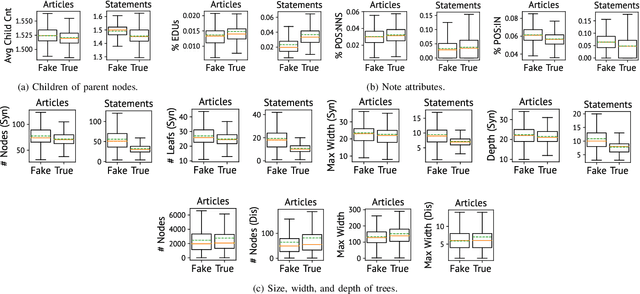
Abstract:We propose the hierarchical recursive neural network (HERO) to predict fake news by learning its linguistic style, which is distinguishable from the truth, as psychological theories reveal. We first generate the hierarchical linguistic tree of news documents; by doing so, we translate each news document's linguistic style into its writer's usage of words and how these words are recursively structured as phrases, sentences, paragraphs, and, ultimately, the document. By integrating the hierarchical linguistic tree with the neural network, the proposed method learns and classifies the representation of news documents by capturing their locally sequential and globally recursive structures that are linguistically meaningful. It is the first work offering the hierarchical linguistic tree and the neural network preserving the tree information to our best knowledge. Experimental results based on public real-world datasets demonstrate the proposed method's effectiveness, which can outperform state-of-the-art techniques in classifying short and long news documents. We also examine the differential linguistic style of fake news and the truth and observe some patterns of fake news. The code and data have been publicly available.
From Fake News to #FakeNews: Mining Direct and Indirect Relationships among Hashtags for Fake News Detection
Nov 20, 2022Abstract:The COVID-19 pandemic has gained worldwide attention and allowed fake news, such as ``COVID-19 is the flu,'' to spread quickly and widely on social media. Combating this coronavirus infodemic demands effective methods to detect fake news. To this end, we propose a method to infer news credibility from hashtags involved in news dissemination on social media, motivated by the tight connection between hashtags and news credibility observed in our empirical analyses. We first introduce a new graph that captures all (direct and \textit{indirect}) relationships among hashtags. Then, a language-independent semi-supervised algorithm is developed to predict fake news based on this constructed graph. This study first investigates the indirect relationship among hashtags; the proposed approach can be extended to any homogeneous graph to capture a comprehensive relationship among nodes. Language independence opens the proposed method to multilingual fake news detection. Experiments conducted on two real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in identifying fake news, especially at an \textit{early} stage of propagation.
"This is Fake! Shared it by Mistake": Assessing the Intent of Fake News Spreaders
Feb 13, 2022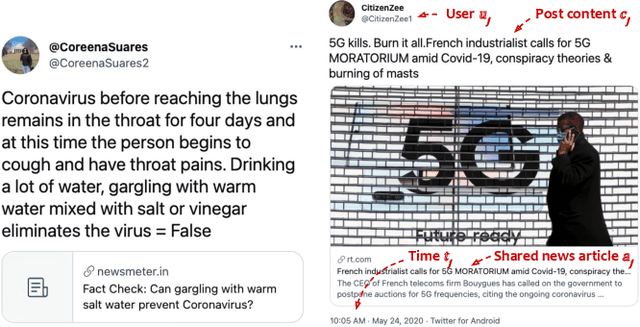

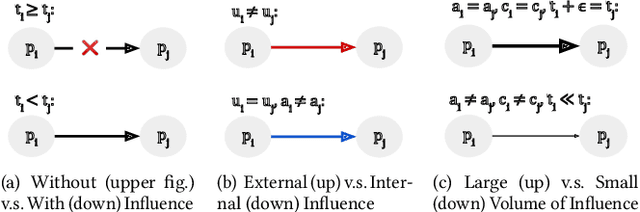
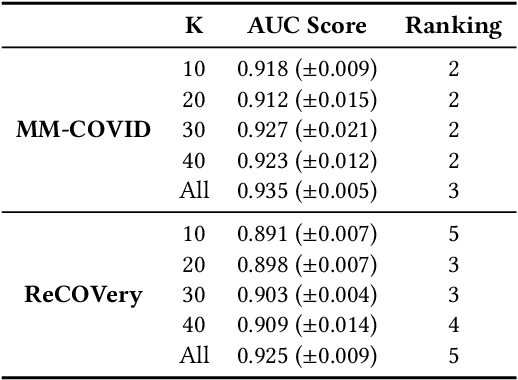
Abstract:Individuals can be misled by fake news and spread it unintentionally without knowing it is false. This phenomenon has been frequently observed but has not been investigated. Our aim in this work is to assess the intent of fake news spreaders. To distinguish between intentional versus unintentional spreading, we study the psychological explanations of unintentional spreading. With this foundation, we then propose an influence graph, using which we assess the intent of fake news spreaders. Our extensive experiments show that the assessed intent can help significantly differentiate between intentional and unintentional fake news spreaders. Furthermore, the estimated intent can significantly improve the current techniques that detect fake news. To our best knowledge, this is the first work to model individuals' intent in fake news spreading.
SAFE: Similarity-Aware Multi-Modal Fake News Detection
Feb 19, 2020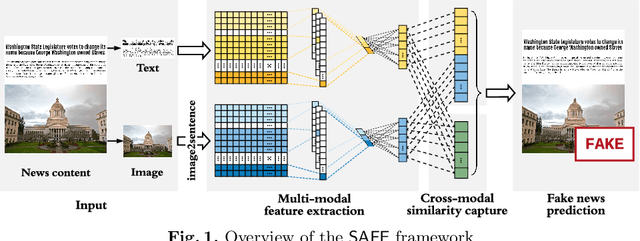
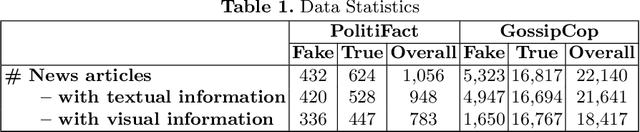

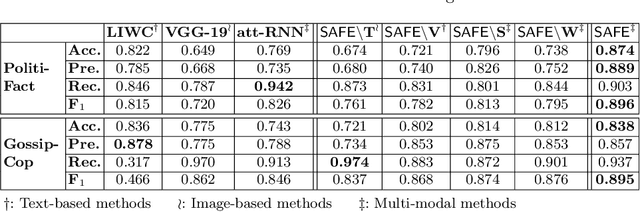
Abstract:Effective detection of fake news has recently attracted significant attention. Current studies have made significant contributions to predicting fake news with less focus on exploiting the relationship (similarity) between the textual and visual information in news articles. Attaching importance to such similarity helps identify fake news stories that, for example, attempt to use irrelevant images to attract readers' attention. In this work, we propose a $\mathsf{S}$imilarity-$\mathsf{A}$ware $\mathsf{F}$ak$\mathsf{E}$ news detection method ($\mathsf{SAFE}$) which investigates multi-modal (textual and visual) information of news articles. First, neural networks are adopted to separately extract textual and visual features for news representation. We further investigate the relationship between the extracted features across modalities. Such representations of news textual and visual information along with their relationship are jointly learned and used to predict fake news. The proposed method facilitates recognizing the falsity of news articles based on their text, images, or their "mismatches." We conduct extensive experiments on large-scale real-world data, which demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Credibility-based Fake News Detection
Nov 02, 2019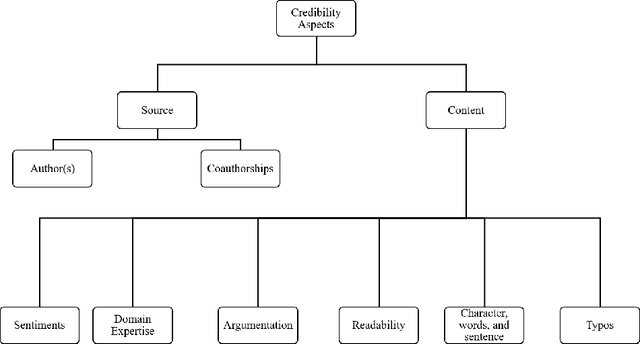
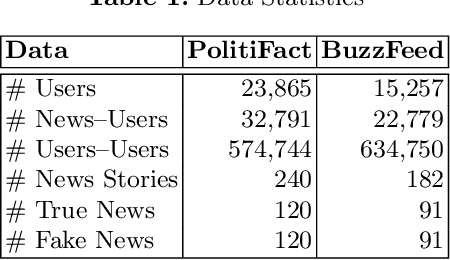
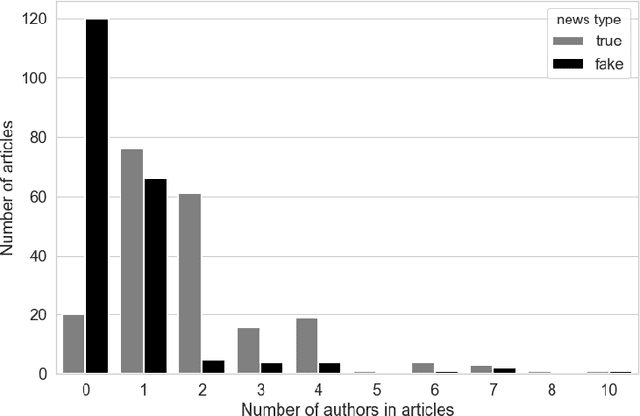

Abstract:Fake news can significantly misinform people who often rely on online sources and social media for their information. Current research on fake news detection has mostly focused on analyzing fake news content and how it propagates on a network of users. In this paper, we emphasize the detection of fake news by assessing its credibility. By analyzing public fake news data, we show that information on news sources (and authors) can be a strong indicator of credibility. Our findings suggest that an author's history of association with fake news, and the number of authors of a news article, can play a significant role in detecting fake news. Our approach can help improve traditional fake news detection methods, wherein content features are often used to detect fake news.
Fake News Early Detection: A Theory-driven Model
Apr 26, 2019
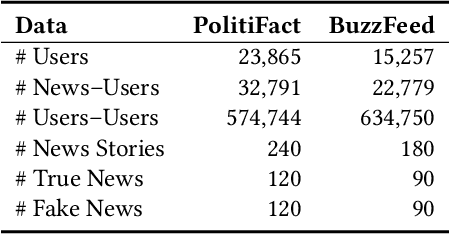
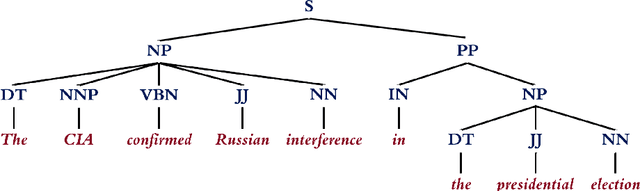

Abstract:The explosive growth of fake news and its erosion of democracy, justice, and public trust has significantly increased the demand for accurate fake news detection. Recent advancements in this area have proposed novel techniques that aim to detect fake news by exploring how it propagates on social networks. However, to achieve fake news early detection, one is only provided with limited to no information on news propagation; hence, motivating the need to develop approaches that can detect fake news by focusing mainly on news content. In this paper, a theory-driven model is proposed for fake news detection. The method investigates news content at various levels: lexicon-level, syntax-level, semantic-level and discourse-level. We represent news at each level, relying on well-established theories in social and forensic psychology. Fake news detection is then conducted within a supervised machine learning framework. As an interdisciplinary research, our work explores potential fake news patterns, enhances the interpretability in fake news feature engineering, and studies the relationships among fake news, deception/disinformation, and clickbaits. Experiments conducted on two real-world datasets indicate that the proposed method can outperform the state-of-the-art and enable fake news early detection, even when there is limited content information.
Fake News: A Survey of Research, Detection Methods, and Opportunities
Dec 02, 2018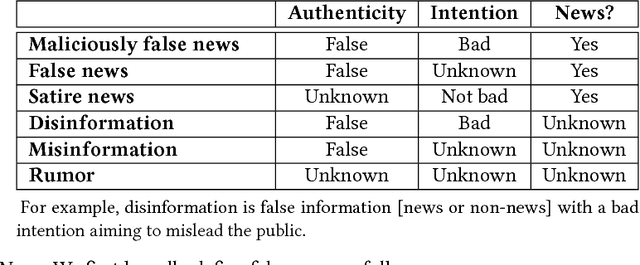
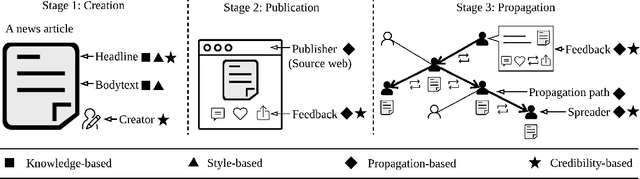
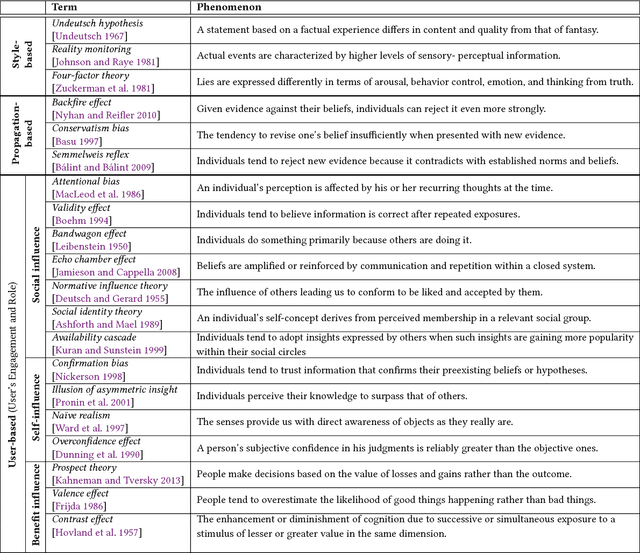
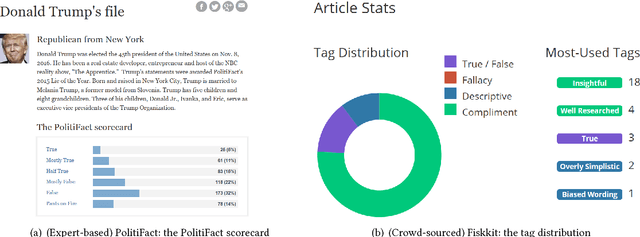
Abstract:The explosive growth in fake news and its erosion to democracy, justice, and public trust has increased the demand for fake news analysis, detection and intervention. This survey comprehensively and systematically reviews fake news research. The survey identifies and specifies fundamental theories across various disciplines, e.g., psychology and social science, to facilitate and enhance the interdisciplinary research of fake news. Current fake news research is reviewed, summarized and evaluated. These studies focus on fake news from four perspective: (1) the false knowledge it carries, (2) its writing style, (3) its propagation patterns, and (4) the credibility of its creators and spreaders. We characterize each perspective with various analyzable and utilizable information provided by news and its spreaders, various strategies and frameworks that are adaptable, and techniques that are applicable. By reviewing the characteristics of fake news and open issues in fake news studies, we highlight some potential research tasks at the end of this survey.
Assessing the Utility of Weather Data for Photovoltaic Power Prediction
Feb 12, 2018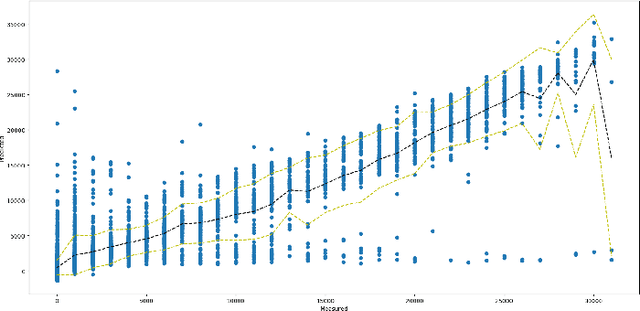
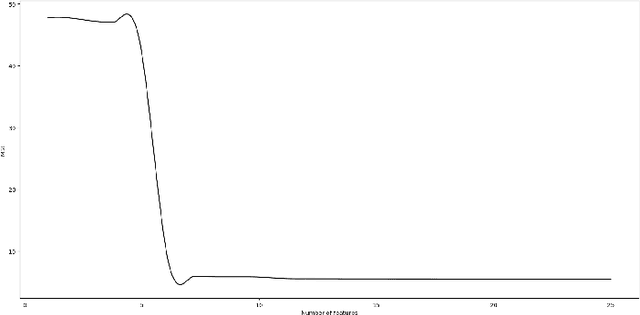
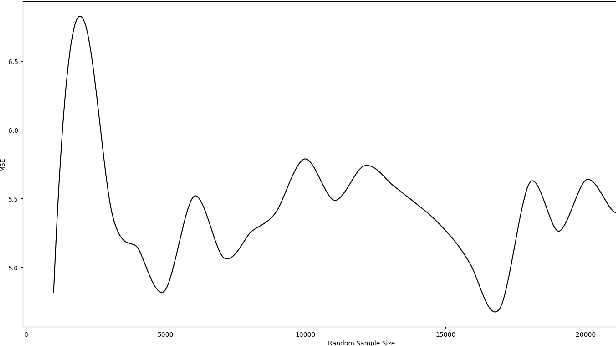
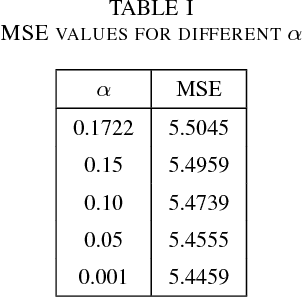
Abstract:Photovoltaic systems have been widely deployed in recent times to meet the increased electricity demand as an environmental-friendly energy source. The major challenge for integrating photovoltaic systems in power systems is the unpredictability of the solar power generated. In this paper, we analyze the impact of having access to weather information for solar power generation prediction and find weather information that can help best predict photovoltaic power.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge